
Best of the Mediterranean Cruise: Monte Carlo, Florence & Dubrovnik
Best of the Mediterranean Cruise: Monte Carlo, Florence & Dubrovnik
Cruise overview
WHY BOOK WITH US?
- ✔ The Deluxe Cruises’ team has extensive experience in ultra-luxury cruising.
- ✔ Call now to speak to our helpful and experienced Cruise Concierge team.
- ✔ Enjoy our Unique Deluxe Cruises Bonus for substantial savings.
- ✔ Our team will tailor your holiday to your exacting requirements.
- ✔ As agents, we work under the protection of each cruise lines ABTA / ATOL licences
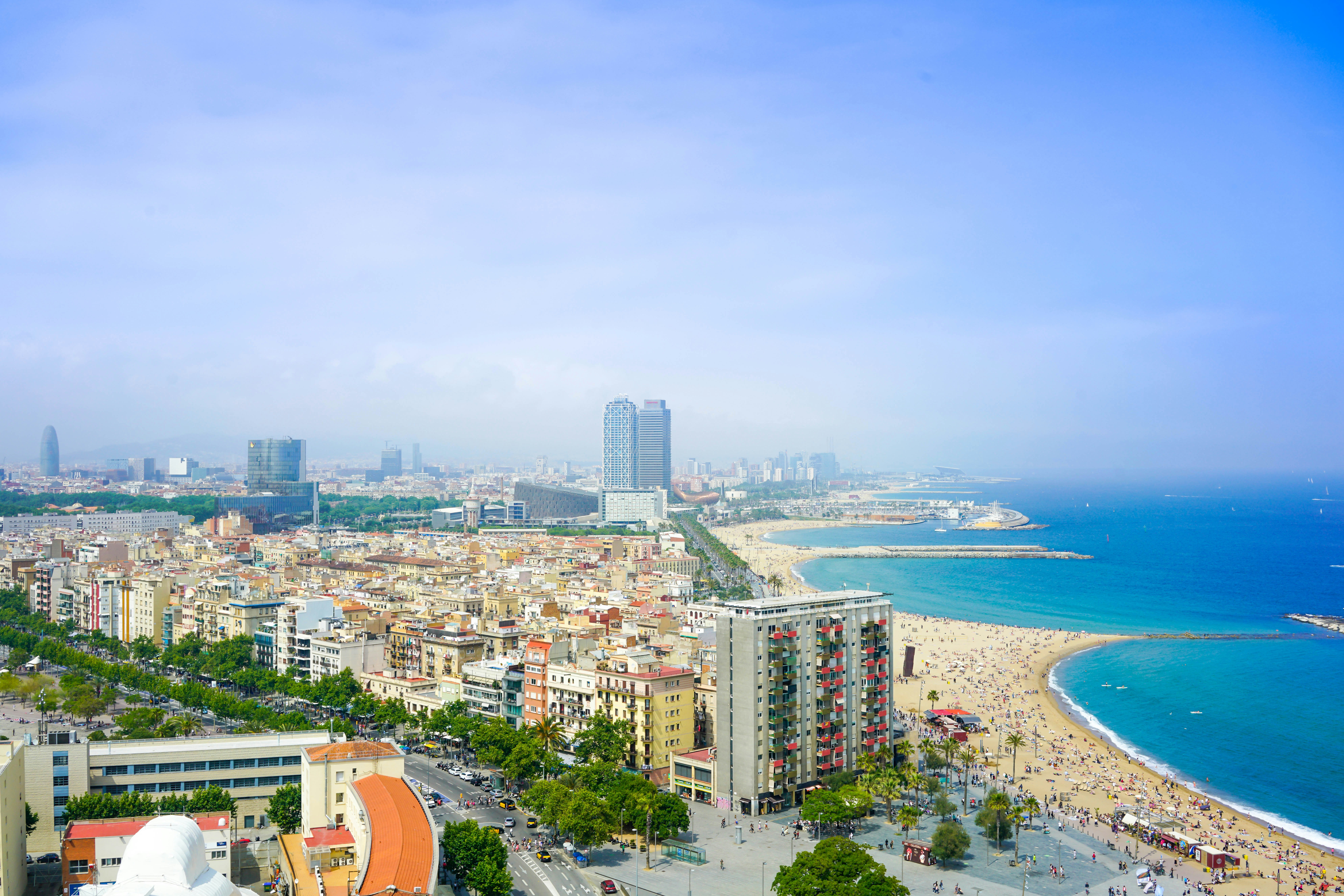
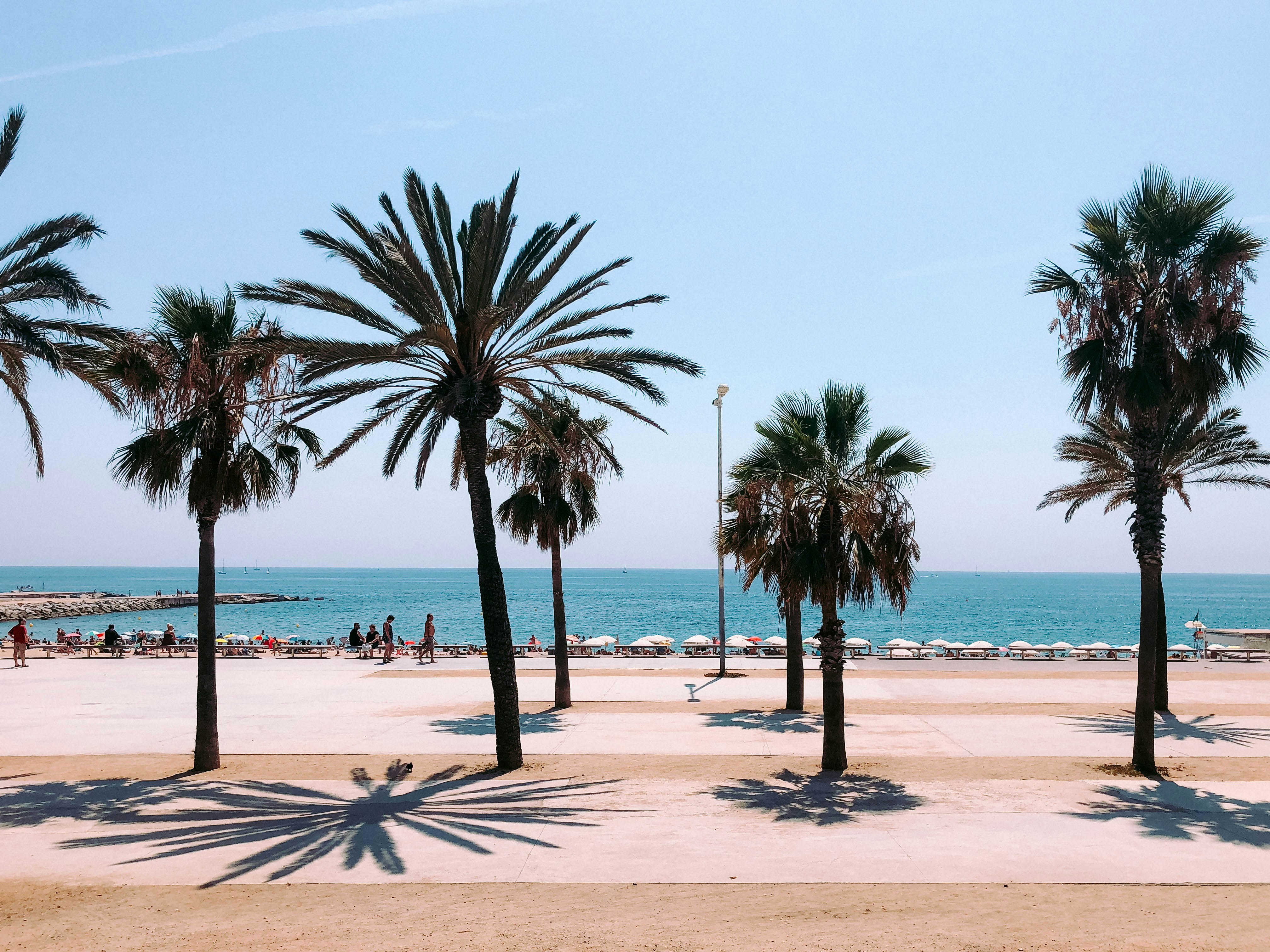
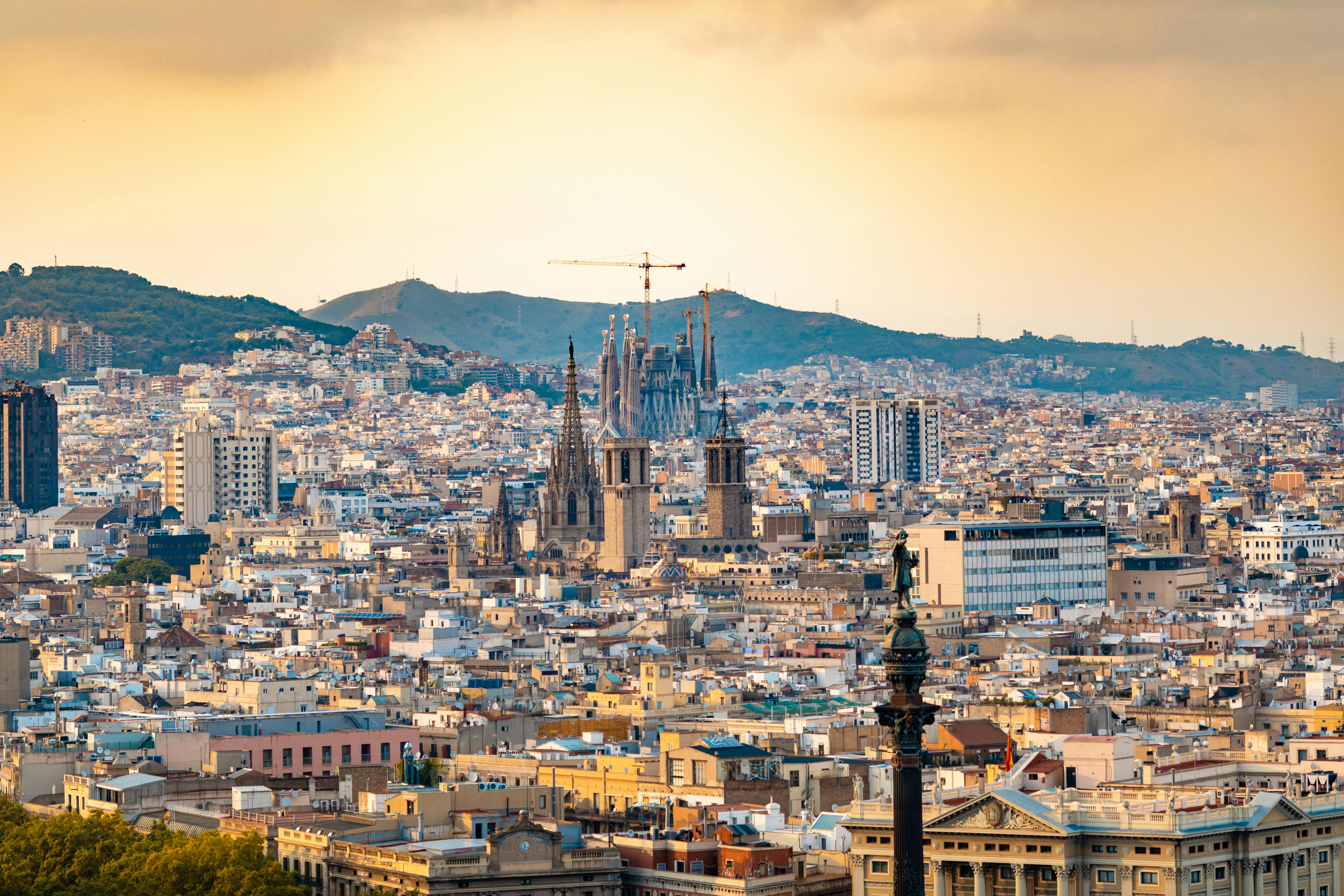
About Barcelona
The infinite variety of street life, the nooks and crannies of the medieval Barri Gòtic, the ceramic tile and stained glass of Art Nouveau facades, the art and music, the throb of street life, the food (ah, the food!)—one way or another, Barcelona will find a way to get your full attention. The capital of Catalonia is a banquet for the senses, with its beguiling mix of ancient and modern architecture, tempting cafés and markets, and sun-drenched Mediterranean beaches. A stroll along La Rambla and through waterfront Barceloneta, as well as a tour of Gaudí's majestic Sagrada Famíliaand his other unique creations, are part of a visit to Spain's second-largest city. Modern art museums and chic shops call for attention, too. Barcelona's vibe stays lively well into the night, when you can linger over regional wine and cuisine at buzzing tapas bars.




