
Asia To Alaska Majesty
Asia To Alaska Majesty
Cruise overview
WHY BOOK WITH US?
- ✔ The Deluxe Cruises’ team has extensive experience in ultra-luxury cruising.
- ✔ Call now to speak to our helpful and experienced Cruise Concierge team.
- ✔ Enjoy our Unique Deluxe Cruises Bonus for substantial savings.
- ✔ Our team will tailor your holiday to your exacting requirements.
- ✔ As agents, we work under the protection of each cruise lines ABTA / ATOL licences
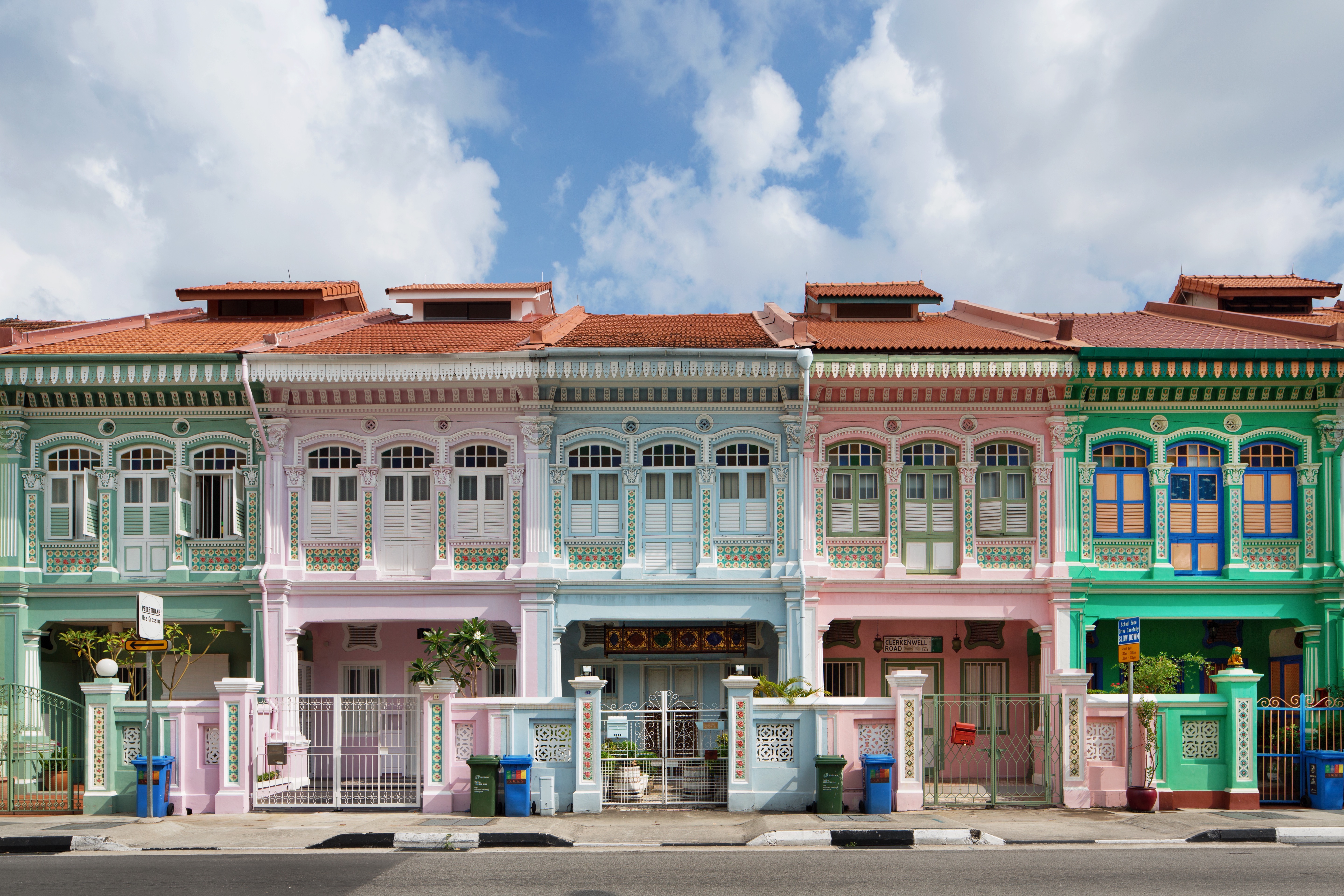