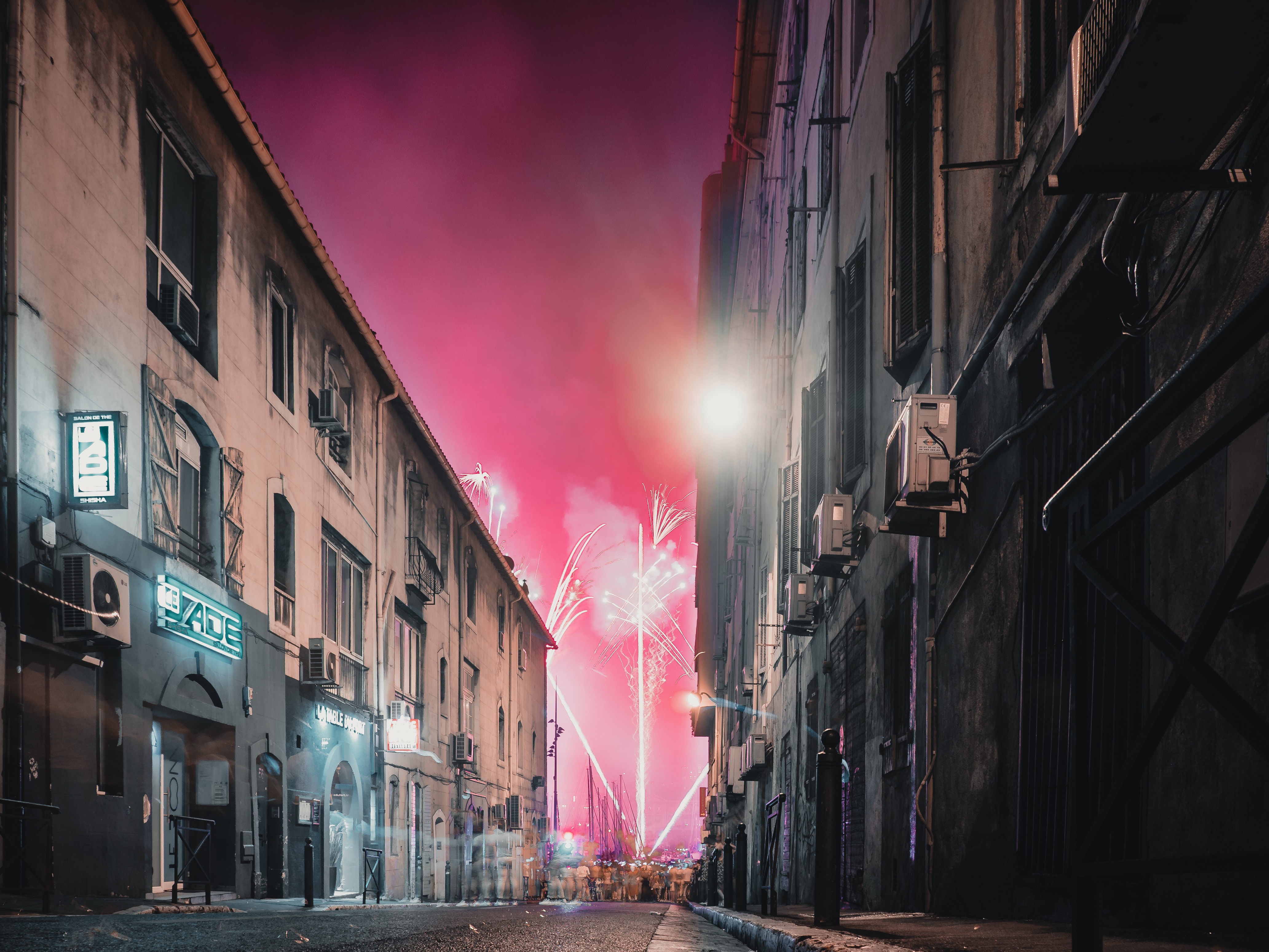
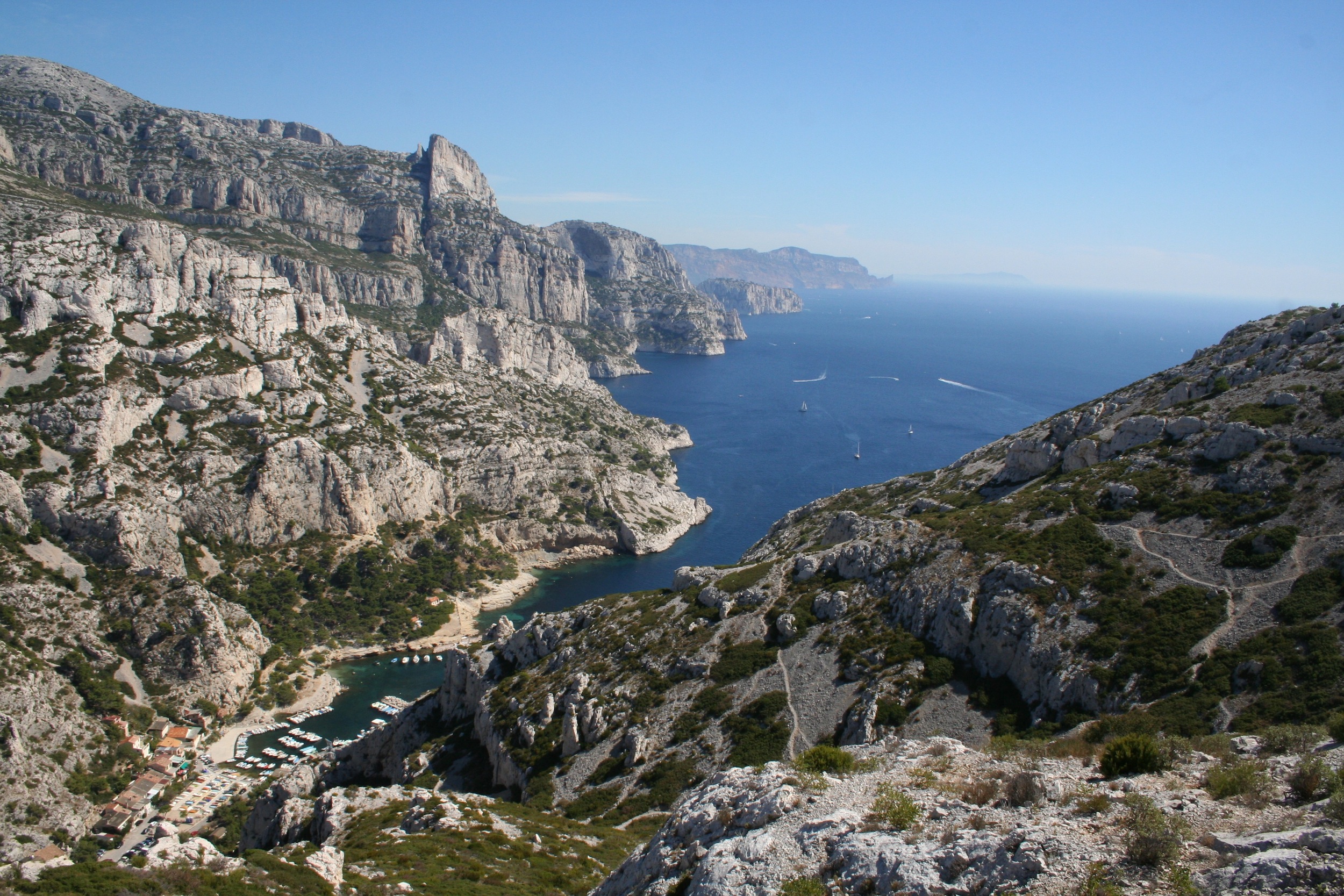
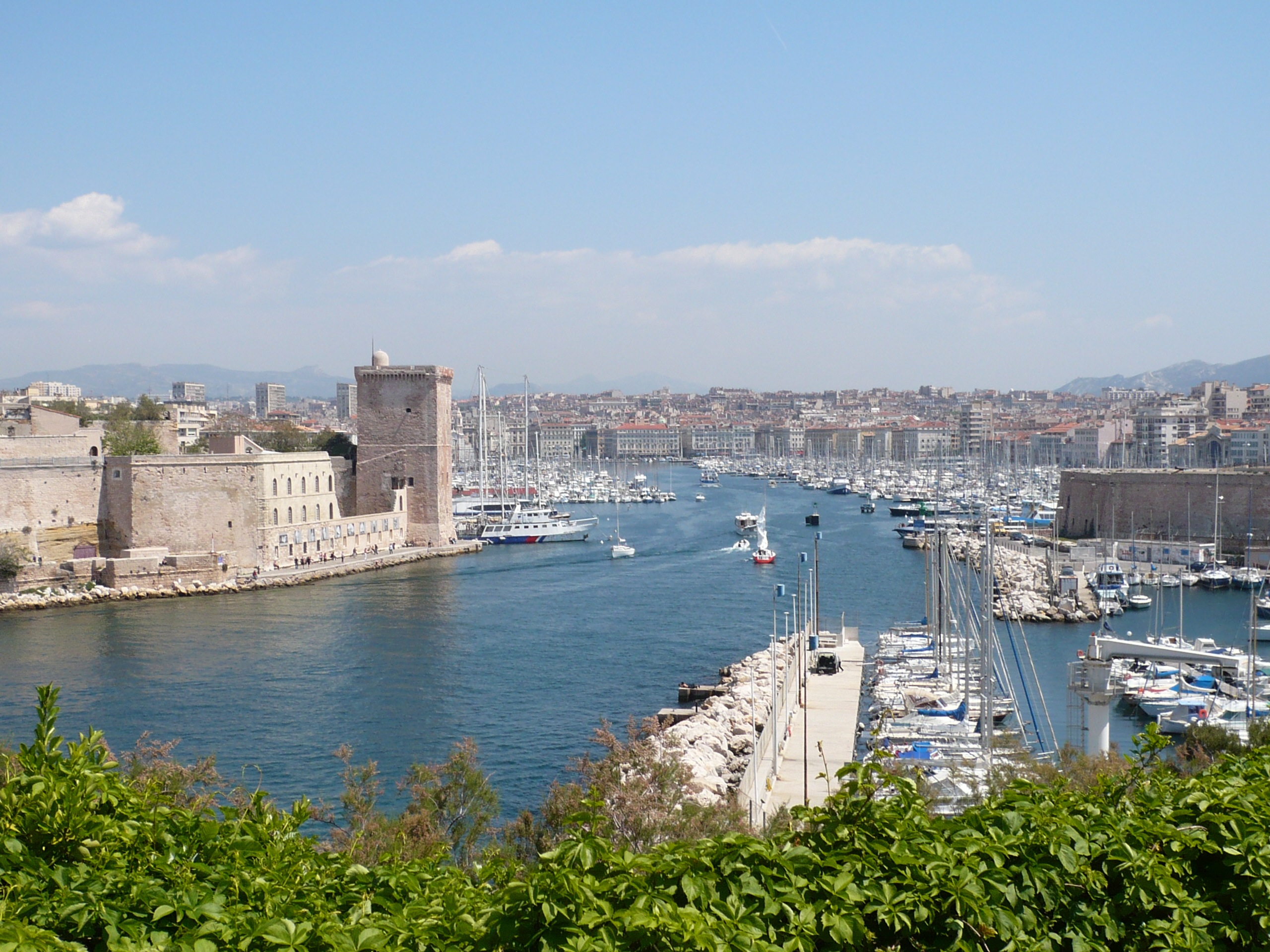
About Marseille
Since being designated a European Capital of Culture for 2013, with an estimated €660 million of funding in the bargain, Marseille has been in the throes of an extraordinary transformation, with no fewer than five major new arts centers, a beautifully refurbished port, revitalized neighborhoods, and a slew of new shops and restaurants. Once the underdog, this time-burnished city is now welcoming an influx of weekend tourists who have colonized entire neighborhoods and transformed them into elegant pieds-à-terre (or should we say, mer). The second-largest city in France, Marseille is one of Europe's most vibrant destinations. Feisty and fond of broad gestures, it is also as complicated and as cosmopolitan now as it was when a band of Phoenician Greeks first sailed into the harbor that is today's Vieux Port in 600 BC. Legend has it that on that same day a local chieftain's daughter, Gyptis, needed to choose a husband, and her wandering eyes settled on the Greeks' handsome commander Protis. Her dowry brought land near the mouth of the Rhône, where the Greeks founded Massalia, the most important Continental shipping port in antiquity. The port flourished for some 500 years as a typical Greek city, enjoying the full flush of classical culture, its gods, its democratic political system, its sports and theater, and its naval prowess. Caesar changed all that, besieging the city in 49 BC and seizing most of its colonies. In 1214 Marseille was seized again, this time by Charles d'Anjou, and was later annexed to France by Henri IV in 1481, but it was not until Louis XIV took the throne that the biggest transformations of the port began; he pulled down the city walls in 1666 and expanded the port to the Rive Neuve (New Riverbank). The city was devastated by plague in 1720, losing more than half its population. By the time of the Revolution, Marseille was on the rebound once again, with industries of soap manufacturing and oil processing flourishing, encouraging a wave of immigration from Provence and Italy. With the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869, Marseille became the greatest boomtown in 19th-century Europe. With a large influx of immigrants from areas as exotic as Tangiers, the city quickly acquired the multicultural population it maintains to this day.
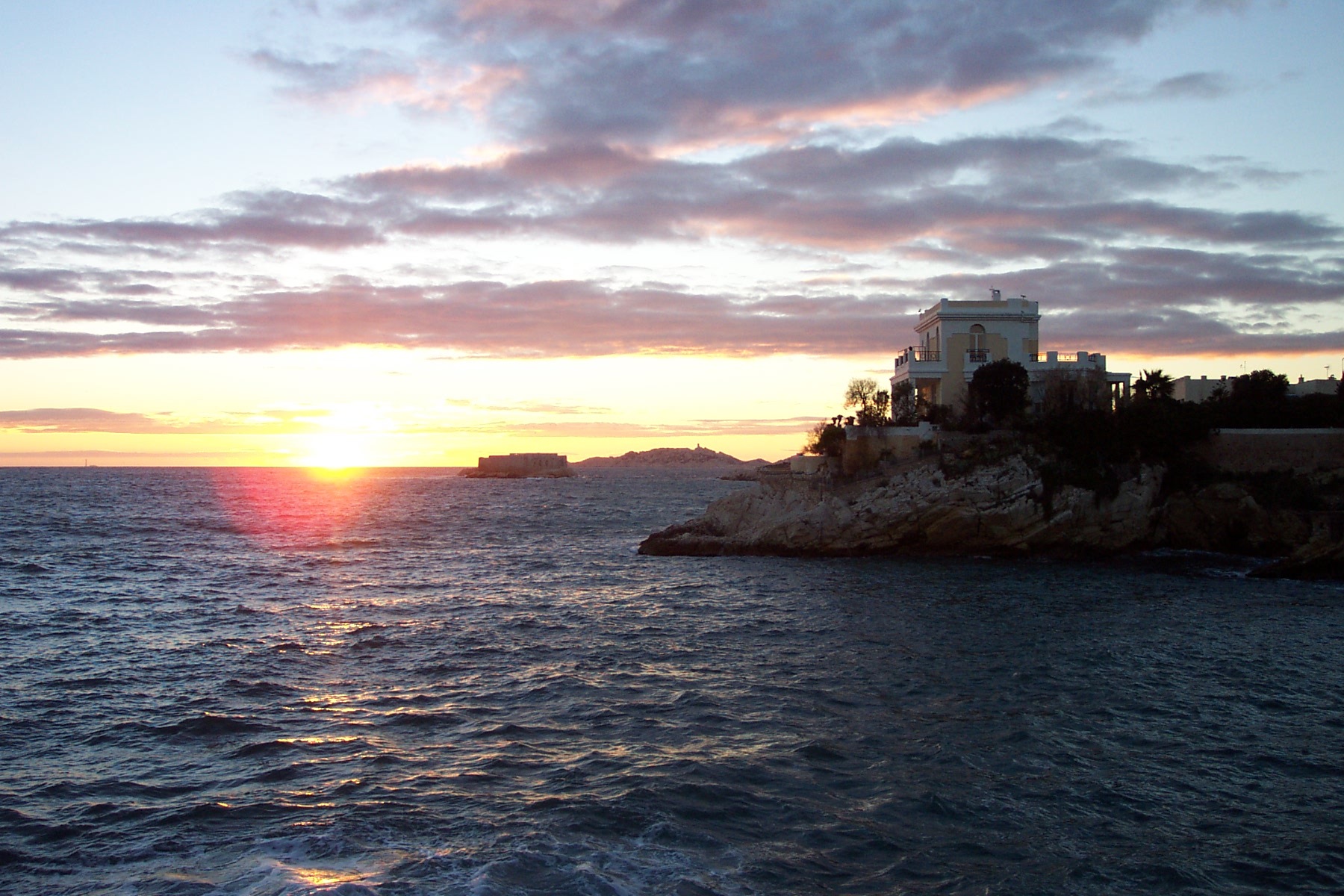
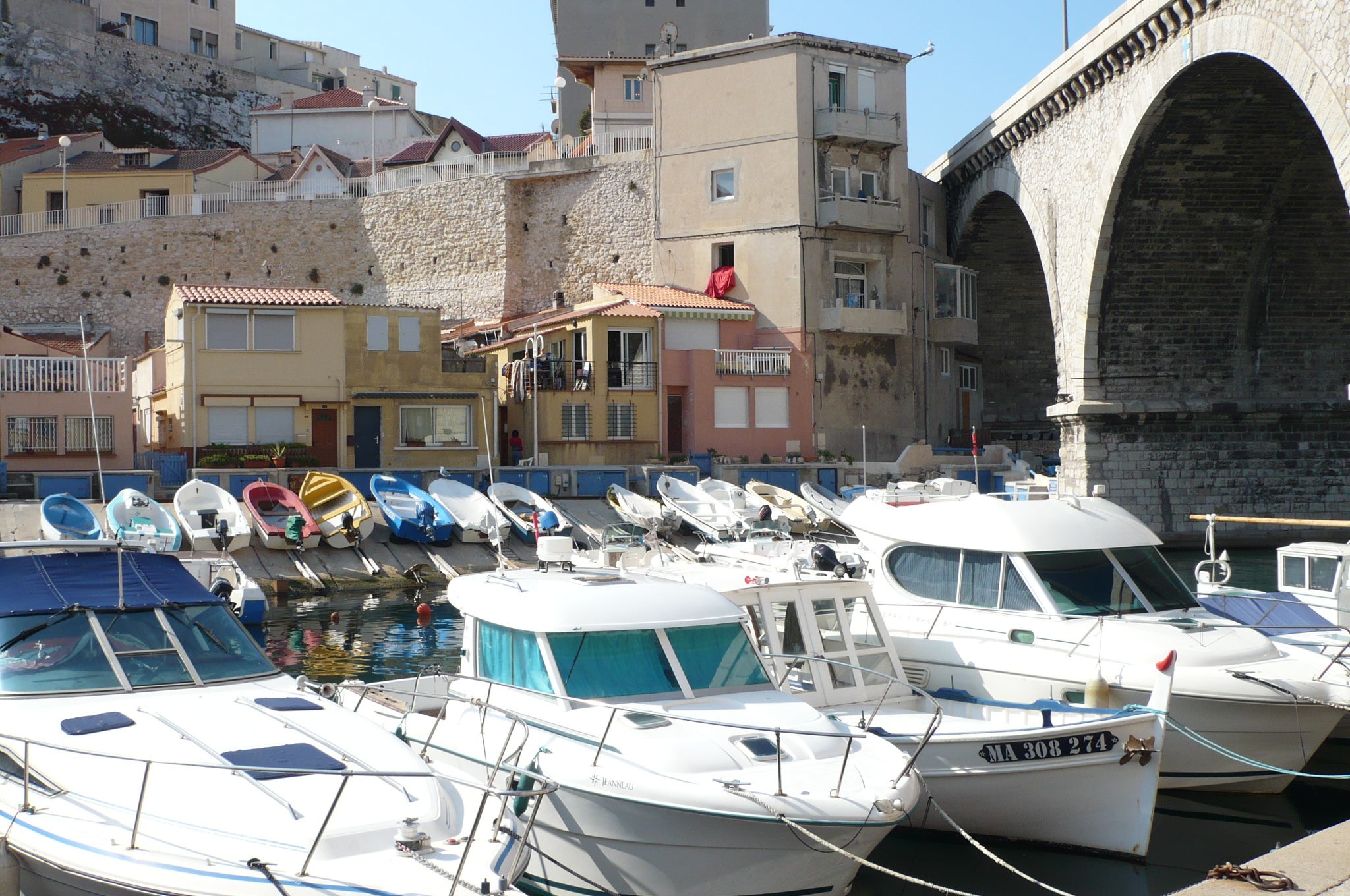
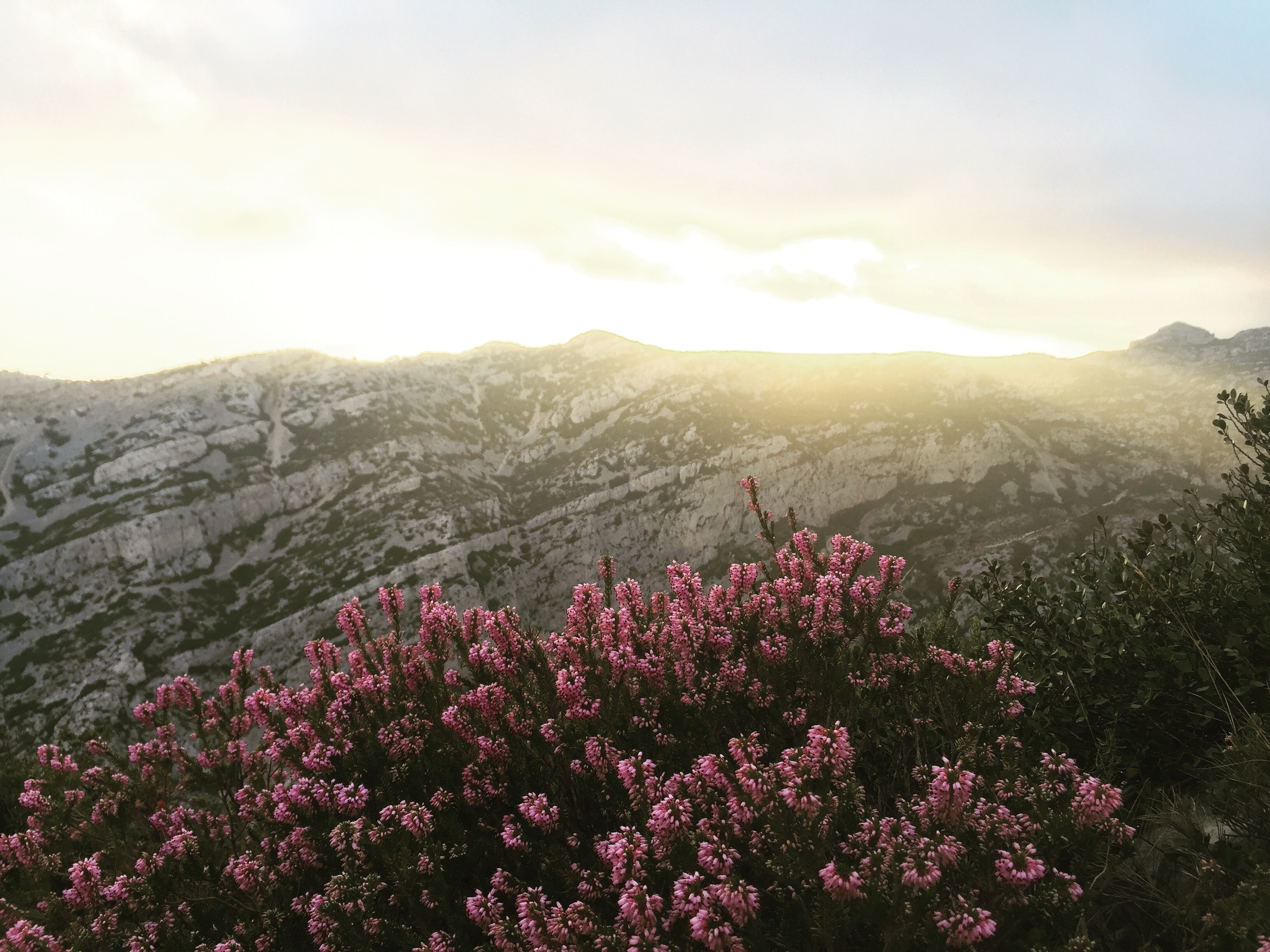
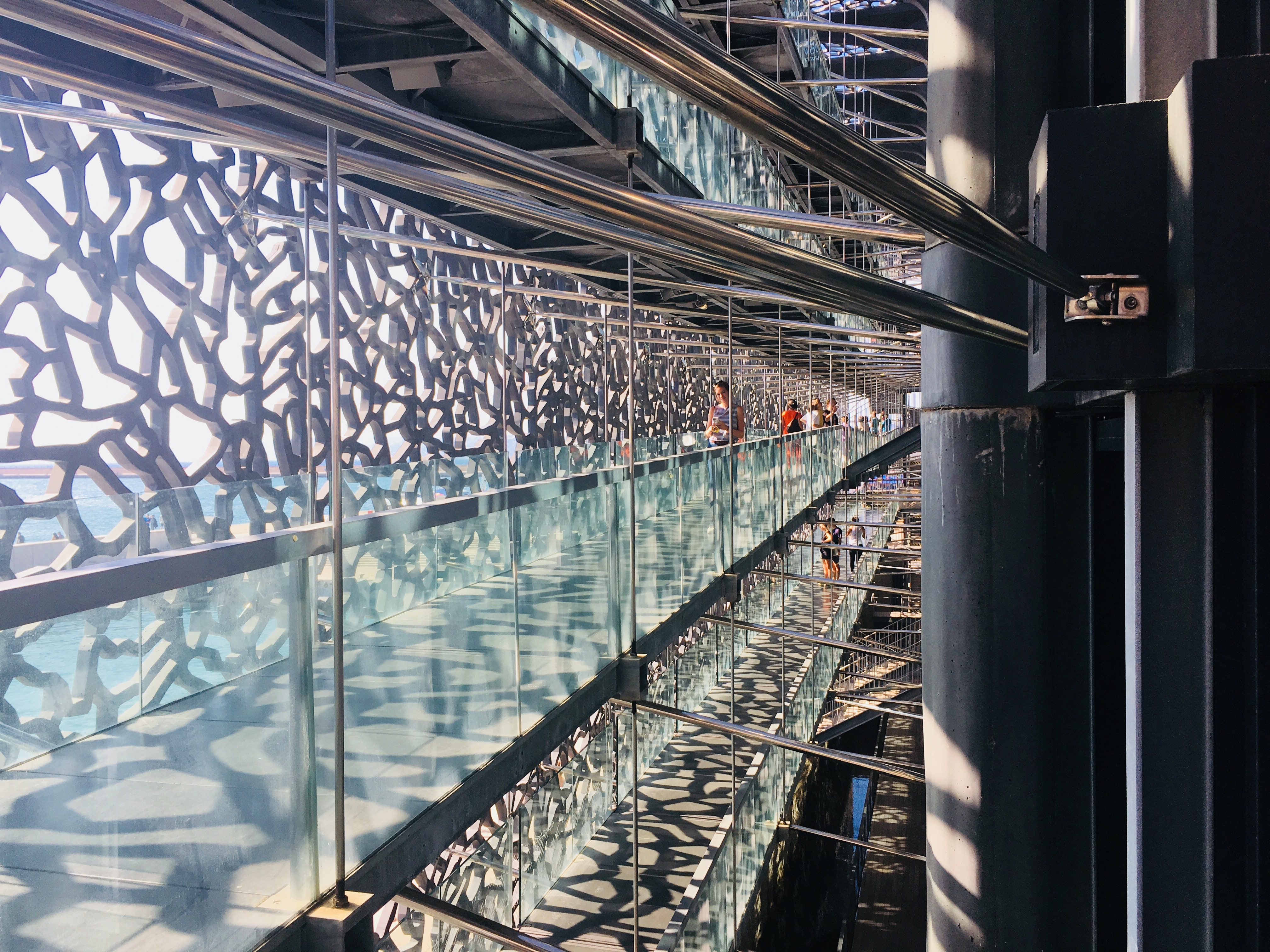









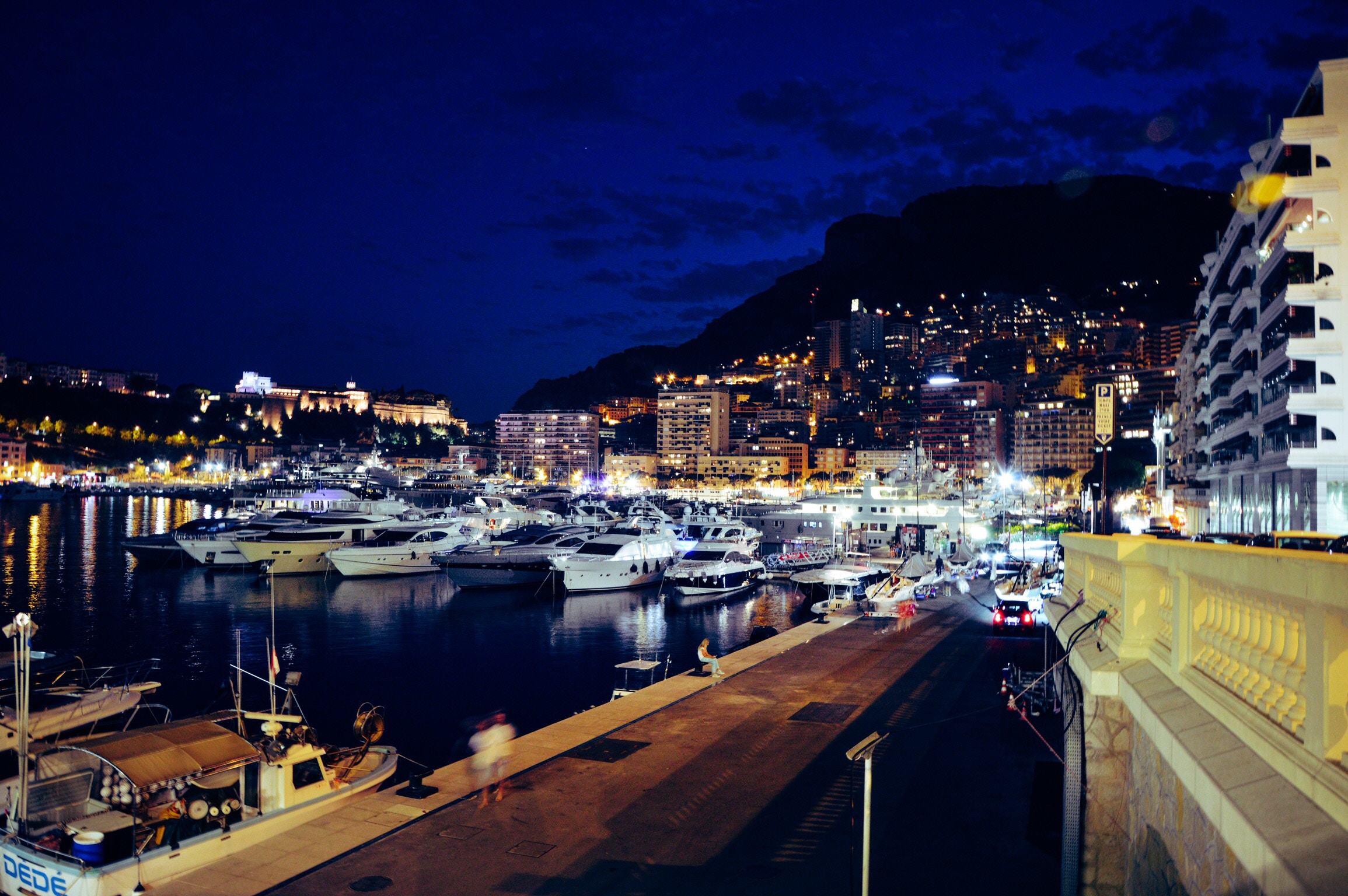
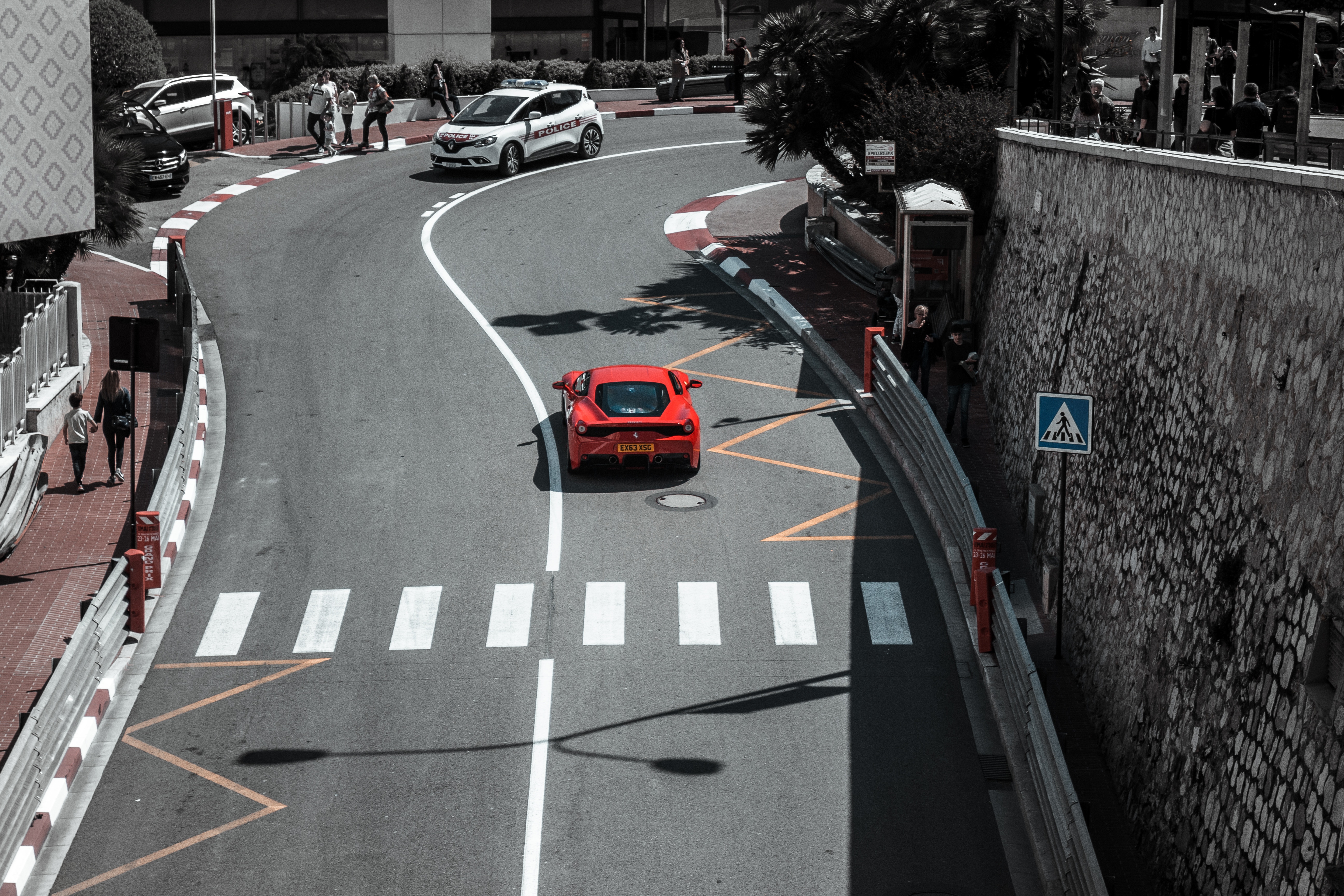
About Monte-Carlo
On one of the best stretches of the Mediterranean, this classic luxury destination is one of the most sought-after addresses in the world. With all the high-rise towers you have to look hard to find the Belle Époque grace of yesteryear. But if you head to the town's great 1864 landmark Hôtel de Paris—still a veritable crossroads of the buffed and befurred Euro-gentry—or enjoy a grand bouffe at its famous Louis XV restaurant, or attend the opera, or visit the ballrooms of the casino, you may still be able to conjure up Monaco's elegant past. Prince Albert II, a political science graduate from Amherst College, traces his ancestry to Otto Canella, who was born in 1070. The Grimaldi dynasty began with Otto's great-great-great-grandson, Francesco Grimaldi, also known as Frank the Rogue. Expelled from Genoa, Frank and his cronies disguised themselves as monks and in 1297 seized the fortified medieval town known today as Le Rocher (the Rock). Except for a short break under Napoléon, the Grimaldis have been here ever since, which makes them the oldest reigning family in Europe. In the 1850s a Grimaldi named Charles III made a decision that turned the Rock into a giant blue chip. Needing revenue but not wanting to impose additional taxes on his subjects, he contracted with a company to open a gambling facility. The first spin of the roulette wheel was on December 14, 1856. There was no easy way to reach Monaco then—no carriage roads or railroads—so no one came. Between March 15 and March 20, 1857, one person entered the casino—and won two francs. In 1868, however, the railroad reached Monaco, and it was filled with Englishmen who came to escape the London fog. The effects were immediate. Profits were so great that Charles eventually abolished all direct taxes. Almost overnight, a threadbare principality became an elegant watering hole for European society. Dukes (and their mistresses) and duchesses (and their gigolos) danced and dined their way through a world of spinning roulette wheels and bubbling champagne—preening themselves for nights at the opera, where such artists as Vaslav Nijinsky, Sarah Bernhardt, and Enrico Caruso came to perform. Along with the tax system, its sensational position on a broad, steep peninsula that bulges into the Mediterranean—its harbor sparkling with luxury cruisers, its posh mansions angling awnings toward the nearly perpetual sun—continues to draw the rich and famous. One of the latest French celebrities to declare himself "Monégasque," thus giving up his French passport, is superchef Alain Ducasse, who said that he made the choice out of affection for Monaco rather than tax reasons. Pleasure boats vie with luxury cruisers in their brash beauty and Titanic scale, and teams of handsome young men—themselves dyed blond and tanned to match—scour and polish every gleaming surface. As you might expect, all this glitz doesn't come cheap. Eating is expensive, and even the most modest hotels cost more here than in nearby Nice or Menton. As for taxis, they don't even have meters so you are completely at the driver's mercy (with prices skyrocketing during events such as the Grand Prix). For the frugal, Monaco is the ultimate day-trip, although parking is as coveted as a room with a view. At the very least you can afford a coffee at Starbucks. The harbor district, known as La Condamine, connects the new quarter, officially known as Monte Carlo with Monaco-Ville (or Le Rocher), a medieval town on the Rock, topped by the palace, the cathedral, and the Oceanography Museum. Have no fear that you'll need to climb countless steps to get to Monaco-Ville, as there are plenty of elevators and escalators climbing the steep cliffs. But shuttling between the lovely casino grounds of Monte Carlo and Old Monaco, separated by a vast port, is a daunting proposition for ordinary mortals without wings, so hop on the No. 1 bus from Saint Roman, or No. 2 from the Jardin Exotique - Both stop at Place du Casino and come up to Monaco Ville.



About Livorno
Livorno is a gritty city with a long and interesting history. In the early Middle Ages it alternately belonged to Pisa and Genoa. In 1421 Florence, seeking access to the sea, bought it. Cosimo I (1519–74) started construction of the harbor in 1571, putting Livorno on the map. After Ferdinando I de' Medici (1549–1609) proclaimed Livorno a free city, it became a haven for people suffering from religious persecution; Roman Catholics from England and Jews and Moors from Spain and Portugal, among others, settled here. The Quattro Mori (Four Moors), also known as the Monument to Ferdinando I, commemorates this. (The statue of Ferdinando I dates from 1595, the bronze Moors by Pietro Tacca from the 1620s.)In the following centuries, and particularly in the 18th, Livorno boomed as a port. In the 19th century the town drew a host of famous Britons passing through on their grand tours. Its prominence continued up to World War II, when it was heavily bombed. Much of the town's architecture, therefore, postdates the war, and it's somewhat difficult to imagine what it might have looked like before. Livorno has recovered from the war, however, as it's become a huge point of departure for container ships, as well as the only spot in Tuscany for cruise ships to dock for the day.Most of Livorno's artistic treasures date from the 17th century and aren't all that interesting unless you dote on obscure baroque artists. Livorno's most famous native artist, Amedeo Modigliani (1884–1920), was of much more recent vintage. Sadly, there's no notable work by him in his hometown.There may not be much in the way of art, but it's still worth strolling around the city. The Mercato Nuovo, which has been around since 1894, sells all sorts of fruits, vegetables, grains, meat, and fish. Outdoor markets nearby are also chock-full of local color. The presence of Camp Darby, an American military base just outside town, accounts for the availability of many American products.If you have time, Livorno is worth a stop for lunch or dinner at the very least.


About Livorno
Livorno is a gritty city with a long and interesting history. In the early Middle Ages it alternately belonged to Pisa and Genoa. In 1421 Florence, seeking access to the sea, bought it. Cosimo I (1519–74) started construction of the harbor in 1571, putting Livorno on the map. After Ferdinando I de' Medici (1549–1609) proclaimed Livorno a free city, it became a haven for people suffering from religious persecution; Roman Catholics from England and Jews and Moors from Spain and Portugal, among others, settled here. The Quattro Mori (Four Moors), also known as the Monument to Ferdinando I, commemorates this. (The statue of Ferdinando I dates from 1595, the bronze Moors by Pietro Tacca from the 1620s.)In the following centuries, and particularly in the 18th, Livorno boomed as a port. In the 19th century the town drew a host of famous Britons passing through on their grand tours. Its prominence continued up to World War II, when it was heavily bombed. Much of the town's architecture, therefore, postdates the war, and it's somewhat difficult to imagine what it might have looked like before. Livorno has recovered from the war, however, as it's become a huge point of departure for container ships, as well as the only spot in Tuscany for cruise ships to dock for the day.Most of Livorno's artistic treasures date from the 17th century and aren't all that interesting unless you dote on obscure baroque artists. Livorno's most famous native artist, Amedeo Modigliani (1884–1920), was of much more recent vintage. Sadly, there's no notable work by him in his hometown.There may not be much in the way of art, but it's still worth strolling around the city. The Mercato Nuovo, which has been around since 1894, sells all sorts of fruits, vegetables, grains, meat, and fish. Outdoor markets nearby are also chock-full of local color. The presence of Camp Darby, an American military base just outside town, accounts for the availability of many American products.If you have time, Livorno is worth a stop for lunch or dinner at the very least.


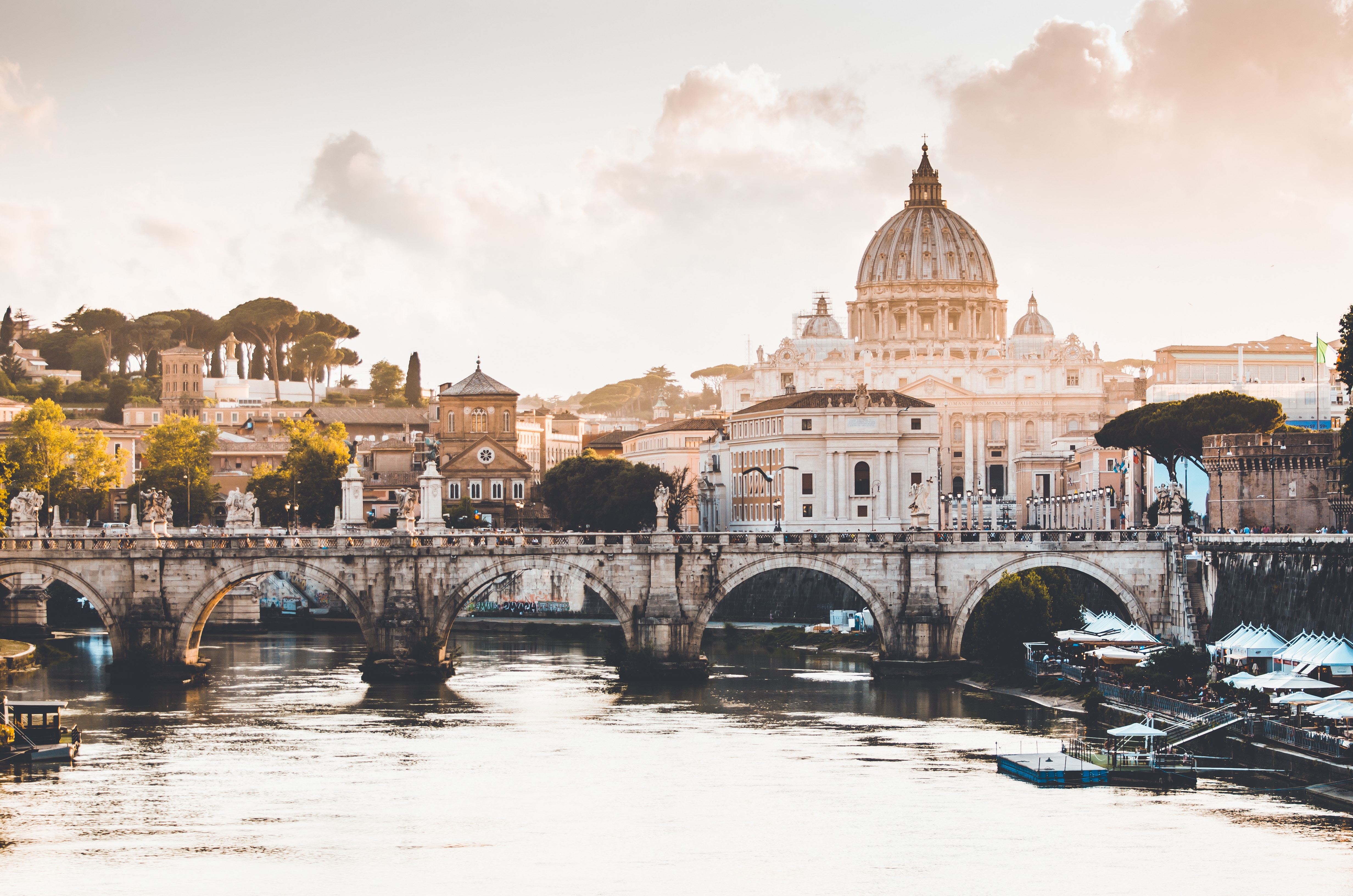
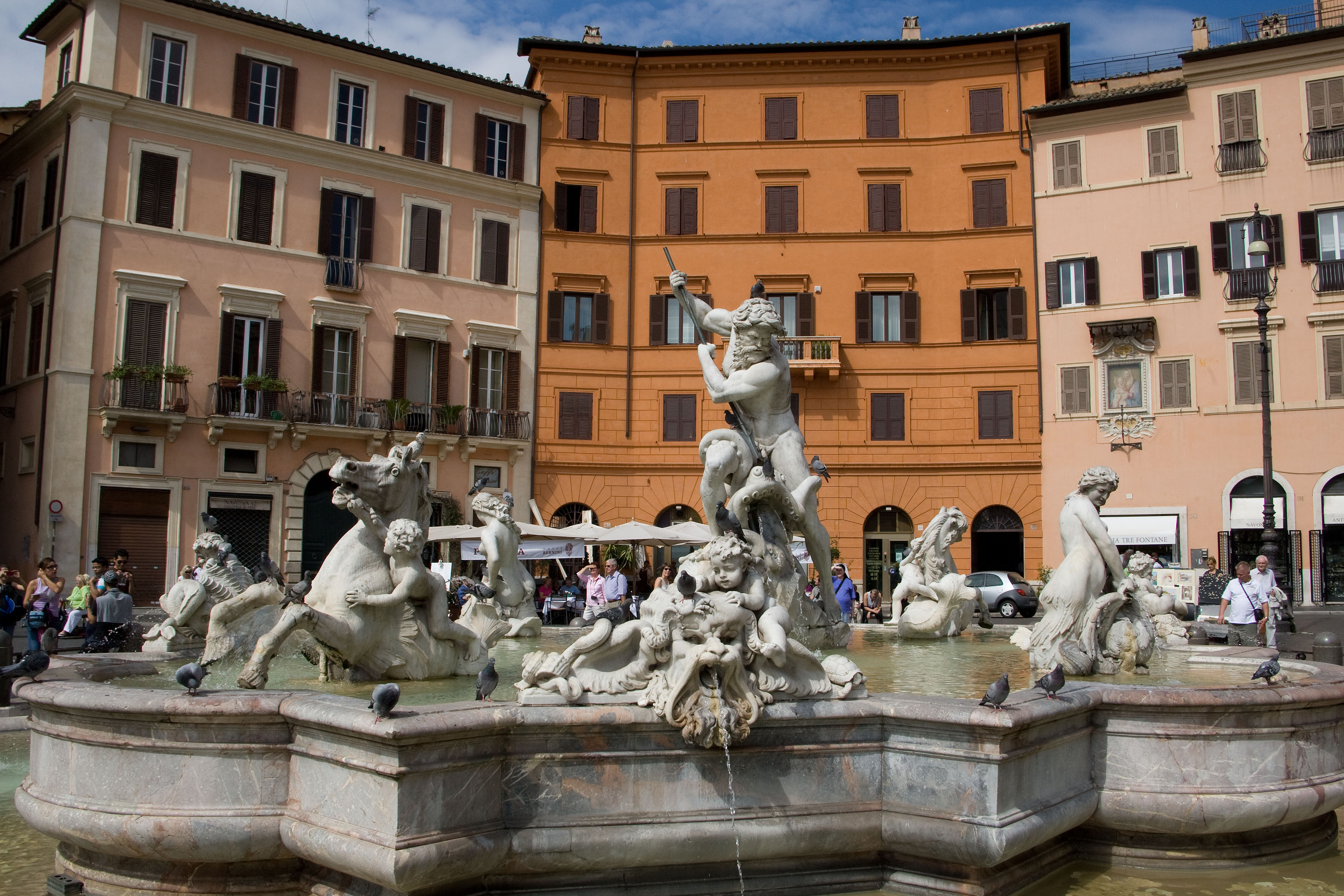
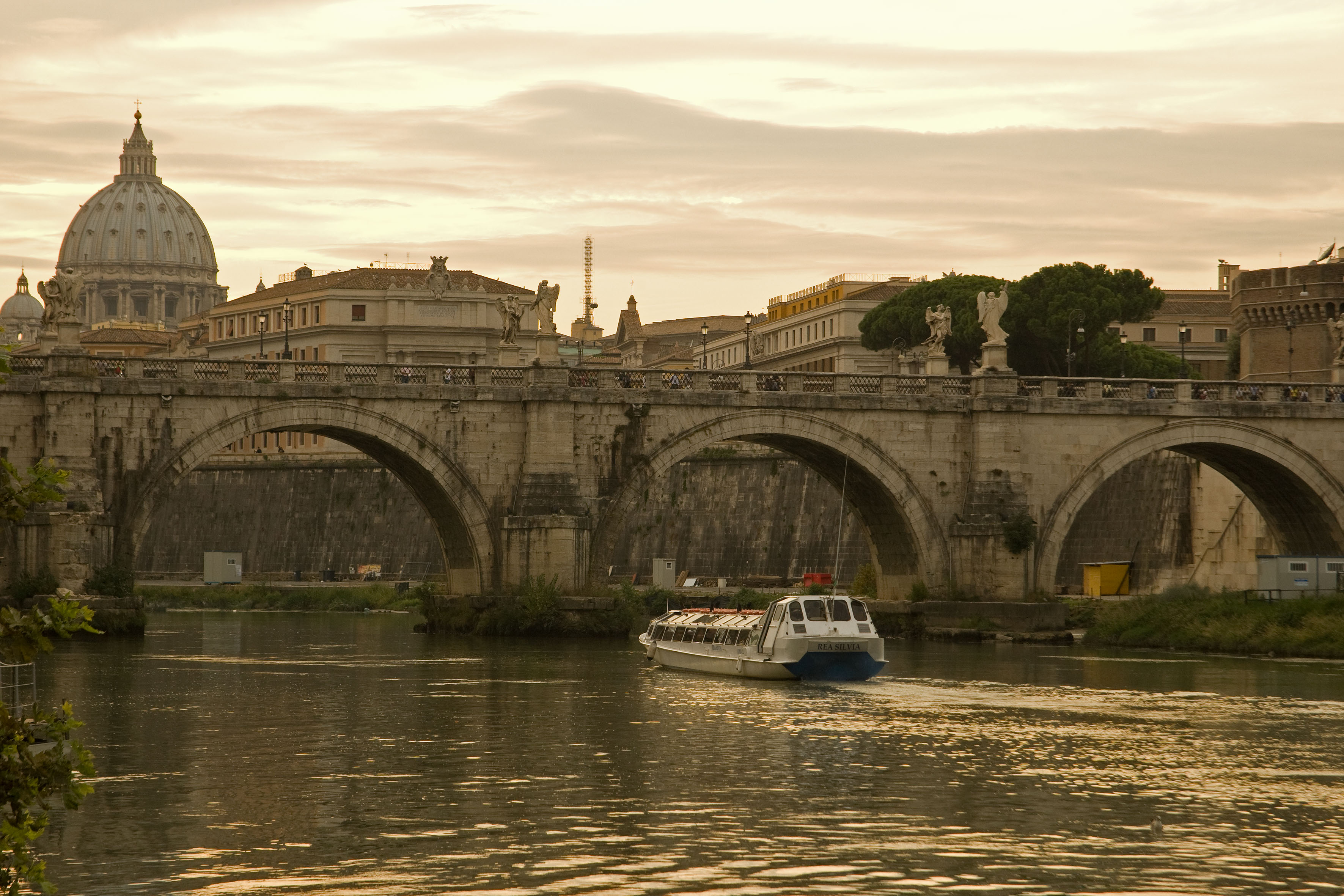
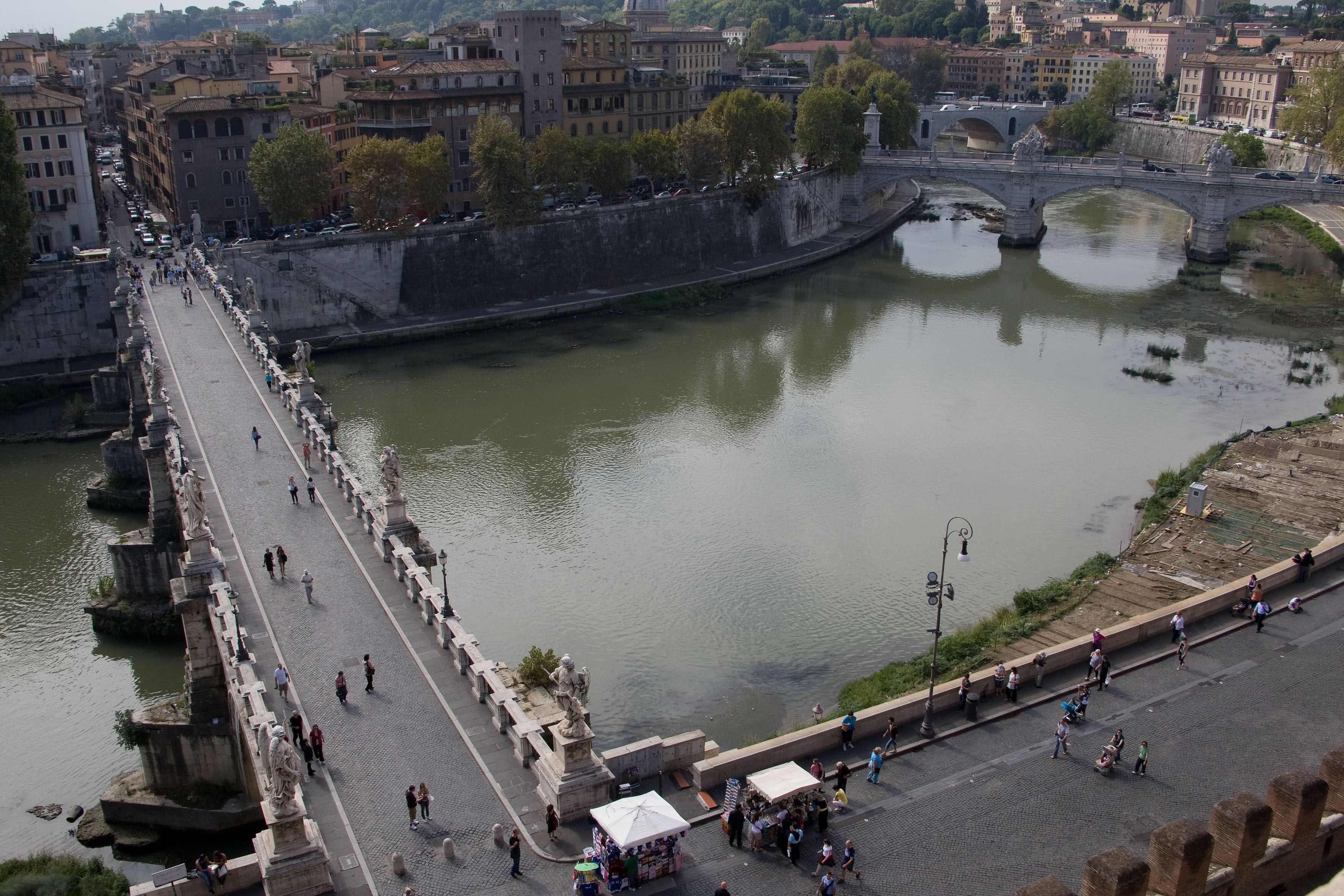
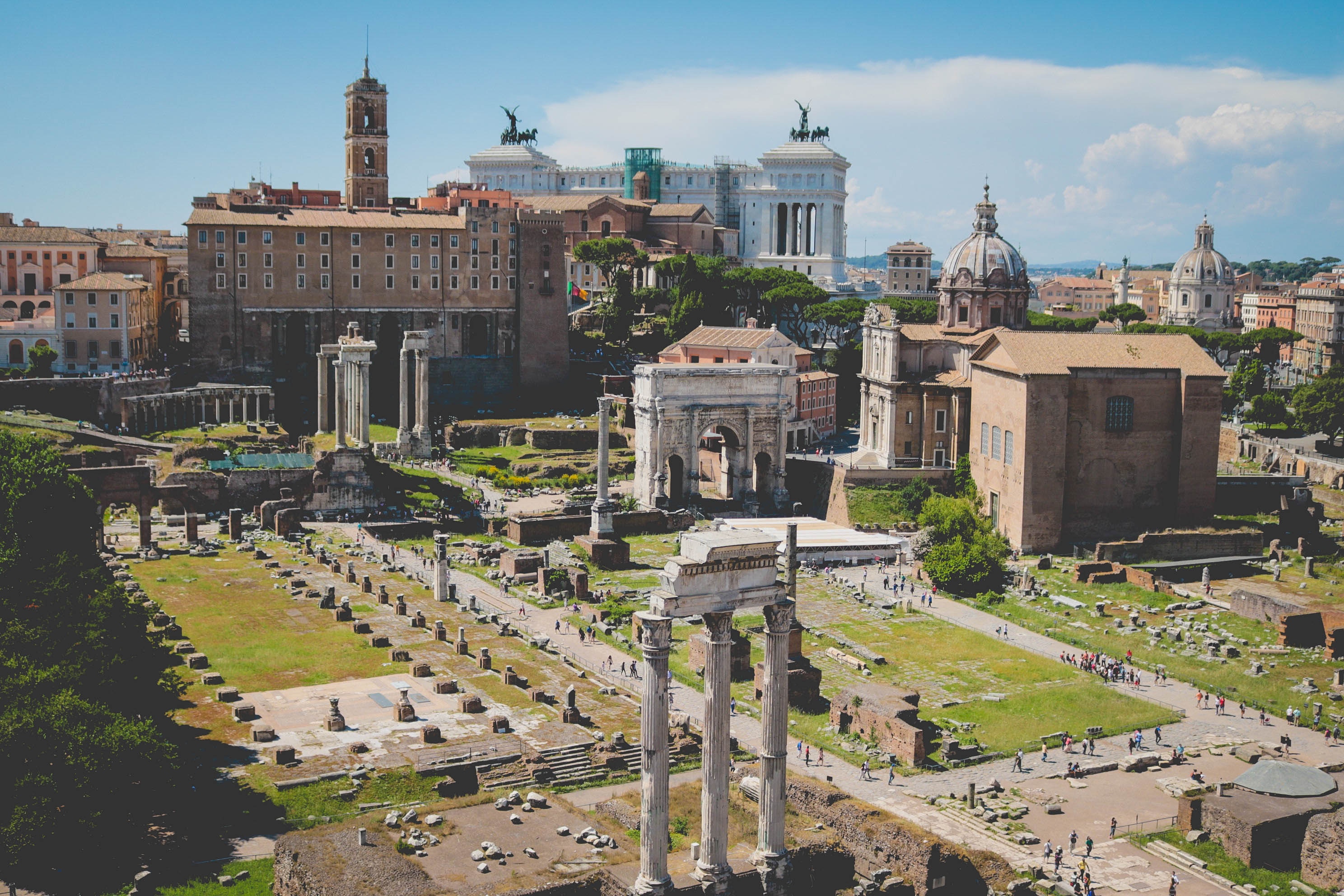
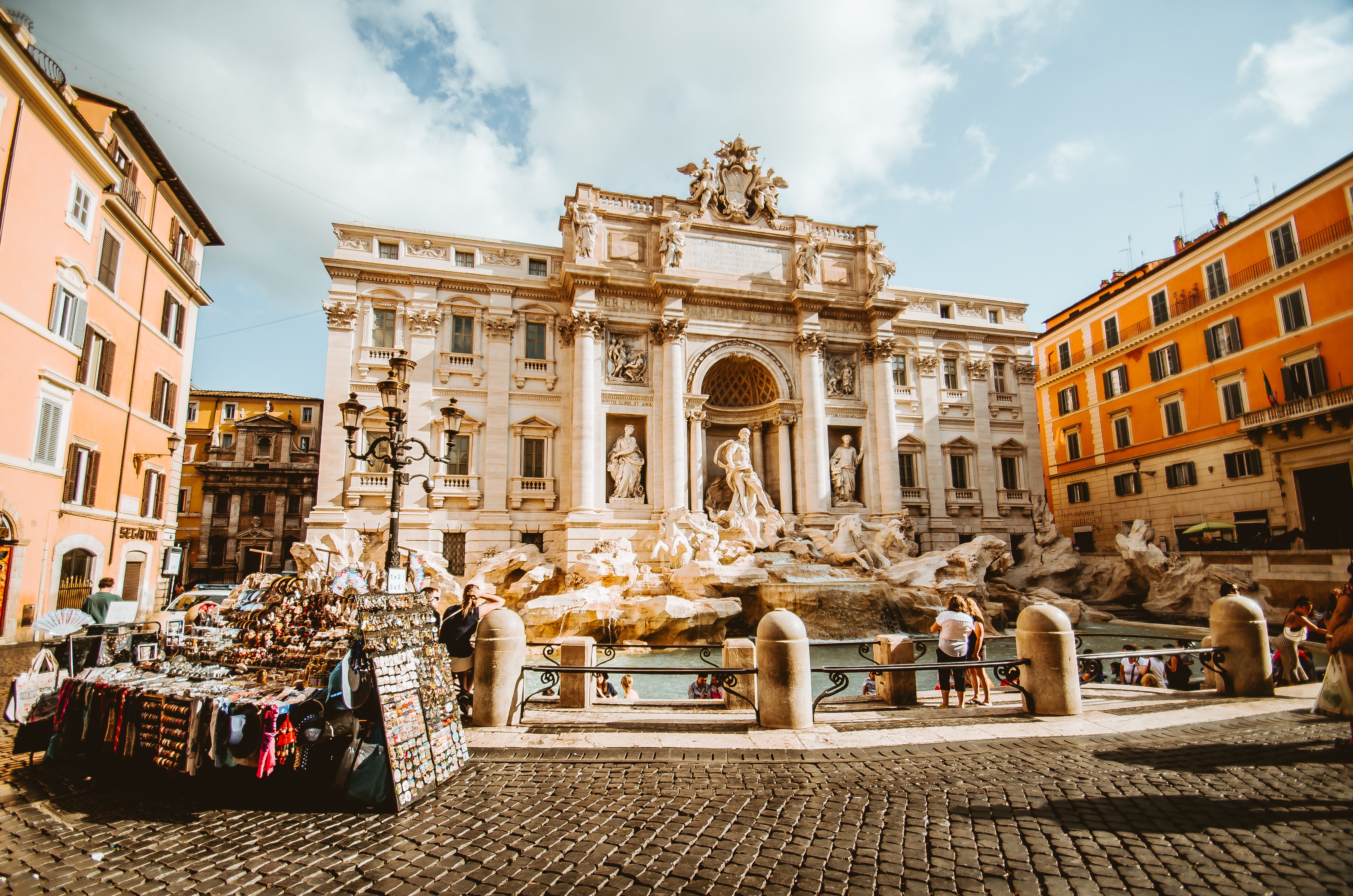
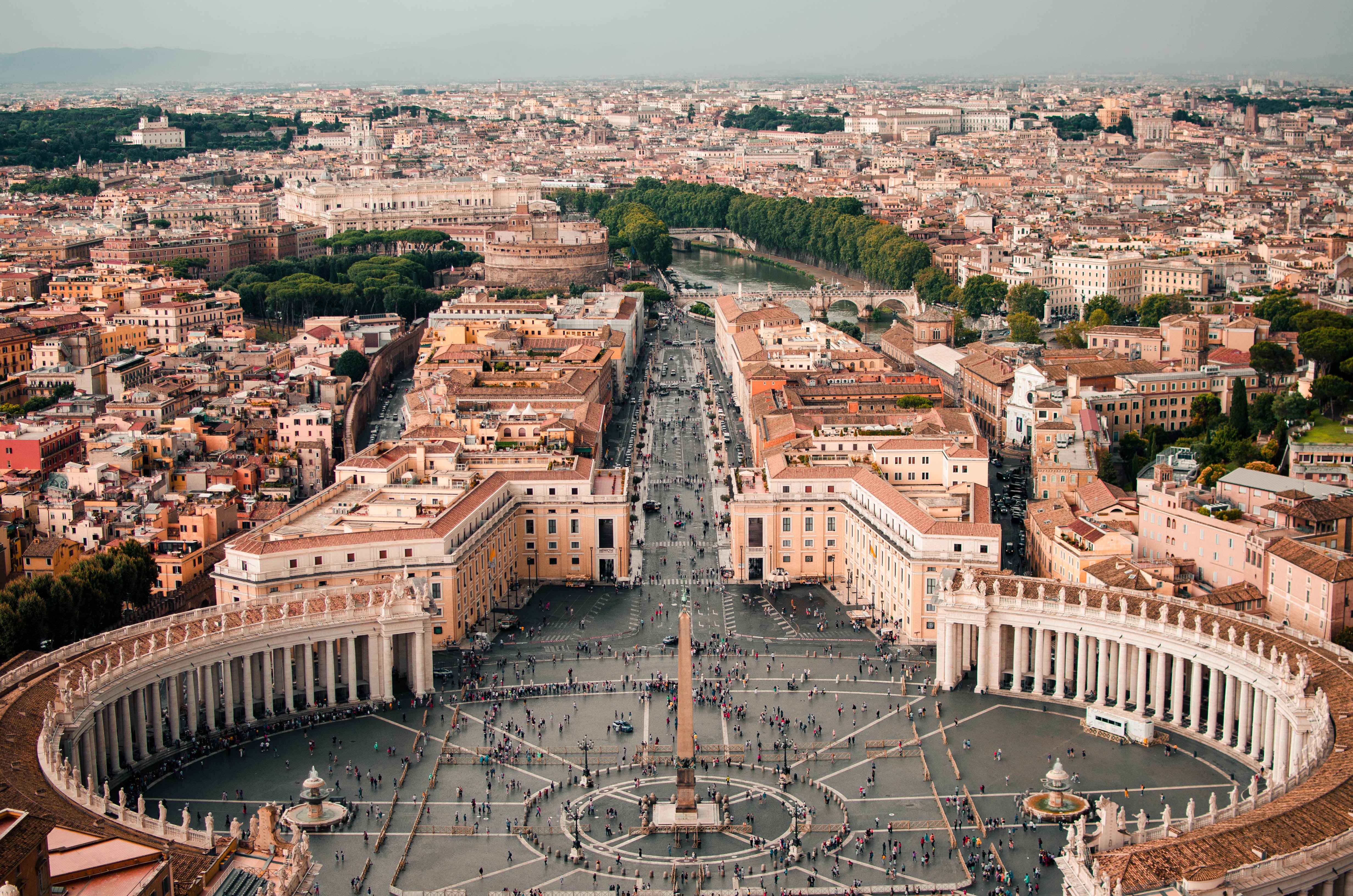
About Civitavecchia
Italy's vibrant capital lives in the present, but no other city on earth evokes its past so powerfully. For over 2,500 years, emperors, popes, artists, and common citizens have left their mark here. Archaeological remains from ancient Rome, art-stuffed churches, and the treasures of Vatican City vie for your attention, but Rome is also a wonderful place to practice the Italian-perfected il dolce far niente, the sweet art of idleness. Your most memorable experiences may include sitting at a caffè in the Campo de' Fiori or strolling in a beguiling piazza.








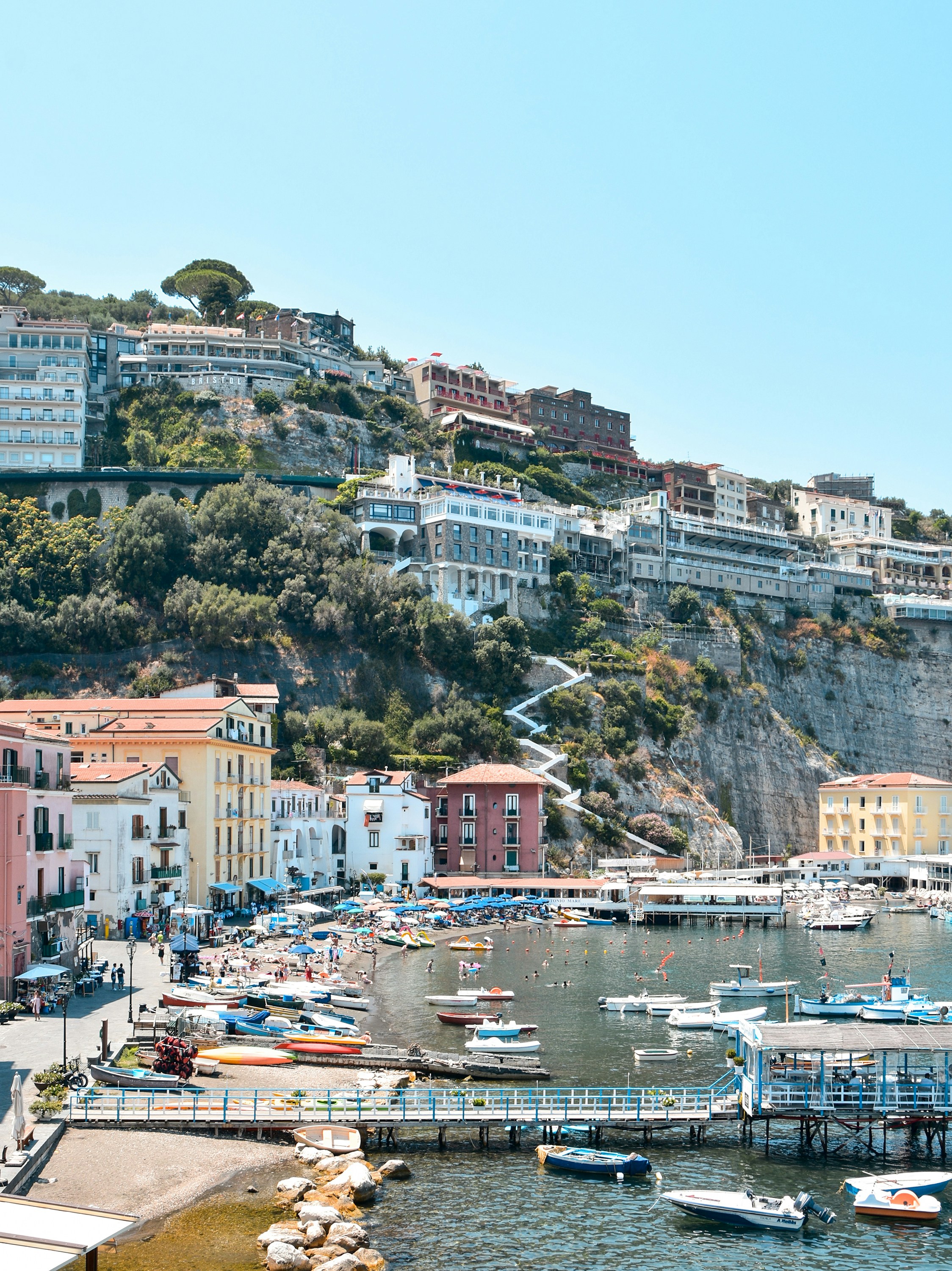
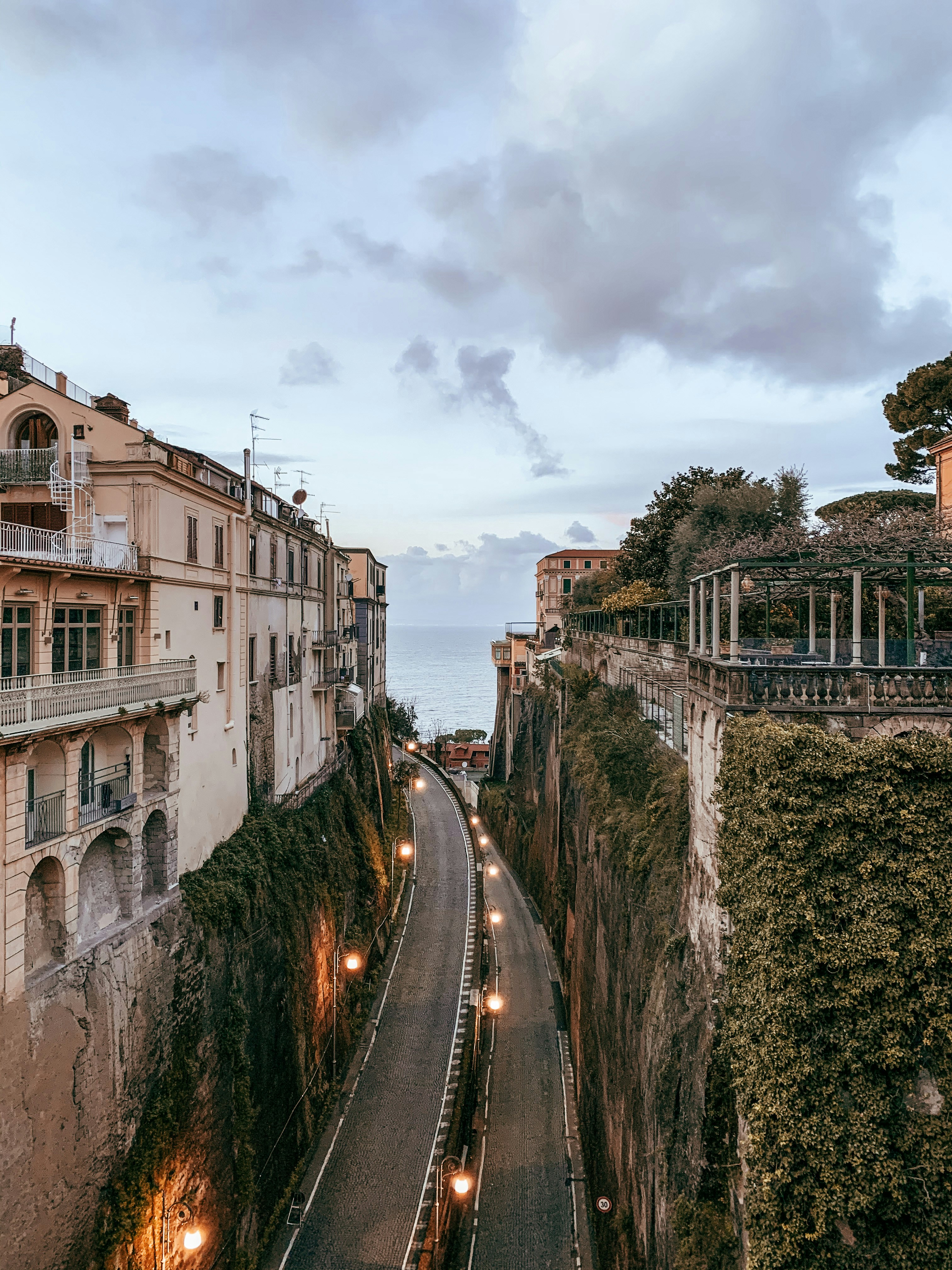
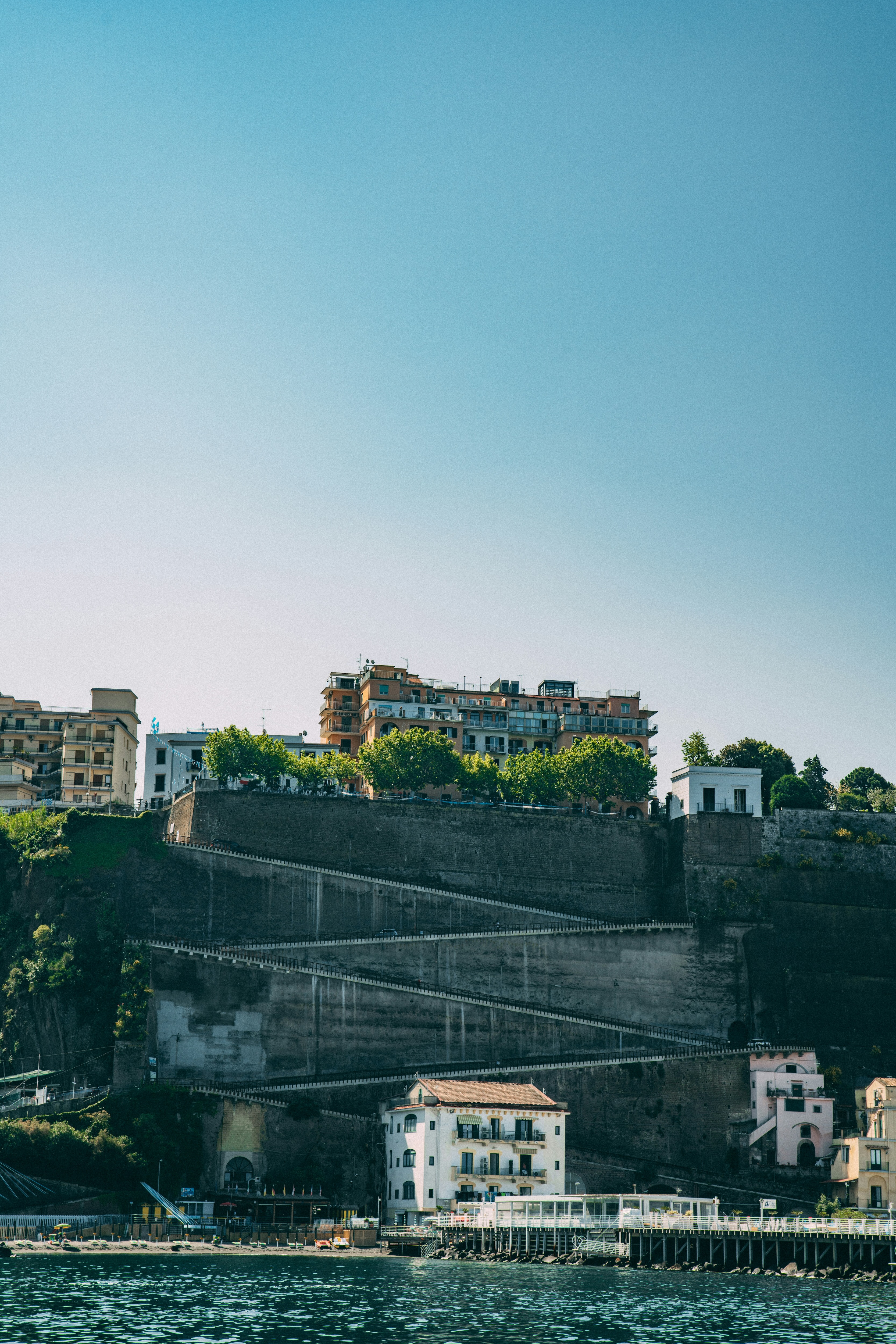
About Sorrento
Sorrento may have become a jumping-off point for visitors to Pompeii, Capri, and Amalfi, but you can find countless reasons to love it for itself. The Sorrentine people are fair-minded and hardworking, bubbling with life and warmth. The tuff cliff on which the town rests is spread over the bay, absorbing sunlight, while orange and lemon trees waft their perfume in spring. Winding along a cliff above a small beach and two harbors, the town is split in two by a narrow ravine formed by a former mountain stream. To the east, dozens of hotels line busy Via Correale along the cliff—many have "grand" included in their names, and some indeed still are. To the west, however, is the historic sector, which still enchants. It's a relatively flat area, with winding, stone-paved lanes bordered by balconied buildings, some joined by medieval stone arches. The central piazza is named after the poet Torquato Tasso, born here in 1544. This part of town is a delightful place to walk through. Craftspeople are often at work in their stalls and shops and are happy to let you watch; in fact, that's the point. Music spots and bars cluster in the side streets near Piazza Tasso.



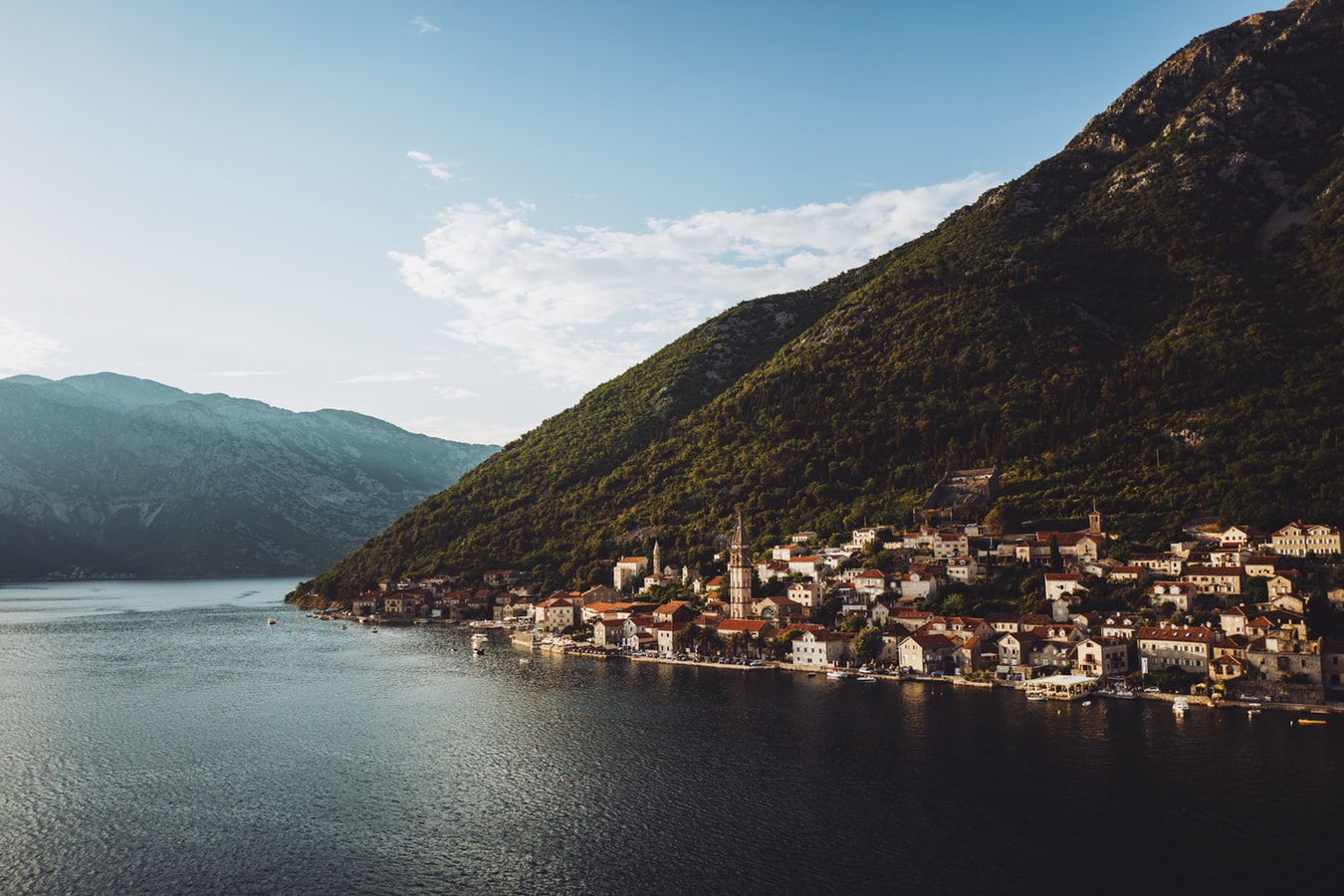
About Kotor
Backed by imposing mountains, tiny Kotor lies hidden from the open sea, tucked into the deepest channel of the Bokor Kotorska (Kotor Bay), which is Europe's most southerly fjord. To many, this town is more charming than its sister UNESCO World Heritage Site, Dubrovnik, retaining more authenticity, but with fewer tourists and spared the war damage and subsequent rebuilding which has given Dubrovnik something of a Disney feel.Kotor's medieval Stari Grad (Old Town) is enclosed within well-preserved defensive walls built between the 9th and 18th centuries and is presided over by a proud hilltop fortress. Within the walls, a labyrinth of winding cobbled streets leads through a series of splendid paved piazzas, rimmed by centuries-old stone buildings. The squares are now haunted by strains from buskers but although many now house trendy cafés and chic boutiques, directions are still given medieval-style by reference to the town’s landmark churches.In the Middle Ages, as Serbia's chief port, Kotor was an important economic and cultural center with its own highly regarded schools of stonemasonry and iconography. From 1391 to 1420 it was an independent city-republic and later, it spent periods under Venetian, Austrian, and French rule, though it was undoubtedly the Venetians who left the strongest impression on the city's architecture. Since the breakup of Yugoslavia, some 70% of the stone buildings in the romantic Old Town have been snapped up by foreigners, mostly Brits and Russians. Porto Montenegro, a new marina designed to accommodate some of the world’s largest super yachts, opened in nearby Tivat in 2011, and along the bay are other charming seaside villages, all with better views of the bay than the vista from Kotor itself where the waterside is congested with cruise ships and yachts. Try sleepy Muo or the settlement of Prčanj in one direction around the bay, or Perast and the Roman mosaics of Risan in the other direction.
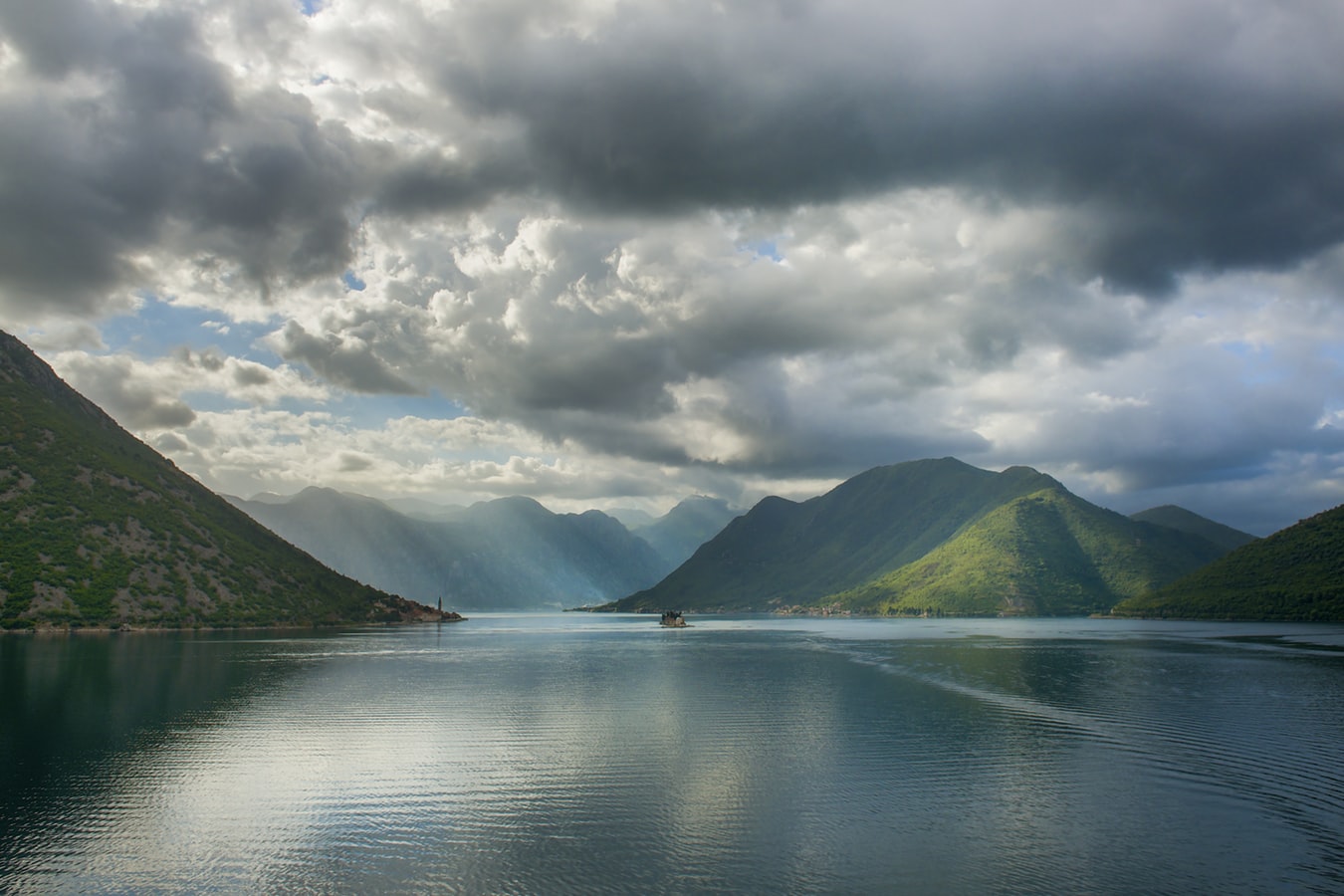
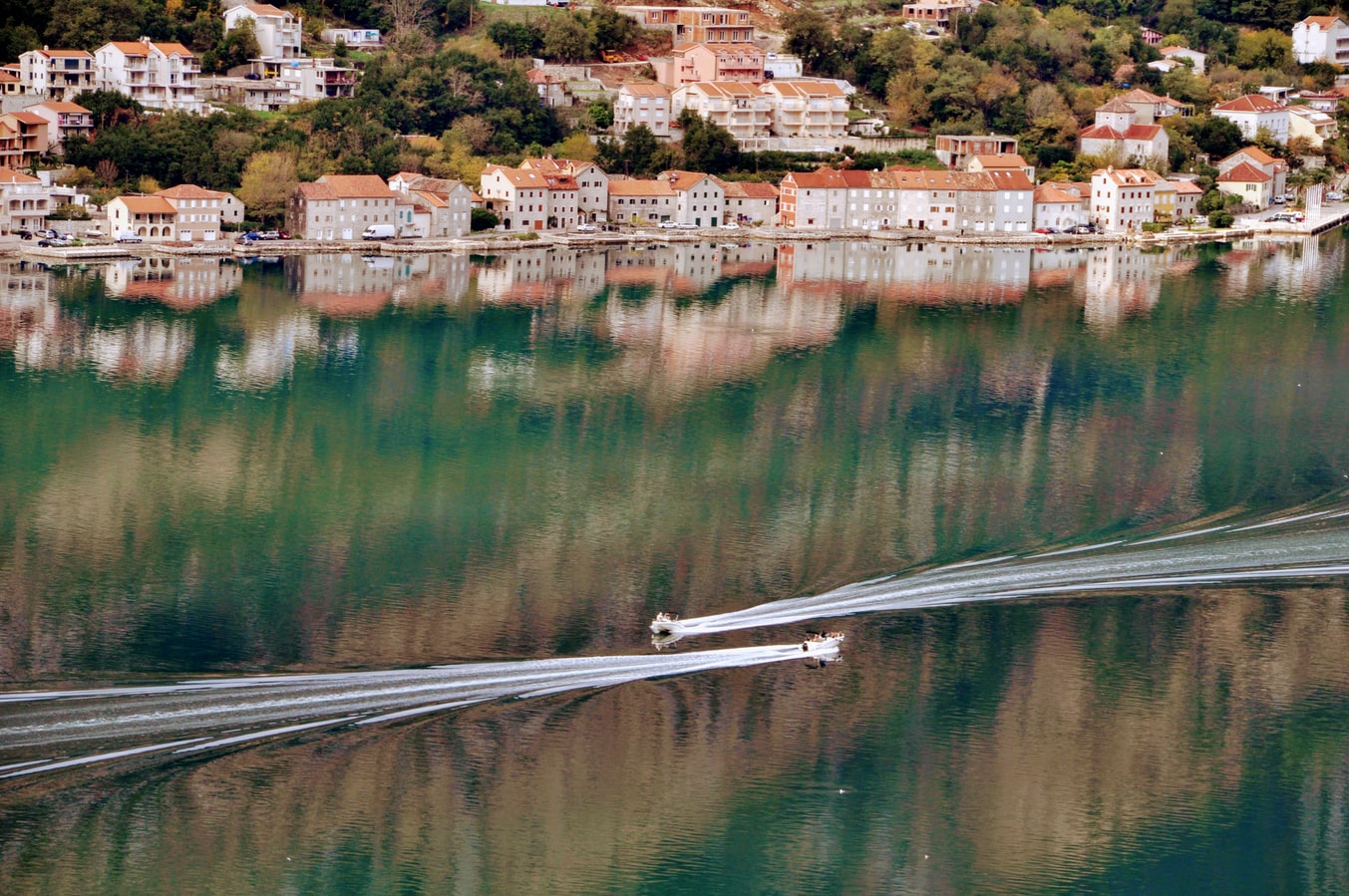
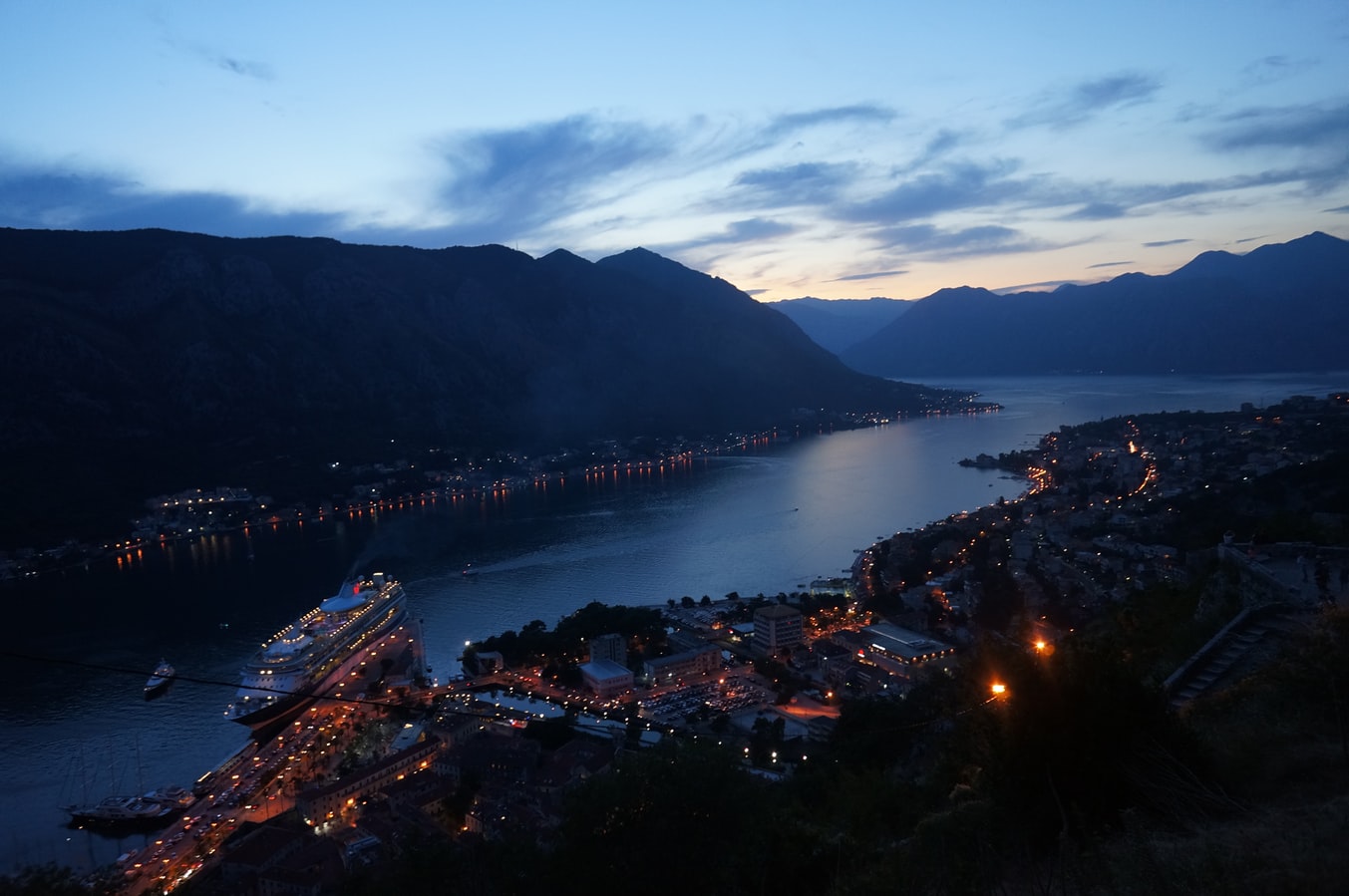
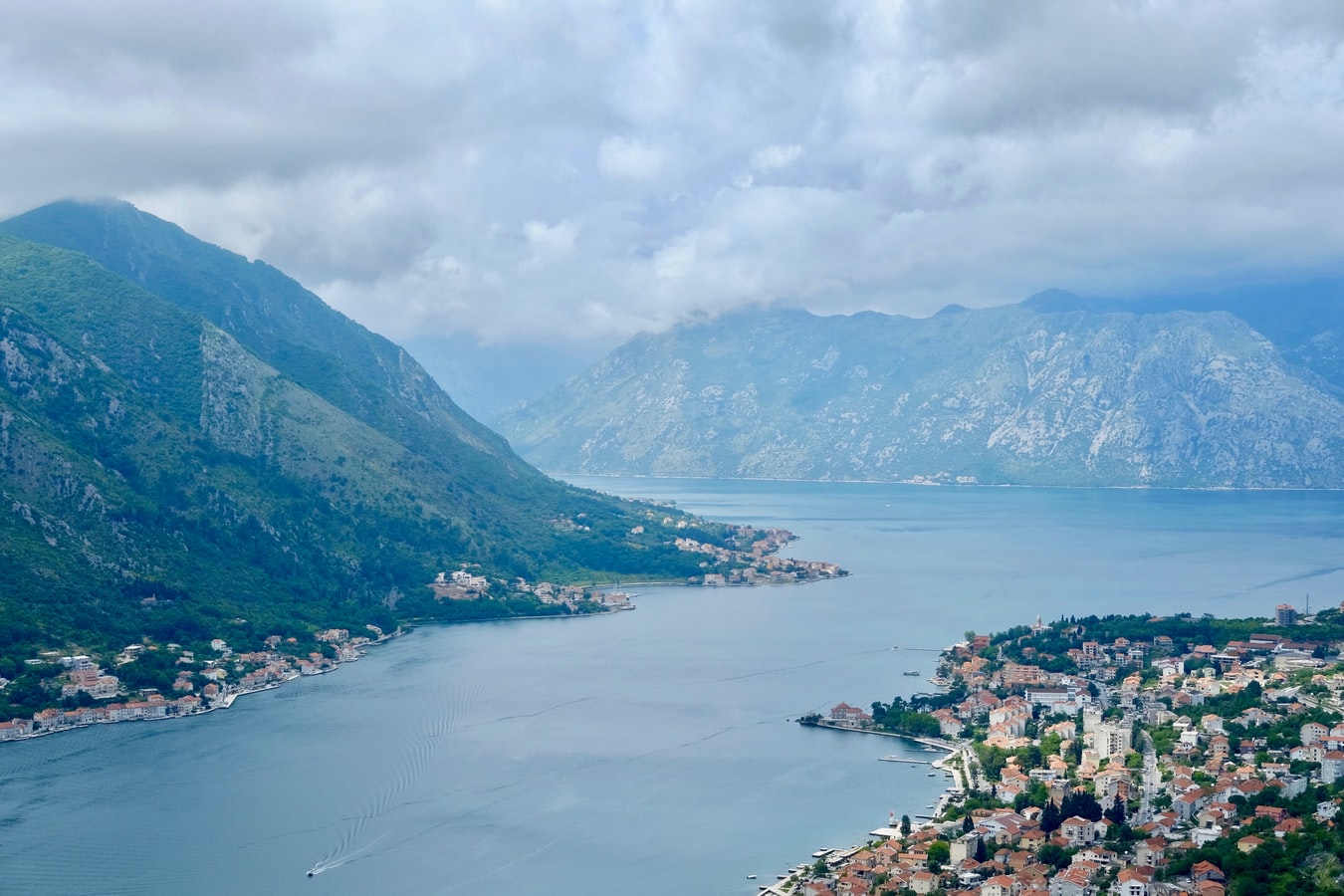





About Dubrovnik
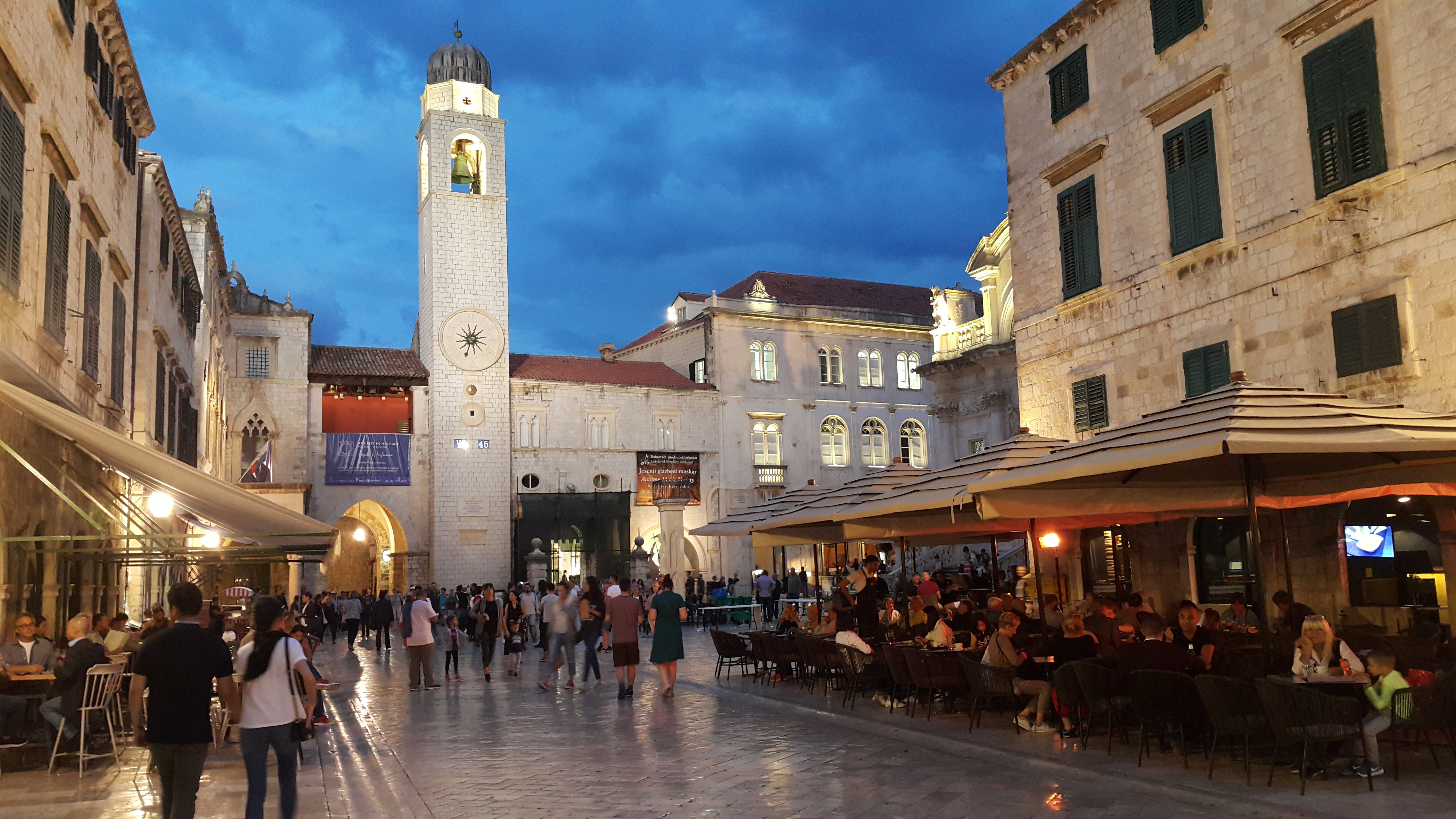
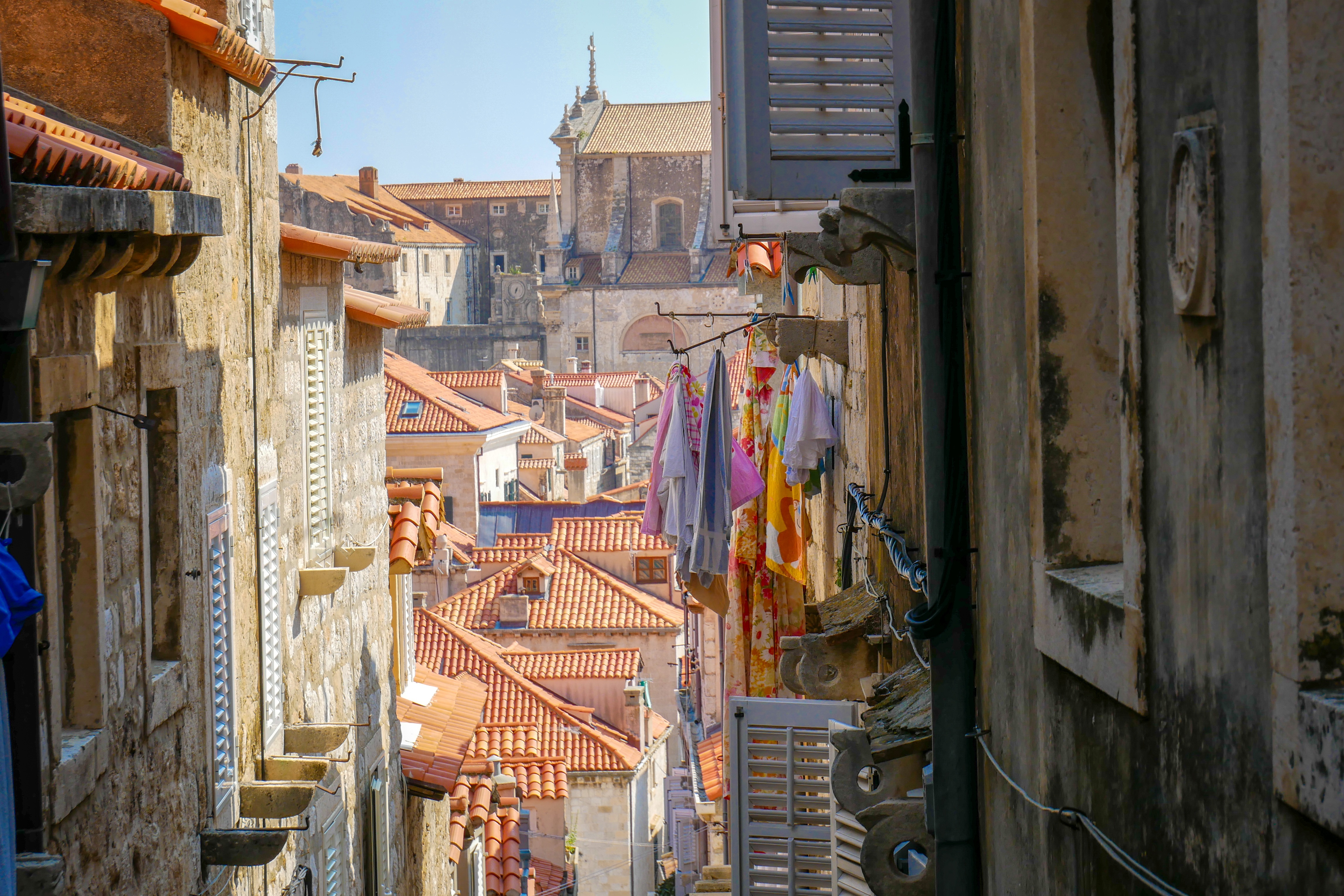
Nothing can prepare you for your first sight of Dubrovnik. Lying 216 km (135 miles) southeast of Split and commanding a jaw-dropping coastal location, it is one of the world's most beautiful fortified cities. Its massive stone ramparts and fortress towers curve around a tiny harbor, enclosing graduated ridges of sun-bleached orange-tiled roofs, copper domes, and elegant bell towers. Your imagination will run wild picturing what it looked like seven centuries ago when the walls were built, without any suburbs or highways around it, just this magnificent stone city rising out of the sea.In the 7th century AD, residents of the Roman city Epidaurum (now Cavtat) fled the Avars and Slavs of the north and founded a new settlement on a small rocky island, which they named Laus, and later Ragusa. On the mainland hillside opposite the island, the Slav settlement called Dubrovnik grew up. In the 12th century the narrow channel separating the two settlements was filled in (now the main street through the Old Town, called Stradun), and Ragusa and Dubrovnik became one. The city was surrounded by defensive walls during the 13th century, and these were reinforced with towers and bastions in the late 15th century.From 1358 to 1808 the city thrived as a powerful and remarkably sophisticated independent republic, reaching its golden age during the 16th century. In 1667 many of its splendid Gothic and Renaissance buildings were destroyed by an earthquake. The defensive walls survived the disaster, and the city was rebuilt in baroque style.Dubrovnik lost its independence to Napoléon in 1808, and in 1815 passed to Austria-Hungary. During the 20th century, as part of Yugoslavia, the city became a popular tourist destination, and in 1979 it was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. During the war for independence, it came under heavy siege. Thanks to careful restoration, few traces of damage remain; however, there are maps inside the Pile and Ploče Gates illustrating the points around the city where damage was done. It’s only when you experience Dubrovnik yourself that you can understand what a treasure the world nearly lost
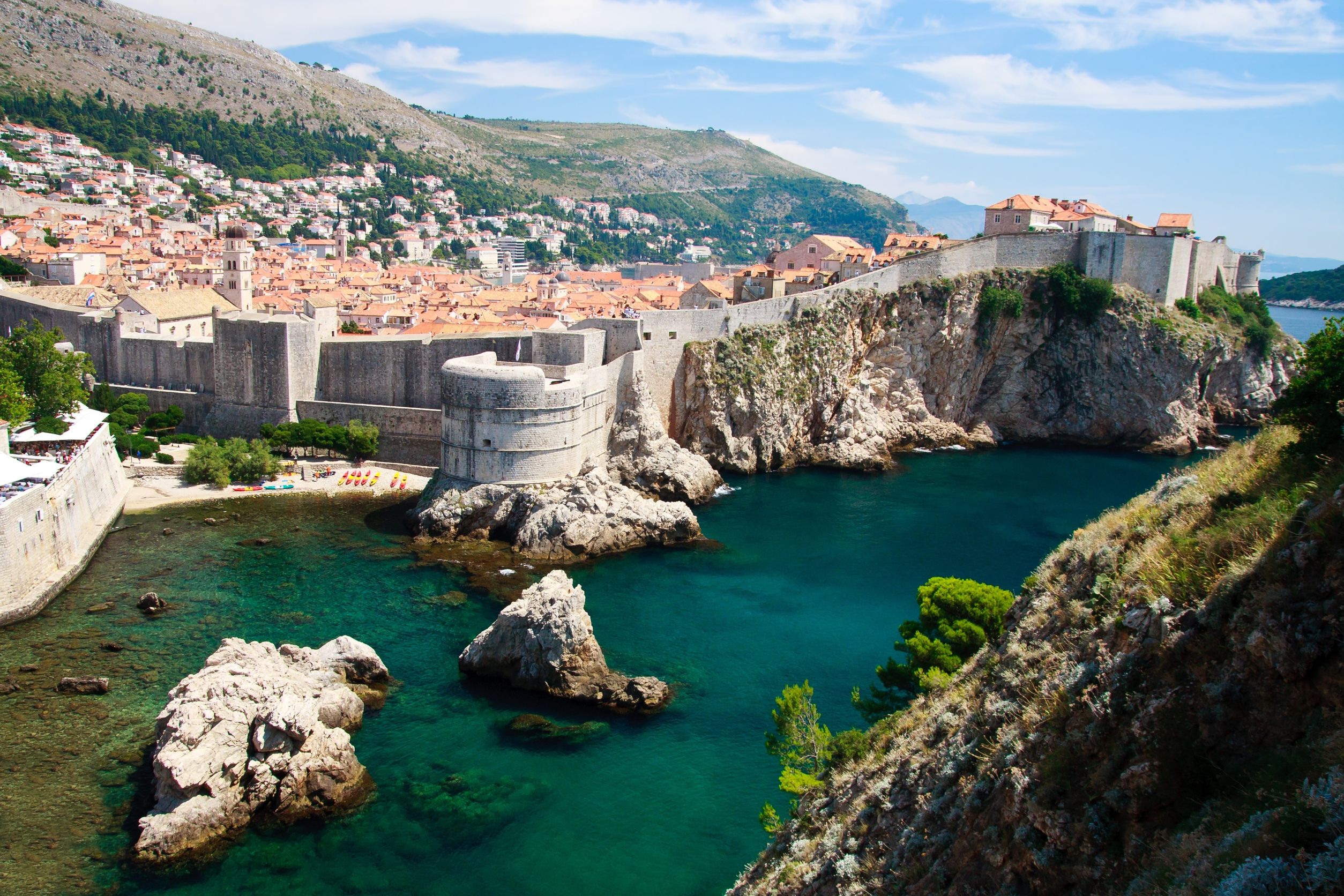






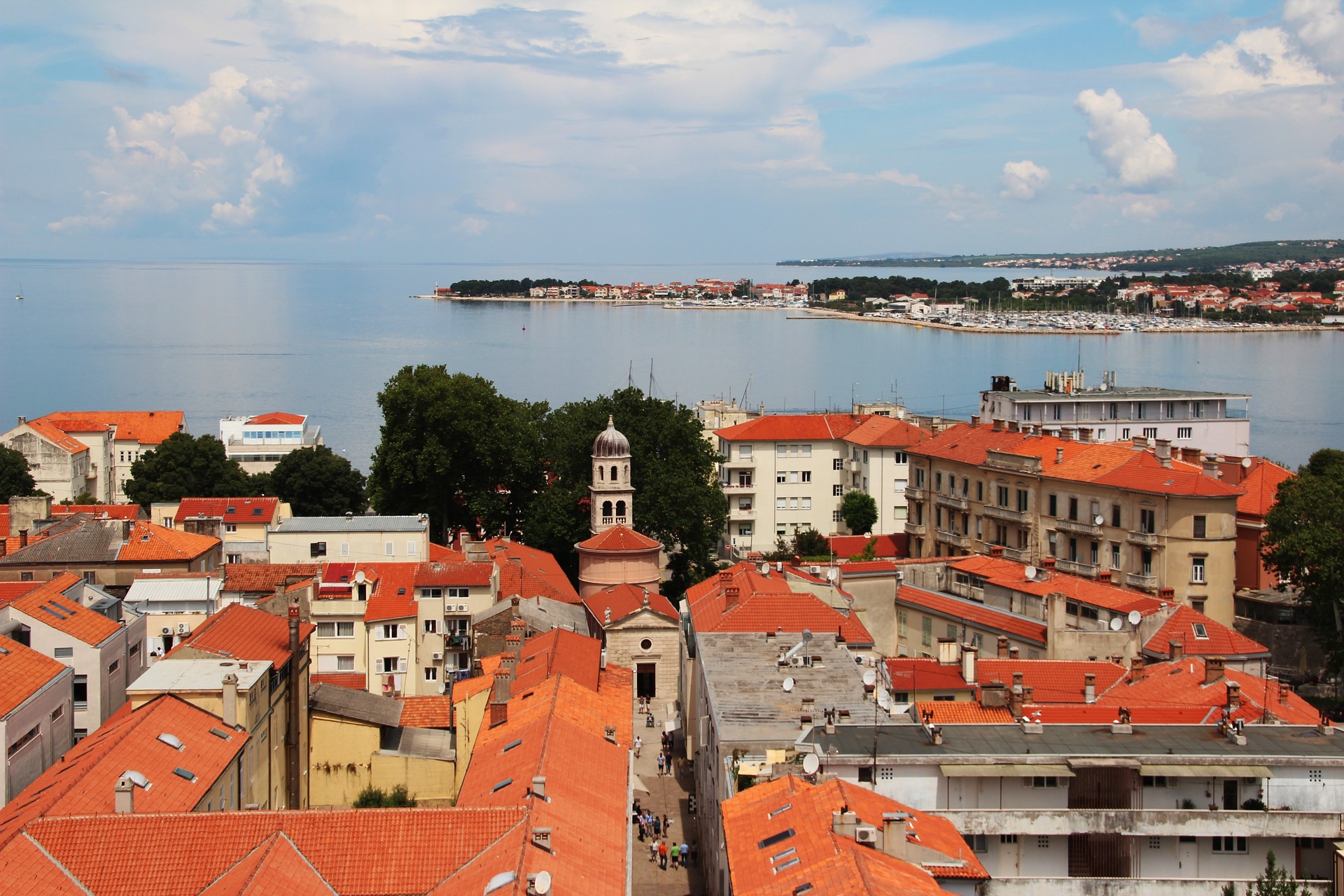
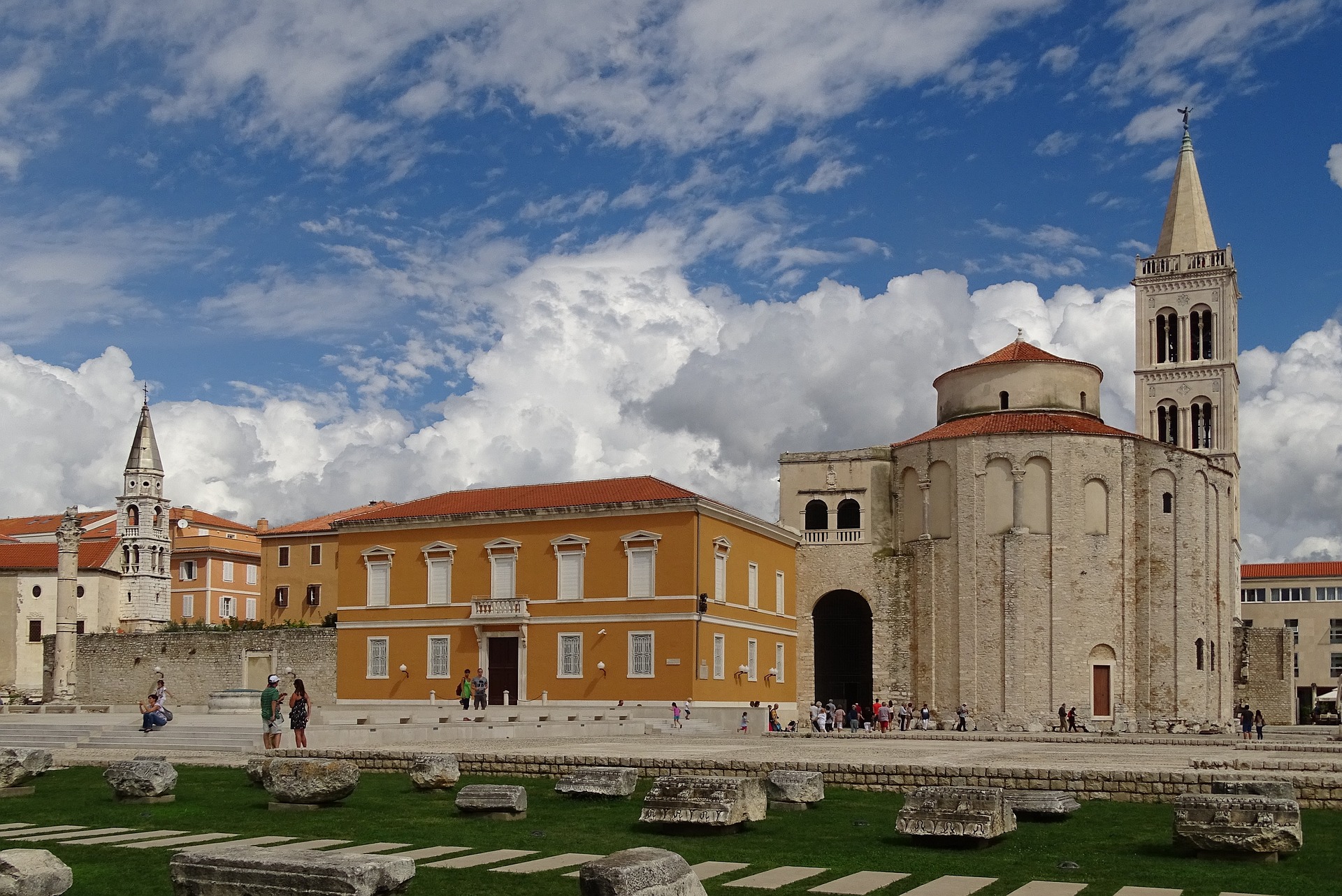
About Zadar
Dalmatia's capital for more than 1,000 years, Zadar is all too often passed over by travelers on their way to Split or Dubrovnik. What they miss out on is a city of more than 73,000 that is remarkably lovely and lively despite—and, in some measure, because of—its tumultuous history. The Old Town, separated from the rest of the city on a peninsula some 4 km (2½ miles) long and just 1,640 feet wide, is bustling and beautiful: the marble pedestrian streets are replete with Roman ruins, medieval churches, palaces, museums, archives, and libraries. Parts of the new town are comparatively dreary, a testament to what a world war followed by decades of communism, not to mention a civil war, can do to the architecture of a city that is 3,000 years old. A settlement had already existed on the site of the present-day city for some 2,000 years when Rome finally conquered Zadar in the 1st century BC; the foundations of the forum can be seen today. Before the Romans came the Liburnians had made it a key center for trade with the Greeks and Romans for 800 years. In the 3rd century BC the Romans began to seriously pester the Liburnians, but required two centuries to bring the area under their control. During the Byzantine era, Zadar became the capital of Dalmatia, and this period saw the construction of its most famous church, the 9th-century St. Donat's Basilica. It remained the region's foremost city through the ensuing centuries. The city then experienced successive onslaughts and occupations—both long and short—by the Osogoths, the Croatian-Hungarian kings, the Venetians, the Turks, the Habsburgs, the French, the Habsburgs again, and finally the Italians before becoming part of Yugoslavia and, in 1991, the independent republic of Croatia. Zadar was for centuries an Italian-speaking city, and Italian is still spoken widely, especially by older people. Indeed, it was ceded to Italy in 1921 under the Treaty of Rapallo (and reverted to its Italian name of Zara). Its occupation by the Germans from 1943 led to intense bombing by the Allies during World War II, which left most of the city in ruins. Zadar became part of Tito's Yugoslavia in 1947, prompting many Italian residents to leave. Zadar's most recent ravages occurred during a three-month siege by Serb forces and months more of bombardment during the Croatian-Serbian war between 1991 and 1995. But you'd be hard-pressed to find outward signs of this today in what is a city to behold. There are helpful interpretive signs in English all around the Old Town, so you certainly won't feel lost when trying to make sense of the wide variety of architectural sites you might otherwise pass by with only a cursory look.


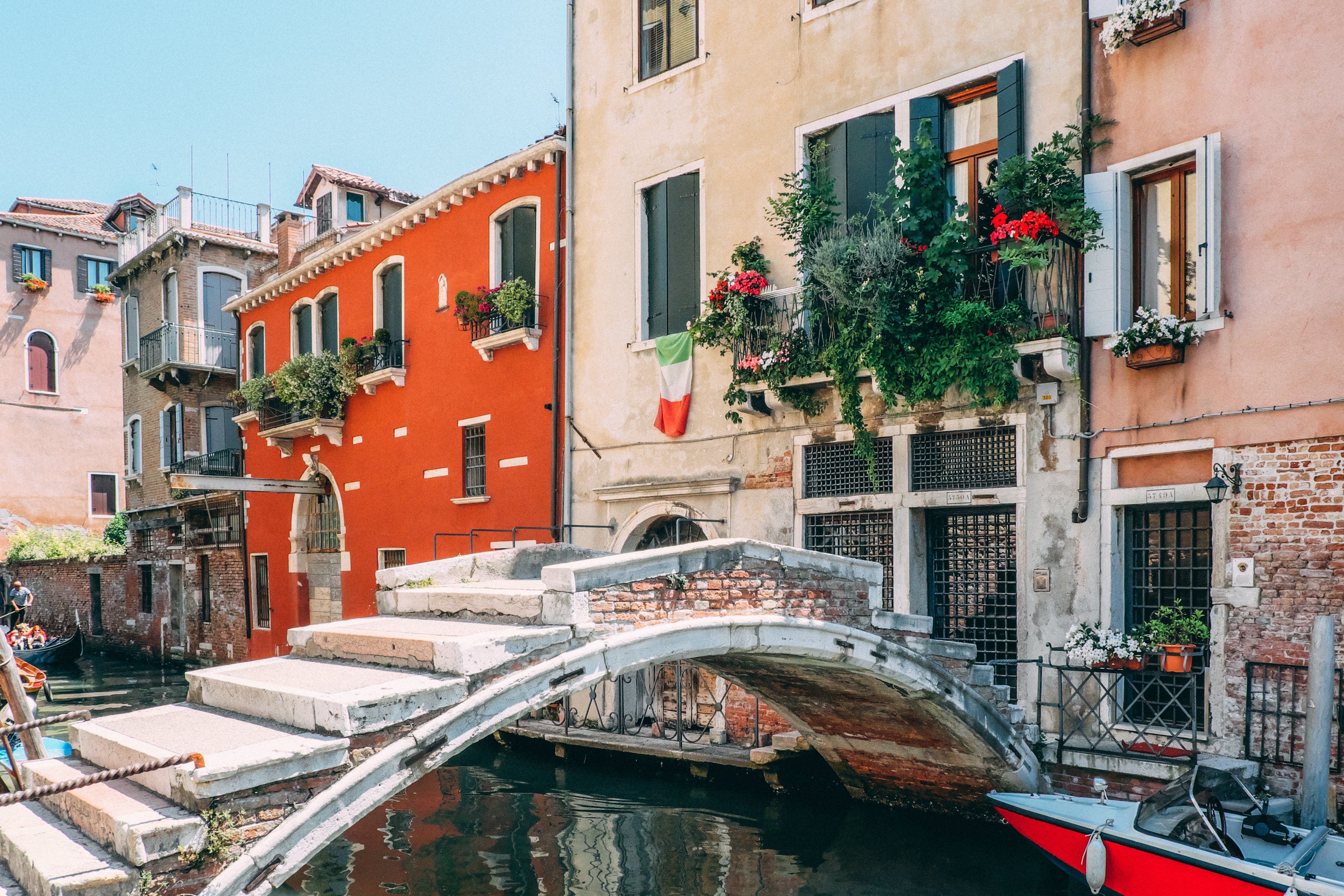
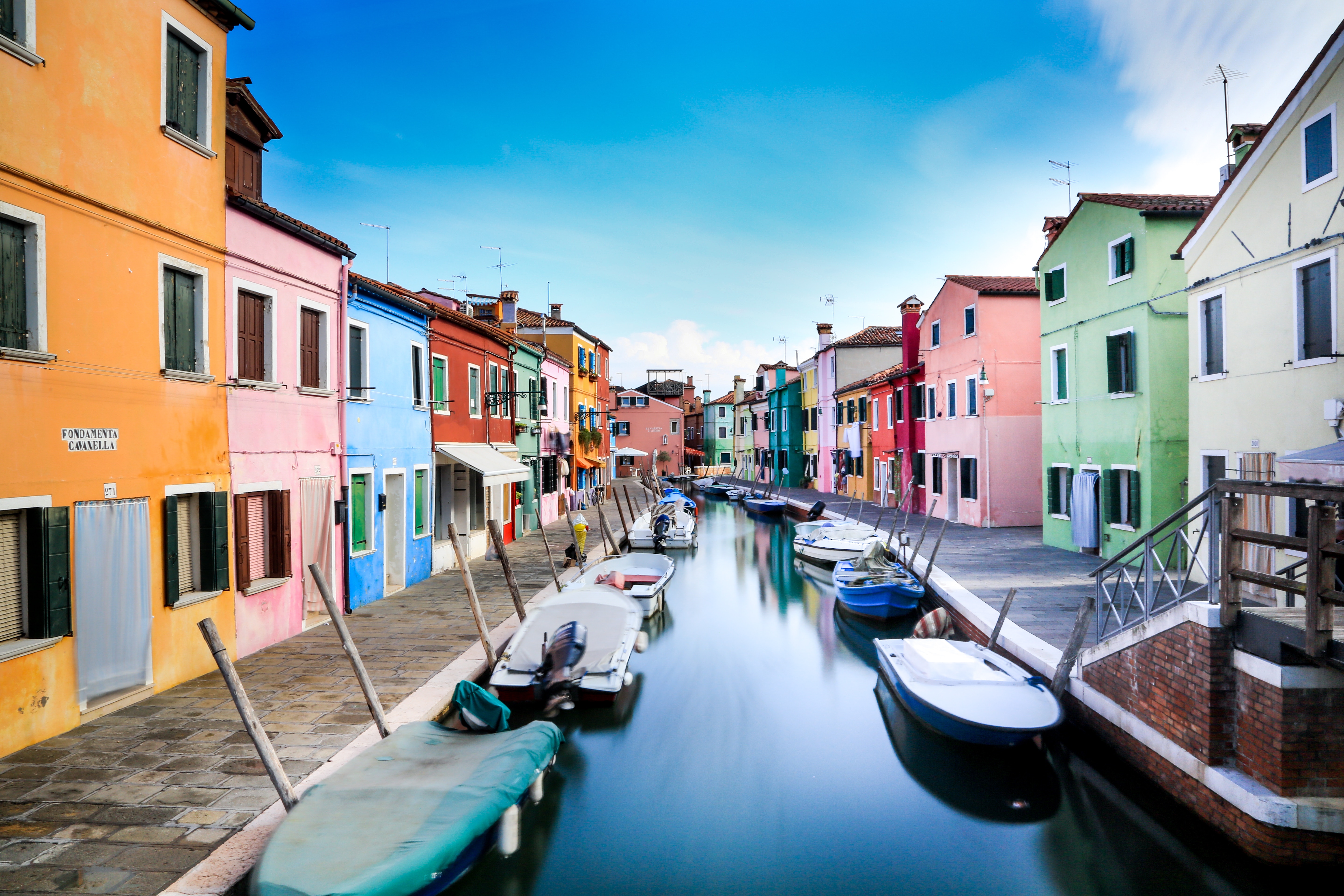
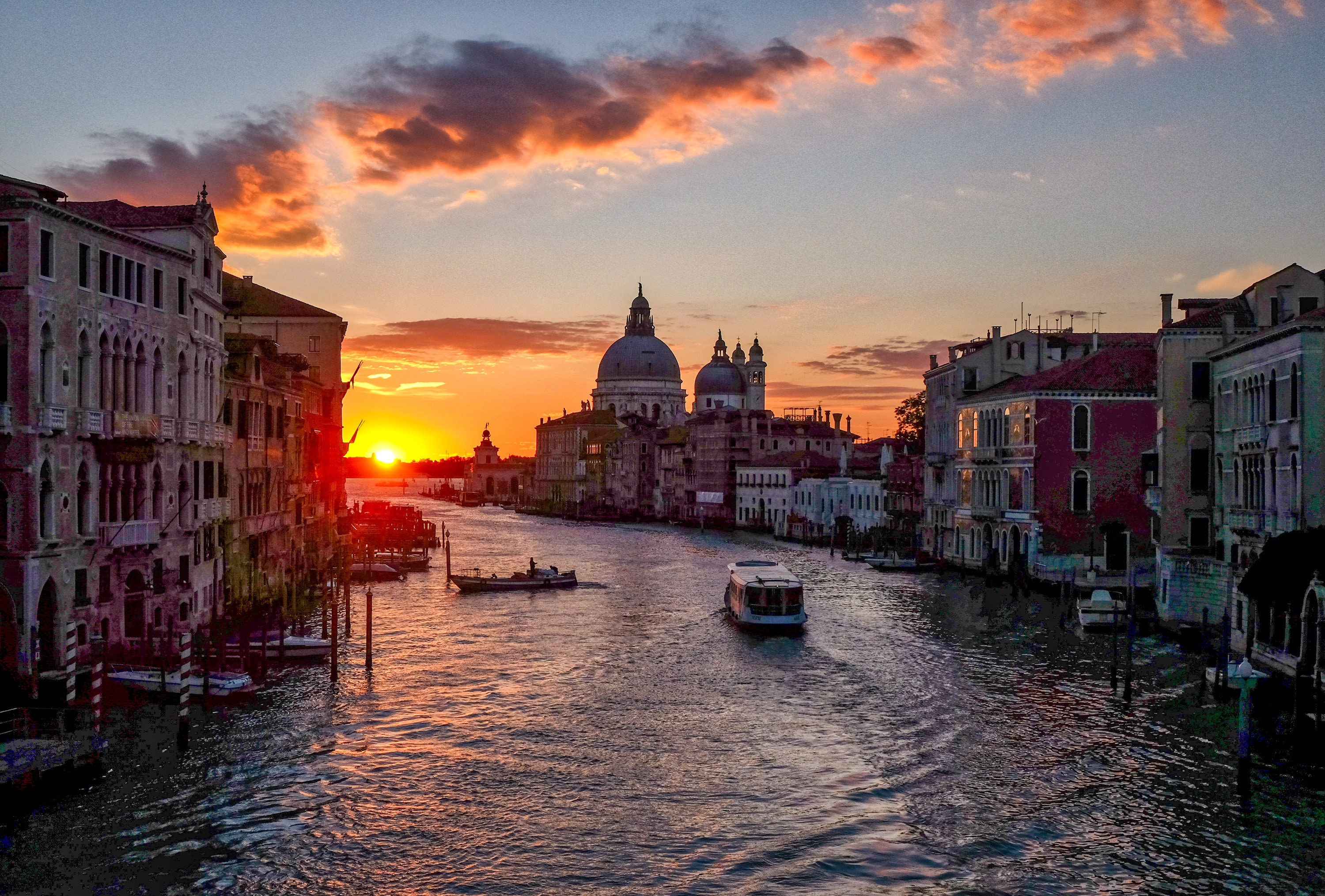
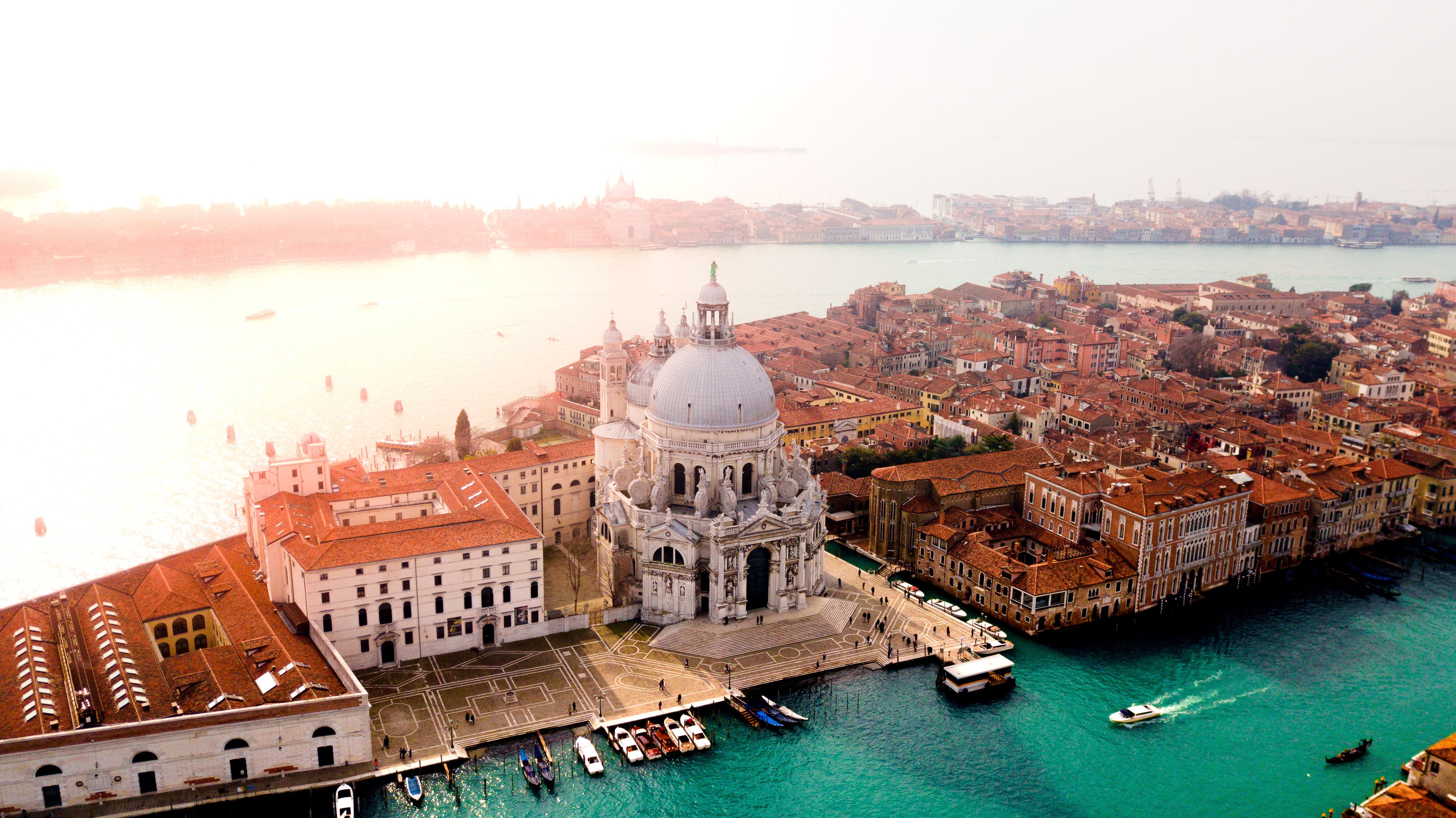
About Venice
Venice is a city unlike any other. No matter how often you've seen it in photos and films, the real thing is more dreamlike than you could imagine. With canals where streets should be, water shimmers everywhere. The fabulous palaces and churches reflect centuries of history in what was a wealthy trading center between Europe and the Orient. Getting lost in the narrow alleyways is a quintessential part of exploring Venice, but at some point you'll almost surely end up in Piazza San Marco, where tourists and locals congregate for a coffee or an aperitif.







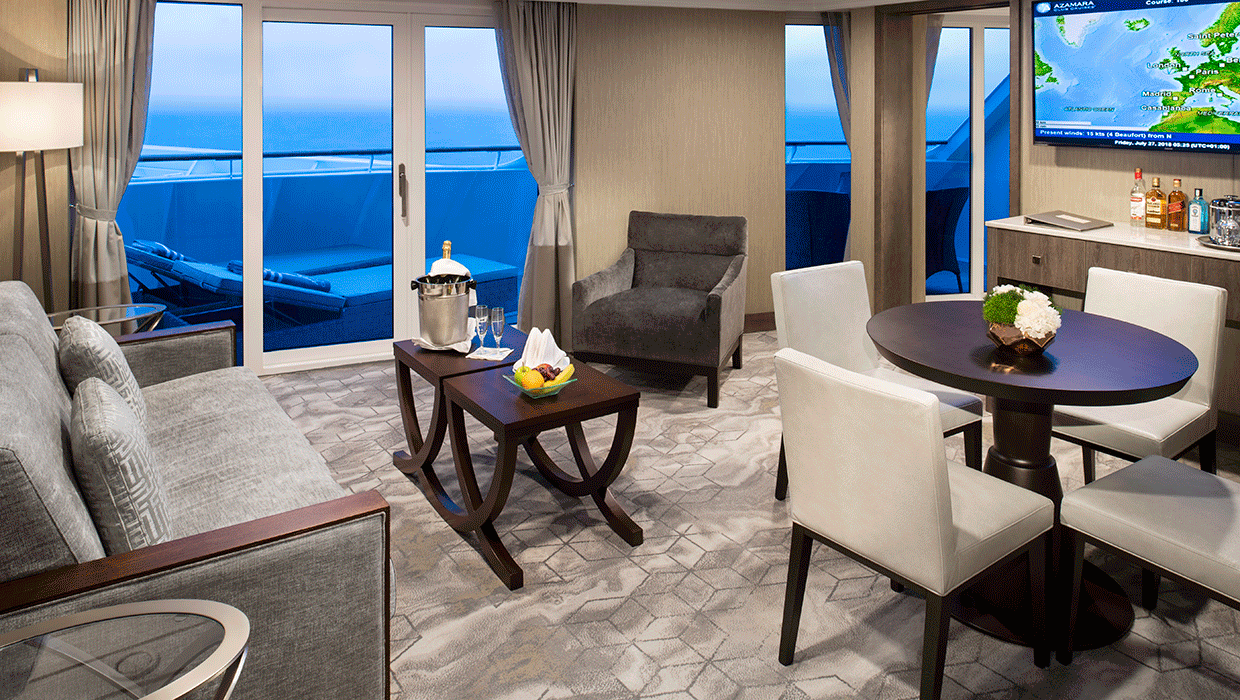
Our largest suites have been transformed with contemporary design elements that are both elegant and organic, with design that draws inspiration from nature—a sandy cliff, flowing river beds, exquisite white sand beaches, and rustling grasses. Enjoy a spacious living room, separate bedroom and all the amenities that come with our most luxurious suite.
Suite Features
- Spacious living room with a separate master bedroom
- Master bedroom with one queen size bed and a flat-screen television
- Flat-screen television in living room
- Marble master bathroom with shower. Journey and Quest suites feature a tub
- Dressing room with vanity and ample closet space
- Floor-to-ceiling sliding glass doors in living room and master bedroom
- Mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voice mail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hair dryer
- Stateroom: 560 sq. ft. (52 sq. m.) Veranda: 233 sq. ft. (21.7 sq. m.)
Included Suite Amenities (For cruises sailing before April 1, 2026)
- $300 Onboard Credit
- Unlimited Standard Wi-Fi
- Laundry - 2 bags/stateroom/week
- Exclusive Acamar Experience Dinner
- Dedicated butler and concierge service
- Full in-suite dining and daily evening hors d'oeuvres
- Complimentary Specialty Dining and exclusive breakfast at Aqualina
- In-room premium spirits and champagne
- Thalassotherapy Pool access
- Personalized assistance planning spa appointments and shore excursions
- Priority check-in
- News delivery
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoeshine service
- Turndown treats
Included Suite Amenities (For cruises on or after April 1, 2026)
- Ultimate Beverage Package
- Unlimited Standard Starlink Wi-Fi
- Unlimited Laundry
- Exclusive Acamar Experience Dinner
- Dedicated butler and concierge service
- Full in-suite dining and daily evening hors d'oeuvres
- Complimentary Specialty Dining and exclusive breakfast at Aqualina
- In-room premium spirits and champagne
- Thalassotherapy Pool access
- Personalized assistance planning spa appointments and shore excursions
- Priority check-in
- News delivery
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoeshine service
- Turndown treats
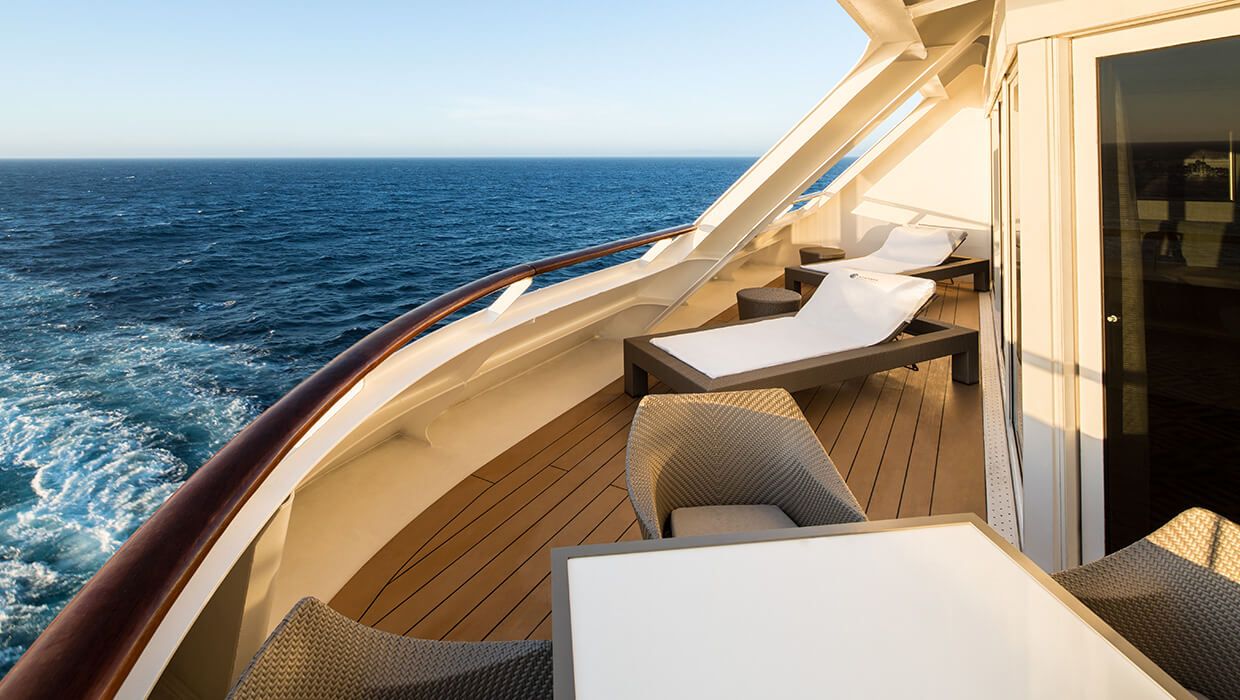





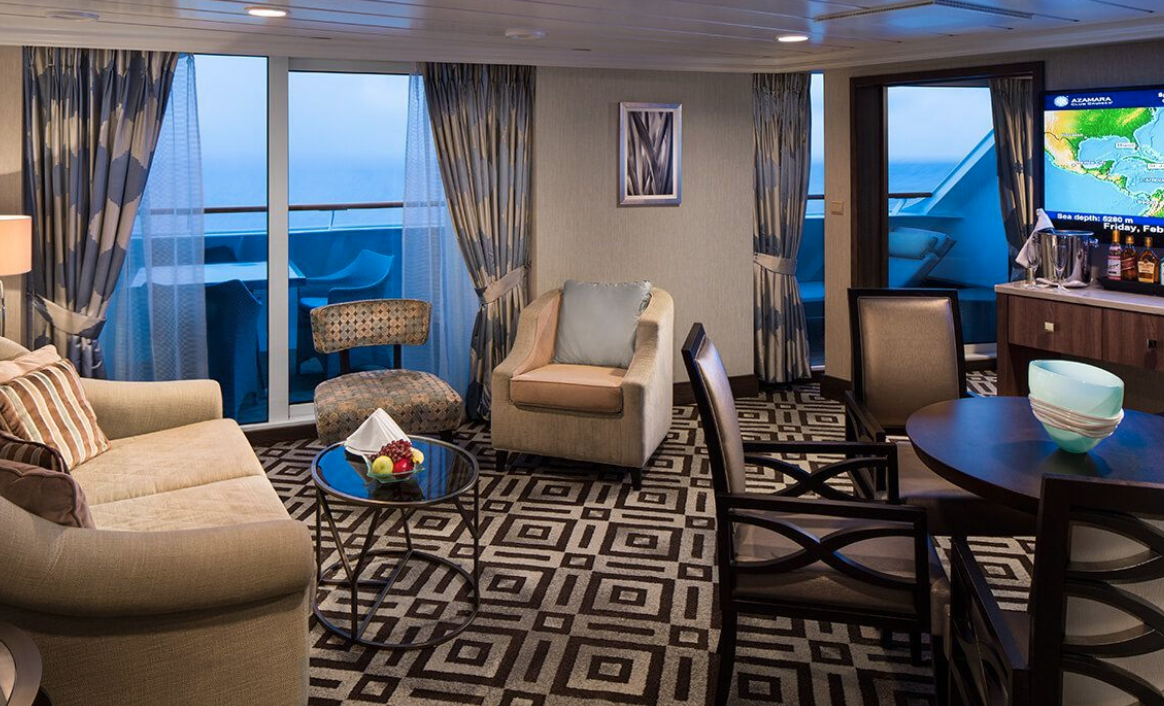
With a large living room and a separate bedroom—plus your own private veranda—your suite offers a restful retreat after your immersive experiences on land. Enjoy elegant, contemporary décor, and rich marble touches. You’ll be spoiled by the attention to detail in these beautiful suites, and of course, all the pampering too.
Suite Features
Spacious living room with a separate master bedroom
- Master bedroom with one queen size bed with a flat-screen television
- Flat-screen television in living room
- Marble master bathroom with shower. Journey and Quest suites feature a tub.
- Dressing room with vanity and ample closet space
- Floor-to-ceiling sliding glass doors in living room and master bedroom
- Mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voice mail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hair dryer
- Stateroom: 440-501 sq. ft. (40.9-46.5 sq. m.) Veranda: 233 sq. ft. (21.7 sq. m.)
Included Suite Amenities (For cruises sailing before April 1, 2026)
- $300 Onboard Credit
- Unlimited Standard Wi-Fi
- Laundry - 2 bags/stateroom/week
- Exclusive Acamar Experience Dinner
- Dedicated butler and concierge service
- Full in-suite dining and daily evening hors d'oeuvres
- Complimentary Specialty Dining and exclusive breakfast at Aqualina
- In-room premium spirits and champagne
- Thalassotherapy Pool access
- Personalized assistance planning spa appointments and shore excursions
- Priority check-in
- News delivery
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoeshine service
- Turndown treats
Included Suite Amenities (For cruises on or after April 1, 2026)
- Ultimate Beverage Package
- Unlimited Standard Starlink Wi-Fi
- Unlimited Laundry
- Exclusive Acamar Experience Dinner
- Dedicated butler and concierge service
- Full in-suite dining and daily evening hors d'oeuvres
- Complimentary Specialty Dining and exclusive breakfast at Aqualina
- In-room premium spirits and champagne
- Thalassotherapy Pool access
- Personalized assistance planning spa appointments and shore excursions
- Priority check-in
- News delivery
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoeshine service
- Turndown treats
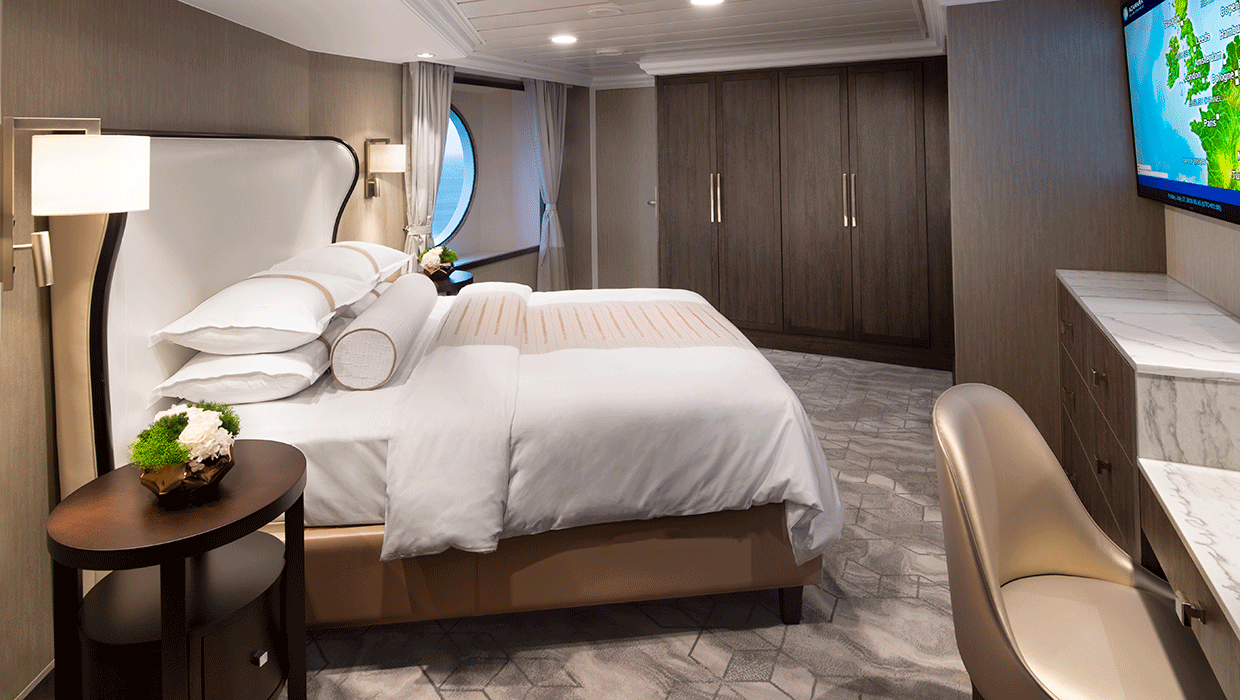
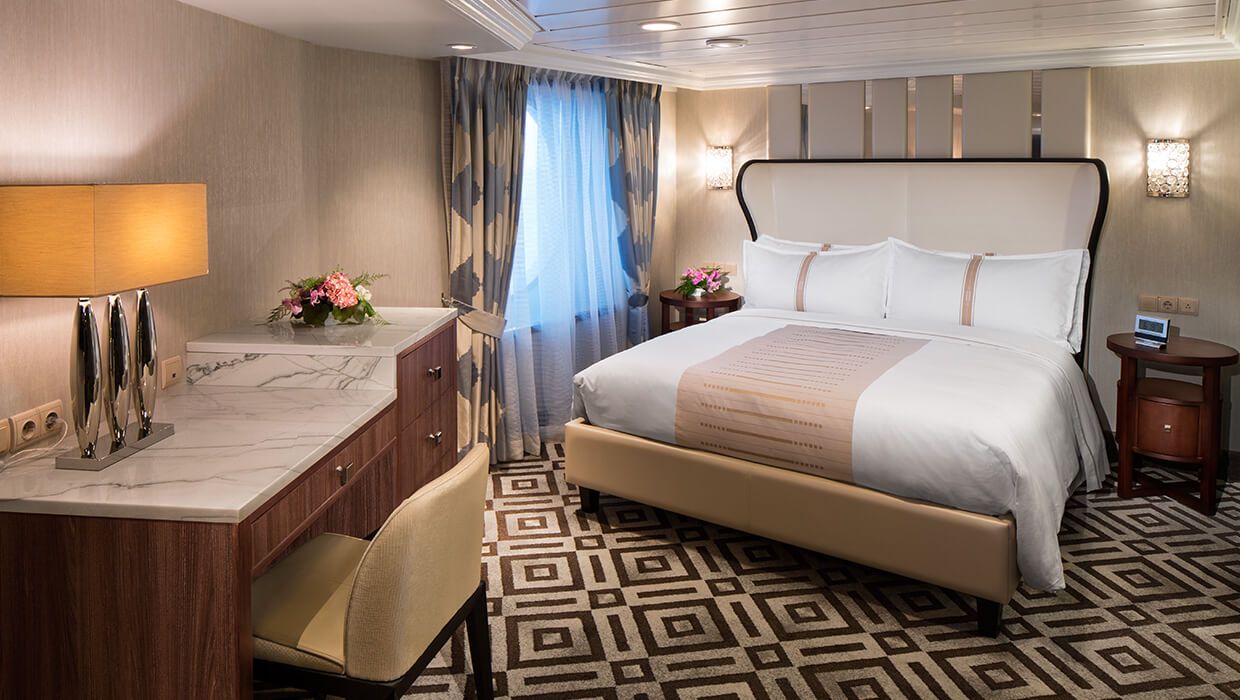




Located next to the tranquil Sanctum Spa, our newest suites are the ultimate in contemporary design, comfort and pampering. With easy access to the Spa, open decks, swimming pool and our great restaurants, the Club Spa Suites surround you with organic, elegant décor, and the finest, most soothing amenities. Suites feature comfortable sitting area, daily delivery of healthy snacks, Frette plush robes and slippers, and in-room spa music. For the ultimate in serene surroundings, the spacious glass-enclosed spa soaking tub and separate rain shower bring the outside in, with views to the endless seas beyond. The perfect place to get away from it all, without being far from anything.
Suite Features
- Two lower beds convertible to one queen size bed
- Spacious glass-enclosed bathtub
- Separate rain shower
- Comfortable sitting area
- Flat-screen television in sitting area
- Floor-to-ceiling sliding glass doors
- Veranda
- Mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voice mail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hair dryer
- Stateroom: 414 sq. ft. (38.5 sq. m.) Veranda: 40 sq. ft. (3.7 sq. m.)
Included Suite Amenities (For cruises sailing before April 1, 2026)
- $300 Onboard Credit
- Unlimited Standard Wi-Fi
- Laundry - 2 bags/stateroom/week
- Exclusive Acamar Experience Dinner
- Dedicated butler and concierge service
- Full in-suite dining and daily evening hors d'oeuvres
- Complimentary Specialty Dining and exclusive breakfast at Aqualina
- In-room premium spirits and champagne
- Thalassotherapy Pool access
- Personalized assistance planning spa appointments and shore excursions
- Priority check-in
- News delivery
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoeshine service
- Turndown treats
- Afternoon In-Suite Tea Service
Included Suite Amenities (For cruises on or after April 1, 2026)
- Ultimate Beverage Package
- Unlimited Standard Starlink Wi-Fi
- Unlimited Laundry
- Exclusive Acamar Experience Dinner
- Dedicated butler and concierge service
- Full in-suite dining and daily evening hors d'oeuvres
- Complimentary Specialty Dining and exclusive breakfast at Aqualina
- In-room premium spirits and champagne
- Thalassotherapy Pool access
- Personalized assistance planning spa appointments and shore excursions
- Priority check-in
- News delivery
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoeshine service
- Turndown treats
- Afternoon In-Suite Tea Service


Spacious and comfortable, our Continent Suites feature fresh new décor inspired by natural elements. With two beds convertible to a queen, a cozy sitting area, breezy balcony and refreshed bathroom with a bathtub or shower, this is your wonderful, refined home away from home.
Suite Features
- Two lower beds convertible to one queen size bed
- Spacious and comfortable sitting area
- Flat-screen television in sitting area
- Roomy bathroom with shower. Some also feature a tub.
- Floor-to-ceiling sliding glass doors
- Veranda
- Mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voice mail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hair dryer
- Stateroom: 266 sq. ft. (24.7 sq. m.) Veranda: 60 sq. ft. (5.6 sq. m.)
Included Suite Amenities (For cruises sailing before April 1, 2026)
- 240 Minutes Standard Wi-Fi
- Laundry - 2 bags/stateroom/week
- Dedicated butler and concierge service
- Exclusive breakfast at Aqualina
- In-room premium spirits and champagne
- Thalassotherapy Pool access
- Personalized assistance planning spa appointments and shore excursions
- Priority check-in
- News delivery
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoeshine-service
- Turndown treats
Included Suite Amenities (For cruises on or after April 1, 2026)
- Unlimited Basic Starlink Wi-Fi
- Laundry - 2 bags/stateroom/week
- Exclusive Acamar Experience Dinner
- Dedicated butler and concierge service
- Full in-suite dining and daily evening hors d'oeuvres
- Complimentary Specialty Dining and exclusive breakfast at Aqualina
- In-room premium spirits and champagne
- Thalassotherapy Pool access
- Personalized assistance planning spa appointments and shore excursions
- Priority check-in
- News delivery
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoeshine-service
- Turndown treats

A spacious, comfortable home away from home. Suite price based on deck and location of the ship.
Spacious and comfortable, our Continent Suites feature fresh new décor inspired by natural elements. With two beds convertible to a queen, a cozy sitting area, breezy balcony and refreshed bathroom with a bathtub or shower, this is your wonderful, refined home away from home.


Refreshing sea breezes and stunning destination views come standard in our staterooms that offer your own private veranda. Greet the day with room service on your balcony, or toast to another stunning sunset. Polished touches and professional service perfectly compliment the warm, friendly attention you'll receive from our staff and crew.
Stateroom Features
- Veranda
- Two lower beds convertible to one Queen size bed
- Sitting area with flat-screen TV
- Refrigerator with mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voicemail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hairdryer
- USB ports under bedside reading lamps
- Stateroom: 175 sq. ft. (16.3 sq. m.) | Veranda: 40 sq. ft. (3.7 sq. m.)
Included Stateroom Amenities
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoe shine-service
- Turndown treats
- Daily news bulletin
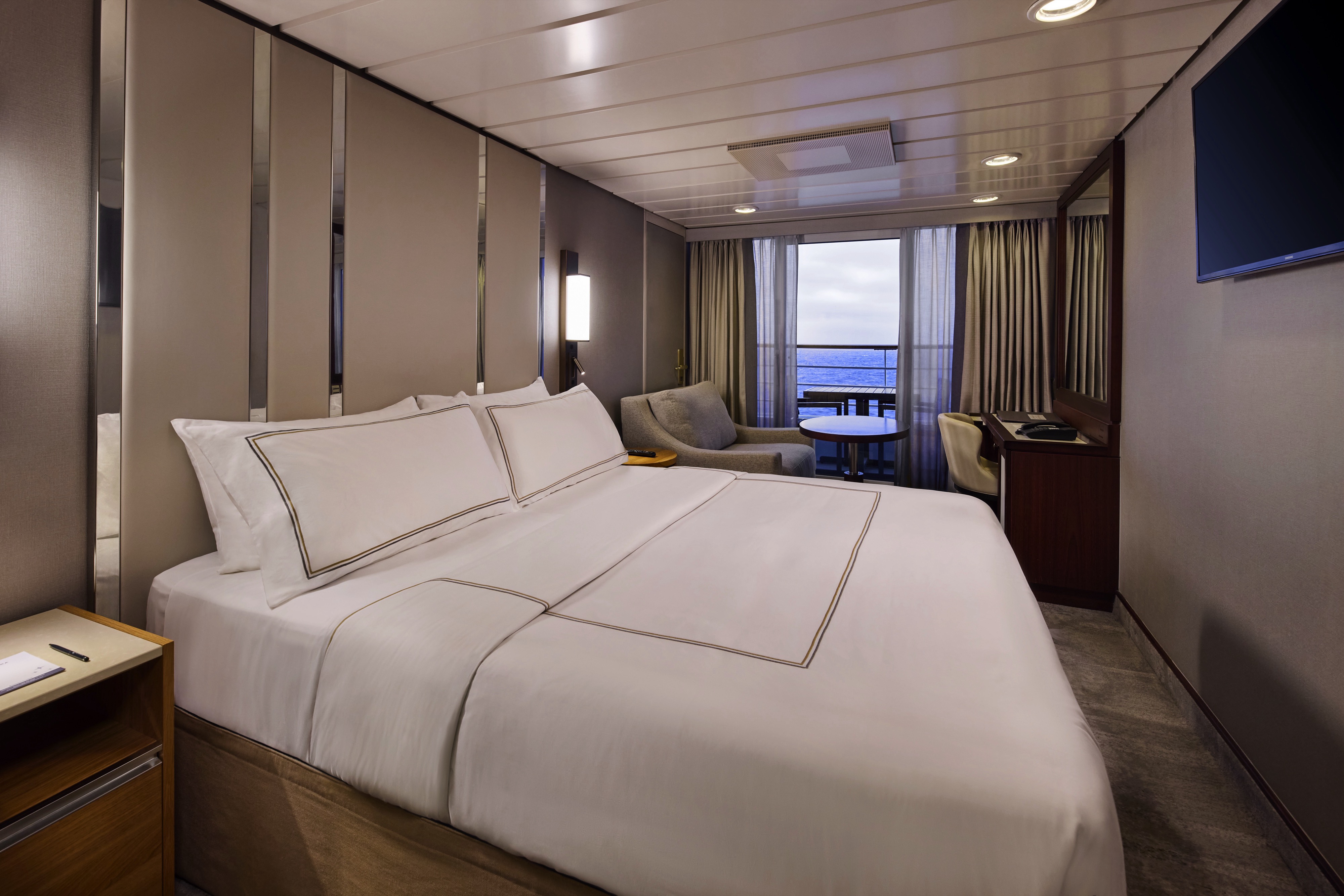

Introducing a new way to see the world with Azamara@. With our Club Veranda Plus Staterooms, enjoy spectacular ocean and destination views, plus a host of guest-favourite amenities—all at a great value. Everything you love about our Club Veranda Staterooms is included, plus extra perks and amenities to elevate your time on board.
Stateroom Features
- Veranda
- Two lower beds convertible to one Queen size bed
- Sitting area with flat-screen TV
- Mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voice mail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hairdryer
- USB ports under bedside reading lamps
- Stateroom: 175 sq. ft. (16.3 sq. m.) | Veranda: 46-64 sq. ft. (4.3-6 sq. m.)
Included Stateroom Amenities
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoe shine-service
- Turndown treats
- Daily news bulletin
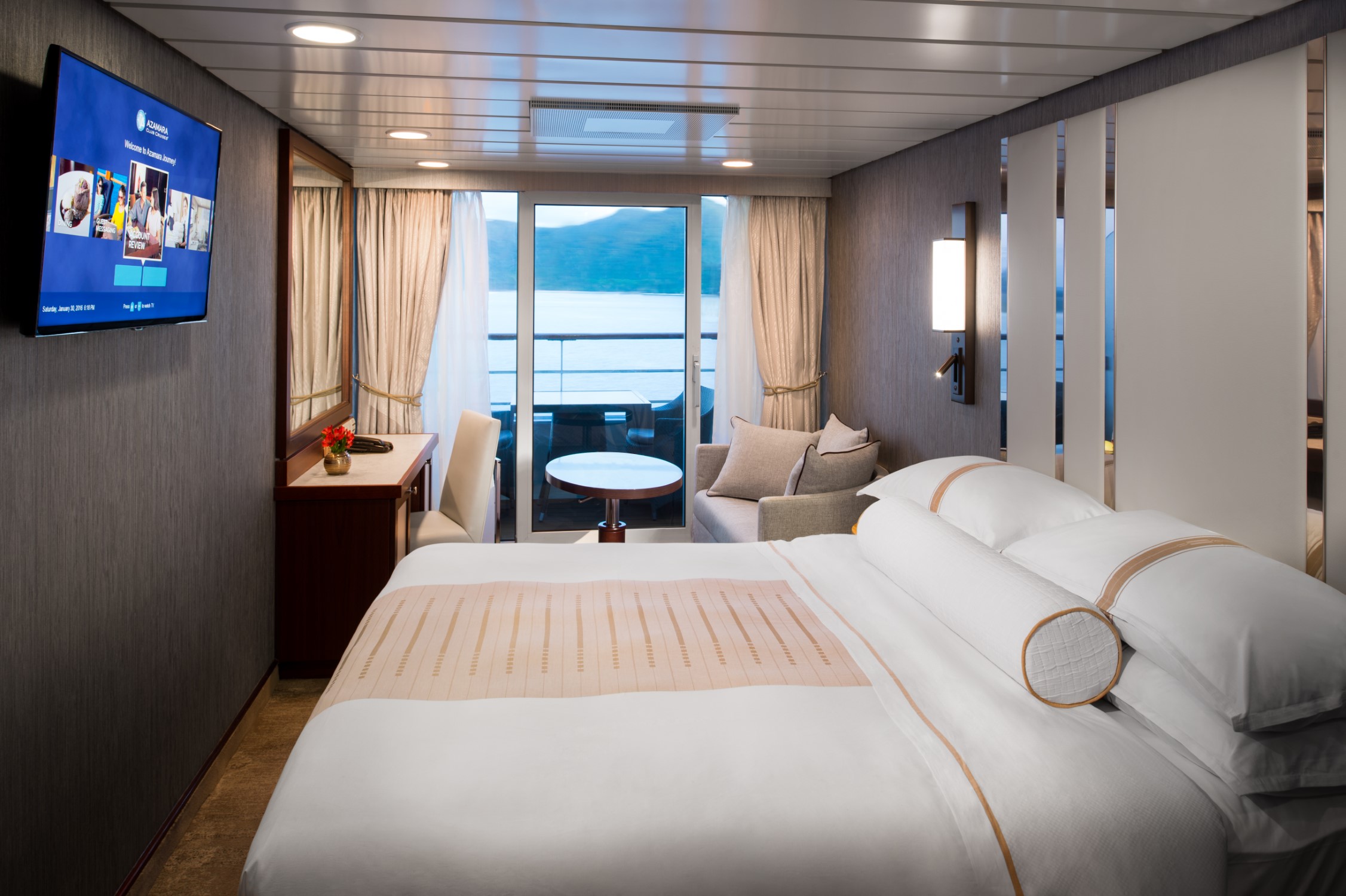

Introducing a new way to see the world with Azamara@. With our Club Veranda Plus Staterooms, enjoy spectacular ocean and destination views, plus a host of guest-favourite amenities—all at a great value. Everything you love about our Club Veranda Staterooms is included, plus extra perks and amenities to elevate your time on board.
Stateroom Features
- Veranda
- Two lower beds convertible to one Queen size bed
- Sitting area with flat-screen TV
- Mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voice mail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hairdryer
- USB ports under bedside reading lamps
- Stateroom: 175 sq. ft. (16.3 sq. m.) | Veranda: 46-64 sq. ft. (4.3-6 sq. m.)
Included Stateroom Amenities
- Complimentary AzAmazing Evenings® event (on most voyages)
- Gratuities
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes and slippers
- Select standard spirits, international beers and wine
- 24-hour room service
- Bottled water, soft drinks, specialty coffees and teas
- Fresh-cut flowers
- Self-service laundry
- Tote bag
- Shuttle service to and from port communities, wher
- Use of umbrella
- Concierge services for personal guidance and reservations
- Shoe shine-service
- Turndown treats
- Daily news bulletin
- Complimentary Internet (120 minutes or 25% off the unlimited internet package) per guest
- One free bag of laundry service per stateroom, every seven days
- One night of complimentary specialty dining for two, every seven days
- Priority embarkation and debarkation
- Complimentary in-room spirits

Refreshing sea breezes and stunning destination views come standard in our staterooms that offer your own private veranda. Greet the day with room service on your balcony, or toast to another stunning sunset. Polished touches and professional service perfectly compliment the warm, friendly attention you'll receive from our staff and crew.
Stateroom Features
- Veranda
- Two lower beds convertible to one Queen size bed
- Sitting area with flat-screen TV
- Refrigerator with mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voicemail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hairdryer
- USB ports under bedside reading lamps
- Stateroom: 175 sq. ft. (16.3 sq. m.) | Veranda: 40 sq. ft. (3.7 sq. m.)
Included Stateroom Amenities
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes
- 24-hour room service
- Tote bag
- Use of umbrella
- Shoe shine-service
- Turndown treats
- Daily news bulletin

Revel in the polished style and stellar service of your own private retreat, boasting a modern and contemporary décor. Enjoy picturesque ocean views outside your window, and all the finer touches included in every stateroom.
Stateroom Features
- Two lower beds convertible to one Queen size bed
- Some staterooms feature sofa bed
- Flat-screen TV
- Refrigerator with mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voicemail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hairdryer
- USB ports under bedside reading lamps
- 143 sq. ft. (13.3 sq m)
- Complimentary AzAmazing Evenings® event (on most voyages)
- Gratuities
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes and slippers
- Select standard spirits, international beers and wine
- 24-hour room service
- Bottled water, soft drinks, specialty coffees and teas
- Fresh-cut flowers
- Self-service laundry
- Tote bag
- Shuttle service to and from port communities, wher
- Use of umbrella
- Concierge services for personal guidance and reservations
- Shoe shine-service
- Turndown treats
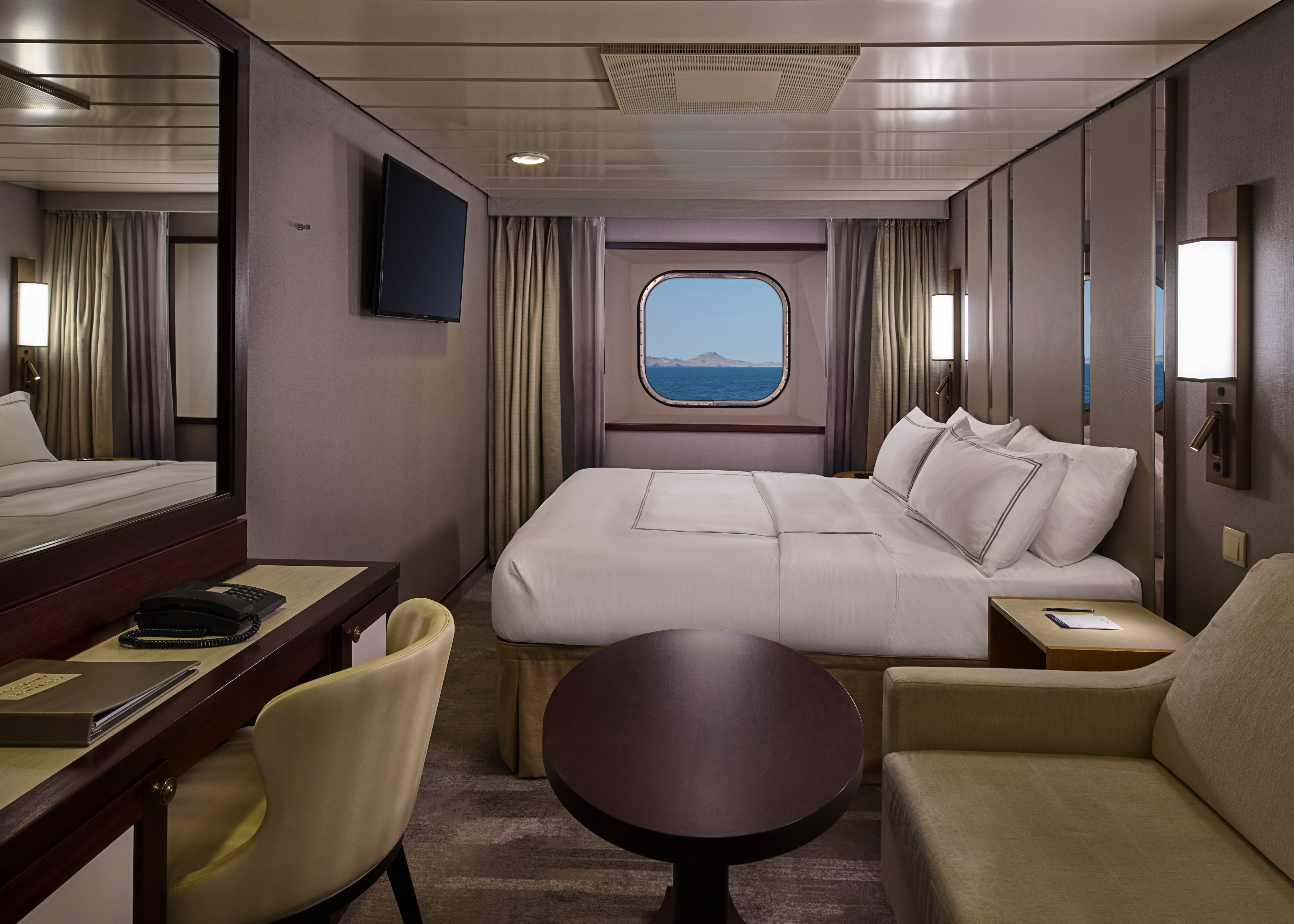

Revel in the polished style and stellar service of your own private retreat, boasting a modern and contemporary décor. Enjoy picturesque ocean views outside your window, and all the finer touches included in every stateroom.
Stateroom Features
- Two lower beds convertible to one Queen size bed
- Some staterooms feature sofa bed
- Flat-screen TV
- Refrigerator with mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voicemail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Handheld hairdryer
- USB ports under bedside reading lamps
- 143 sq. ft. (13.3 sq m)Included
Included Stateroom Amenities
- Complimentary AzAmazing Evenings® event (on most voyages)
- Gratuities
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes and slippers
- Select standard spirits, international beers and wine
- 24-hour room service
- Bottled water, soft drinks, specialty coffees and teas
- Fresh-cut flowers
- Self-service laundry
- Tote bag
- Shuttle service to and from port communities, wher
- Use of umbrella
- Concierge services for personal guidance and reservations
- Shoe shine-service
- Turndown treats

Explore the world in comfort and luxury in this stylish, elegant stateroom featuring all the amenities of a boutique hotel at sea. Relax with plush cotton robes, 24-hour room service, and more.
Stateroom Features
- Two lower beds convertible to one Queen size bed
- Flat-screen television
- Refrigerator with mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voicemail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hairdryer
- USB ports under bedside reading lamps
- Stateroom: 158 sq. ft. (14.7 sq. m.)
Included Stateroom Amenities
- Complimentary AzAmazing Evenings® event (on most voyages)
- Gratuities
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes and slippers
- Select standard spirits, international beers and wine
- 24-hour room service
- Bottled water, soft drinks, specialty coffees and teas
- Fresh-cut flowers
- Self-service laundry
- Tote bag
- Shuttle service to and from port communities, wher
- Use of umbrella
- Concierge services for personal guidance and reservations
- Shoe shine-service
- Turndown treats
- Daily news bulletin
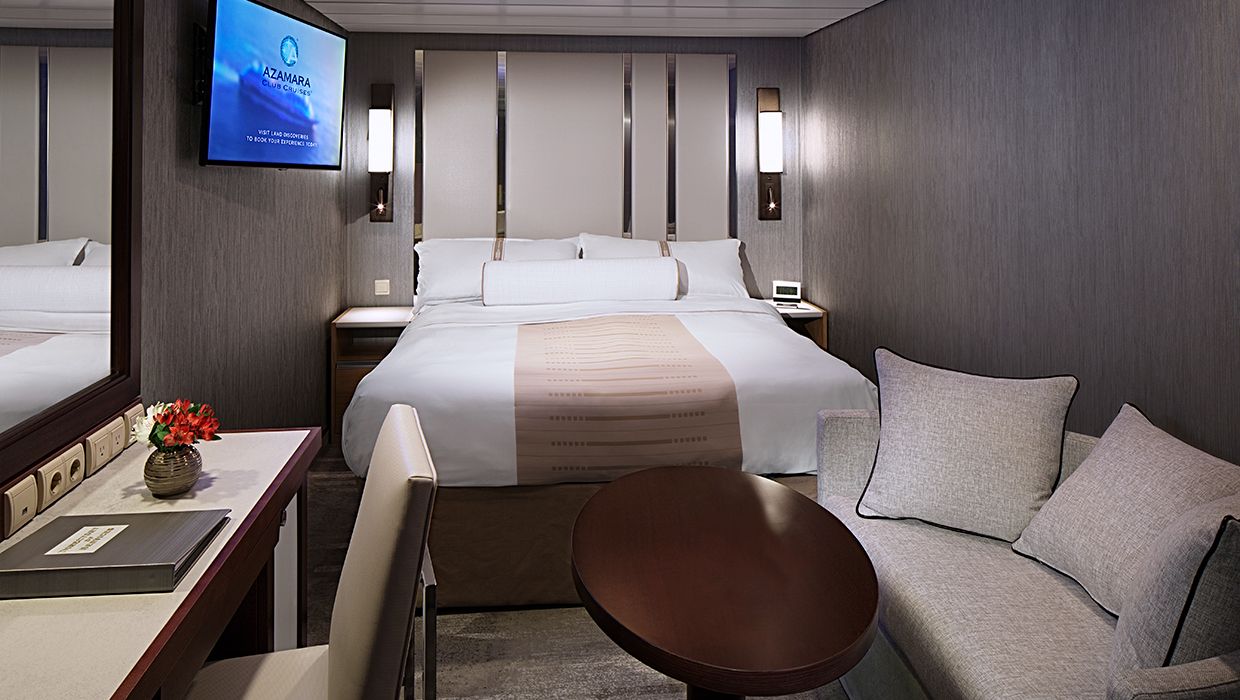

Explore the world in comfort and luxury in this stylish, elegant stateroom featuring all the amenities of a boutique hotel at sea. Relax with plush cotton robes, 24-hour room service, and more.
With the polished style and stellar service of a Club Interior Stateroom, you'll enjoy our plush cotton robes, slippers upon request, French bath products, and 24-hour room service.
Stateroom Features
- Two lower beds convertible to one Queen size bed
- Flat-screen television
- Refrigerator with mini-bar
- Thermostat-controlled air conditioner
- Direct-dial telephone with voicemail
- Writing desk
- In-room safe
- Hand-held hairdryer
- USB ports under bedside reading lamps
- Stateroom: 158 sq. ft. (14.7 sq. m.)
Included Stateroom Amenities
- Complimentary AzAmazing Evenings® event (on most voyages)
- Gratuities
- Luxurious cotton bed linens with duvet
- Terry bathrobes and slippers
- Select standard spirits, international beers and wine
- 24-hour room service
- Bottled water, soft drinks, specialty coffees and teas
- Fresh-cut flowers
- Self-service laundry
- Tote bag
- Shuttle service to and from port communities, wher
- Use of umbrella
- Concierge services for personal guidance and reservations
- Shoe shine-service
- Turndown treats
- Daily news bulletin

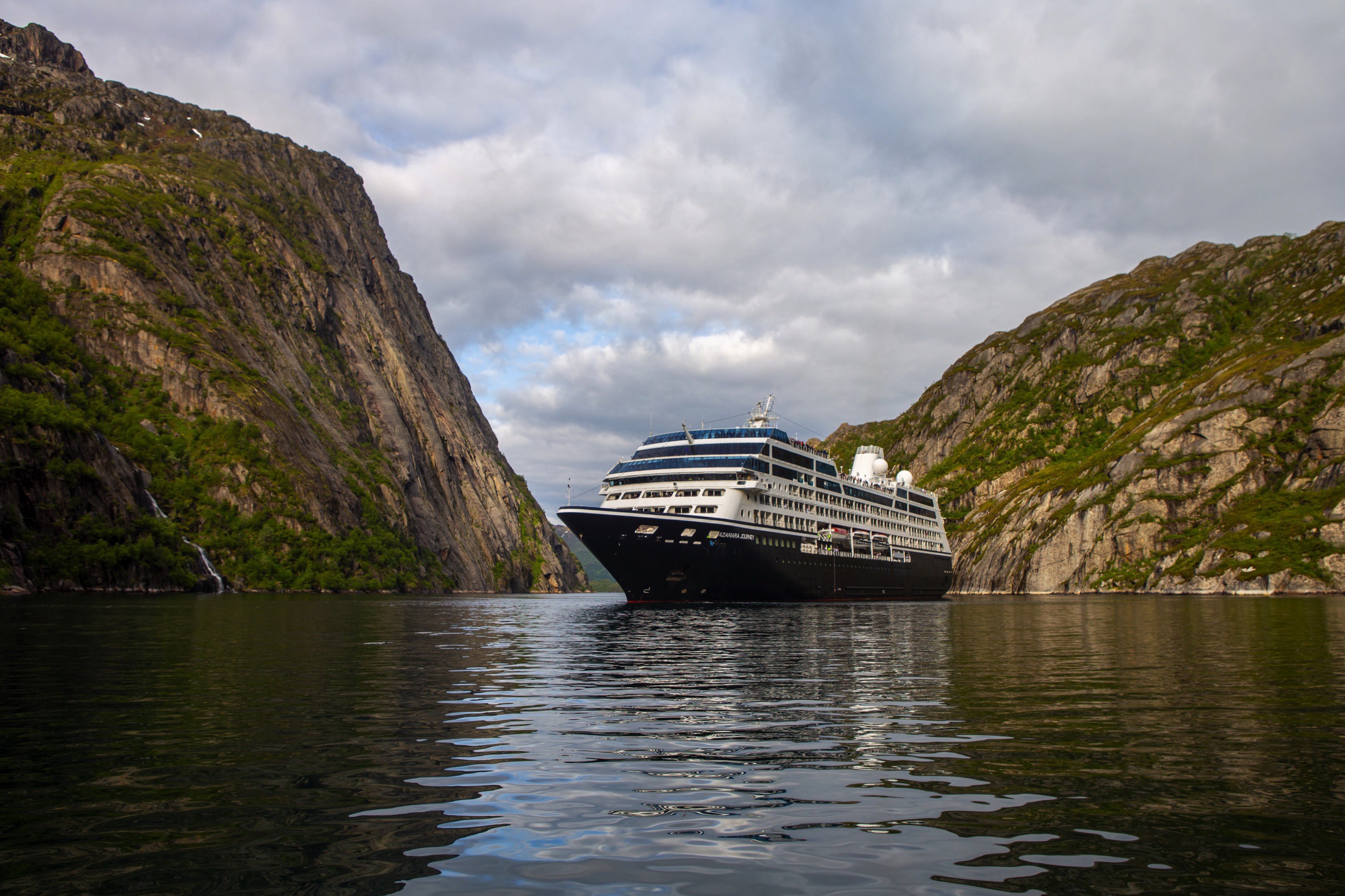
Azamara Journey
A luxurious boutique hotel at sea, the Azamara Journey is a mid-sized ship with a deck plan that’s intimate but never crowded, and offers everything modern cruisers are looking for—plus some unexpected extras.

Ship Facts
| Launch Year | 2000 | ||||||||||
| Refit Year | 2016 | ||||||||||
| Language | en-US | ||||||||||
| Gross Tonnage | 30277 | ||||||||||
| Length | 182 | ||||||||||
| Width | 25 | ||||||||||
| Currency | USD | ||||||||||
| Speed | 18 | ||||||||||
| Capacity | 690 | ||||||||||
| Crew Count | 408 | ||||||||||
| Deck Count | 8 | ||||||||||
| Cabin Count | 355 | ||||||||||
| Large Cabin Count | N/A | ||||||||||
| Wheelchair Cabin Count | 6 | ||||||||||
| Electrical Plugs |
|
Deck 11
- Sun Deck
- Shuffle Board

Deck 10
- The Living Room
- Card Room
- In Touch
- Elevators
- Table Tennis
- Jogging Track
- The Drawing Room
- Prime C Speciality Dining
- Aqualina Speciality Dining
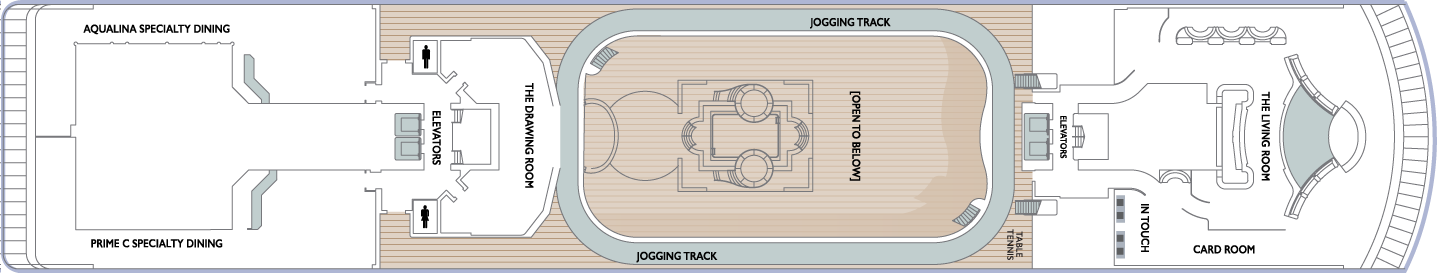
Deck 9
- The Sanctum Spa Terrace
- Salon
- The Sanctum Spa
- Fitness Center
- Pool
- Pool Bar
- Elevators
- Swirl & Top
- The Patio
- Windows Café
- Sunset Bar
- Spa Suites
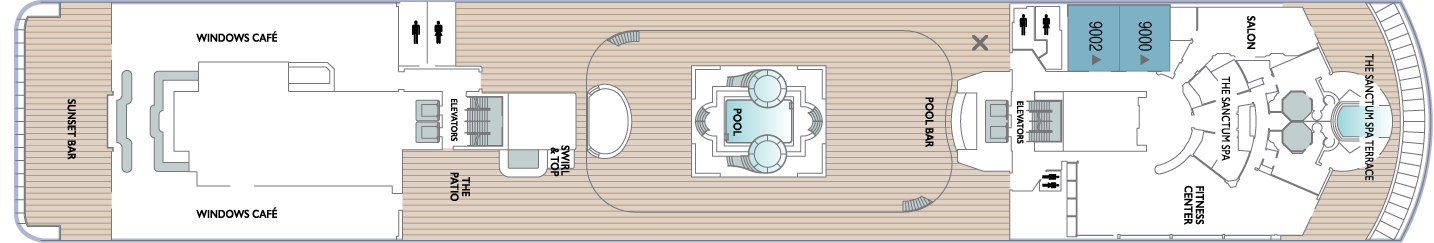
Deck 8
- Veranda Plus Staterooms
- World Owner's Suite
- Continent Suite
- Interior Staterooms

Deck 7
- Veranda Plus Staterooms
- World Owner's Suite
- Ocean Suite
- Veranda Staterooms
- Oceanview Staterooms
- Interior Staterooms
- Self Service Laundry
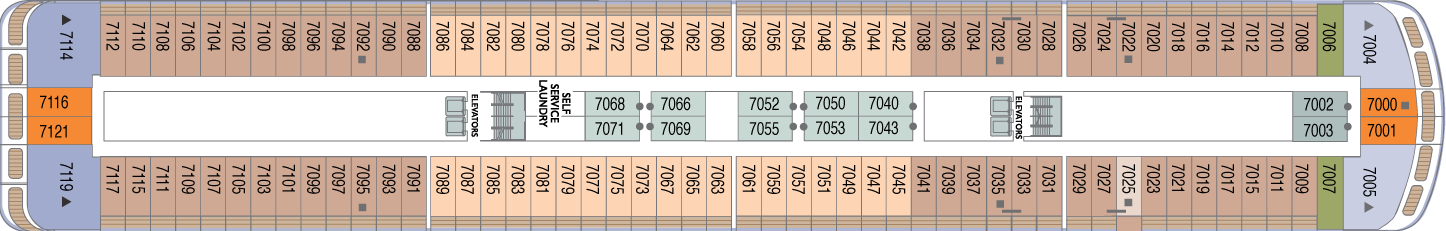
Deck 6
- Veranda Plus Staterooms
- Veranda Staterooms
- World Owner's Suite
- Continent Suite
- Ocean Suite
- Oceanview Staterooms
- Interior Staterooms

Deck 5
- Cabaret Lounge
- Elevators
- Shore Excursions
- Cruise Again
- The Den
- Photo Shop
- The Journey Shops
- Indulgences
- Mosaic Café
- Discoveries Bar
- Discoveries Restaurant
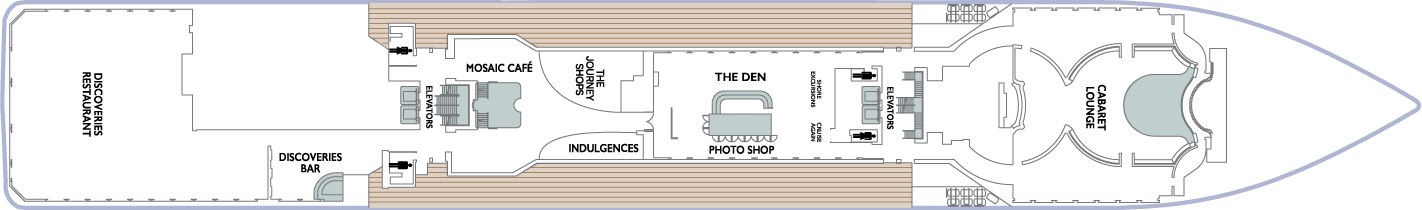
Deck 4
- Oceanview Staterooms
- Interior Staterooms
- Medical Facility
- Guest Relations
- Concierge

Azamara offers a choice of six distinctive dining options, including room service. Whether you’re a fan of haute cuisine or down-home cooking, expect the same delicious quality. Bon appétit! Buon appetito! ¡Buen provecho! No matter how you say it, you’re in for a real treat.
Pre-Cruise Specialty Dining Reservations
All guests can now book pre-cruise reservations for Prime C, Aqualina, or Chef’s Table—our most sought-after specialty dining experiences.
Priority Access
Pre-cruise dining reservations open 150 days before sailing for suite guests and Azamara Circle Discoverer-level and above. All other guests may begin booking 140 days prior.
Aqualina
At Aqualina, you’ll find some of Italy’s most authentic dishes. Pastas made from scratch, traditional recipes, and scrumptious vegetarian dishes that make sure there’s something for everyone. Plus our famous desserts: Sorrento lemon liqueur mousse, hazelnut chocolate soufflé and more.
Prime C
Your choice of steak, cooked to perfection. Herb-coated rack of lamb, duck confit and Chilean sea bass—all paired with savory sides. At Prime C, you’re in for more than delectable dining. Expect a great evening with stunning views and lush décor.
Discoveries Restaurant
Discover the world through dishes and flavors from the places we visit. Of course, you’ll also enjoy a wide variety of nightly selections such as filet mignon with black truffle sauce. Choose being seated at a table for two or as part of a larger group of fellow guests.
Windows Café
Our daily themed dinner often takes its inspiration from the region we’re visiting—Indian, Mexican, Spanish, Italian. We also create an extra live station made from local ingredients purchased in port: Greek salad made with local feta (Greece), pasta prepared with local mushrooms (Italy), fresh Mussels served with garlic bread (Netherlands).
The Patio And Swirl & Top
Casual “pool grill” by day. A sit-down al fresco dining experience by night. Taste your way around the world with exclusive personalized dishes using local flavors of the places we visit. Plus a self-serve frozen yogurt station—Swirl & Top. With a variety of flavors and your choice of toppings, it’s the perfect way to cool off.
Mosaic Café
Stylish and cozy, Mosaic offers your favorite coffee drinks exactly as you like them. Relax in a comfortable seat and enjoy. It’s the perfect spot to start or end your day, and it just might become your favorite place on the ship.
Room Service
The best time for room service? Whenever you say it is, 24-hours a day. Order from the full breakfast menu between 6:30 AM and 10:00 AM, and we’ll deliver at your appointed time. Lunch and dinner room service features a menu of hearty soups, fresh salads, gourmet sandwiches, pizzas and desserts.
Sit back and enjoy your evenings on a high note with our onboard entertainment. From local cultural shows to our playbill that features a variety of amazing performances to keep you entertained while onboard.
Bars, Lounges & Gathering Spots
A cozy nook to sip coffee. An intimate space to raise a glass and celebrate. A lively setting to catch the latest shows and international entertainment. Watch the world go by, drink in hand from any of Azamara’s bars, lounges, and gathering spaces.
White Night
Join Azamara officers and crew for our signature dinner and entertainment event hosted al fresco on the pool deck (weather permitting). With an array of delicious food and engaging entertainment, your White Night experience will almost certainly be one of the most memorable times from your cruise. And don’t forget to bring something white to wear for the evening.
Club Crooner
Step into a swanky nightclub as the great songs of the most magnificent artists come alive on stage. From classic crooners such as Frank Sinatra and Tony Bennett, to current songbirds such as Natalie Cole and Michael Bublé, there’s a song for every time and everyone. Enjoy a beverage, sit back, and be serenaded by the melodies of our lives with CLUB CROONER!
The Living Room
The idea of the Living Room is just that. To “live in” and to enjoy time with friends and fellow guests! Much of the room is furnished as a living room, with clusters of large comfortable chairs and sofas....
Discoveries Lounge
This congenial bar is a favorite gathering place for great conversations and delicious drinks. Bar service includes a full selection of fine wines, mixed drinks, and premium spirits…plus the entertaining banter of Azamara’s friendly bartenders.
Cabaret Lounge
Enjoy live performances of professional full-stage musical revues, classical soloists, bands and other entertainment in a cabaret nightclub with a full bar and cozy tables.
Sunset Bar
Adjacent to Windows Café, the Sunset Bar is a welcoming outdoor patio with covered and open-air seating, and a bar. It's the perfect place for dining alfresco, enjoying a refreshing drink, taking in the sights of your favourite port, or simply watching the world sail by.
Mosaic Cafe & Mosaic Cafe @ Night
Our onboard coffee corner may very well become your favorite nook on the ship. With elegant and comfortable furniture, it's bound to be one of the the most stylish places, too. Find all your favorite coffee drinks crafted just the way you like. Slip right into a comfortable seat and sip for a while—you never know who'll walk by.
Pool Bar
Our Pool Bar serves refreshments while enjoying the Pool during the day, and cocktails of your choice in the evening.
The Wine Cellar
You’ll be hard-pressed to find such a collection of limited production, small label and rare vintage wines anywhere on the high seas! And with vintages from France to California, and Argentina to South Africa, you’re sure to find a wine to suit your palate and your journey. Our knowledgeable sommeliers can help you pick the perfect wines for your evening meal.
Performances
And the Beat Goes On
Join your Signature Singers and Dancers as they commemorate the greatest hits of all time in And the Beat Goes On. The night celebrates a wide variety of musical genres while exploring the influence of mainstream media in honoring the iconic cultural trends throughout the years. Featuring music from The Beatles, Earth Wind and Fire, Journey, Madonna, Ricky Martin, Katy Perry and much more. We will be sure to have you singing and dancing all night long in AND THE BEAT GOES ON!
Six Strings
The guitars are tuned, the amps are cranked up and the microphones are hot as Azamara prepares you for a night of energetic dancing, powerful vocals and iconic guitar riffs in Six Strings. The evening guarantees a Good Time with ultimate nostalgia as our Signature Singers and Dancers celebrate the most renowned classic rock artists such as Aerosmith, The Beatles, Pat Benatar, The Rolling Stones, Queen and more. Don’t miss SIX STRINGS!
Oh, What A Night
Get ready to be transported to the world’s most beloved travel destinations in one exhilarating night. As we explore all four seasons in a new city, travel along with our dynamic Signature Singers & Dancers as they sing and dance their way through an eclectic mix of music from around the world. Come and experience Oh, What A Night!
The Pool
While spending daytime sun-drenched and relaxed by the pool, don’t think of missing Azamara’s famous White Night party held at least once on every cruise (weather permitting). Colourful décor and linen-draped tables, a fabulous buffet feast, and boutique wines on the house make this an event like no other. Not to forget the fun and fast-paced show our entertainment team puts on.
The Ship Shop
Pick up sundries, casual wear and swim fashions, sunglasses, accessories, music and shipboard keepsakes. This is a great place for small gifts to take back home.
Indulgences
Aptly named, Indulgences will satisfy your desires for the finer things in life. If you are looking for designer jewellery, it's the perfect place to window shop or to find that extra special purchase.
Photo Shop
Our photographers capture both fun and professional photos throughout the voyage, whether it is your portrait, or photos of the destinations you visit. You can also find an assortment of supplies for your own photographic endeavours.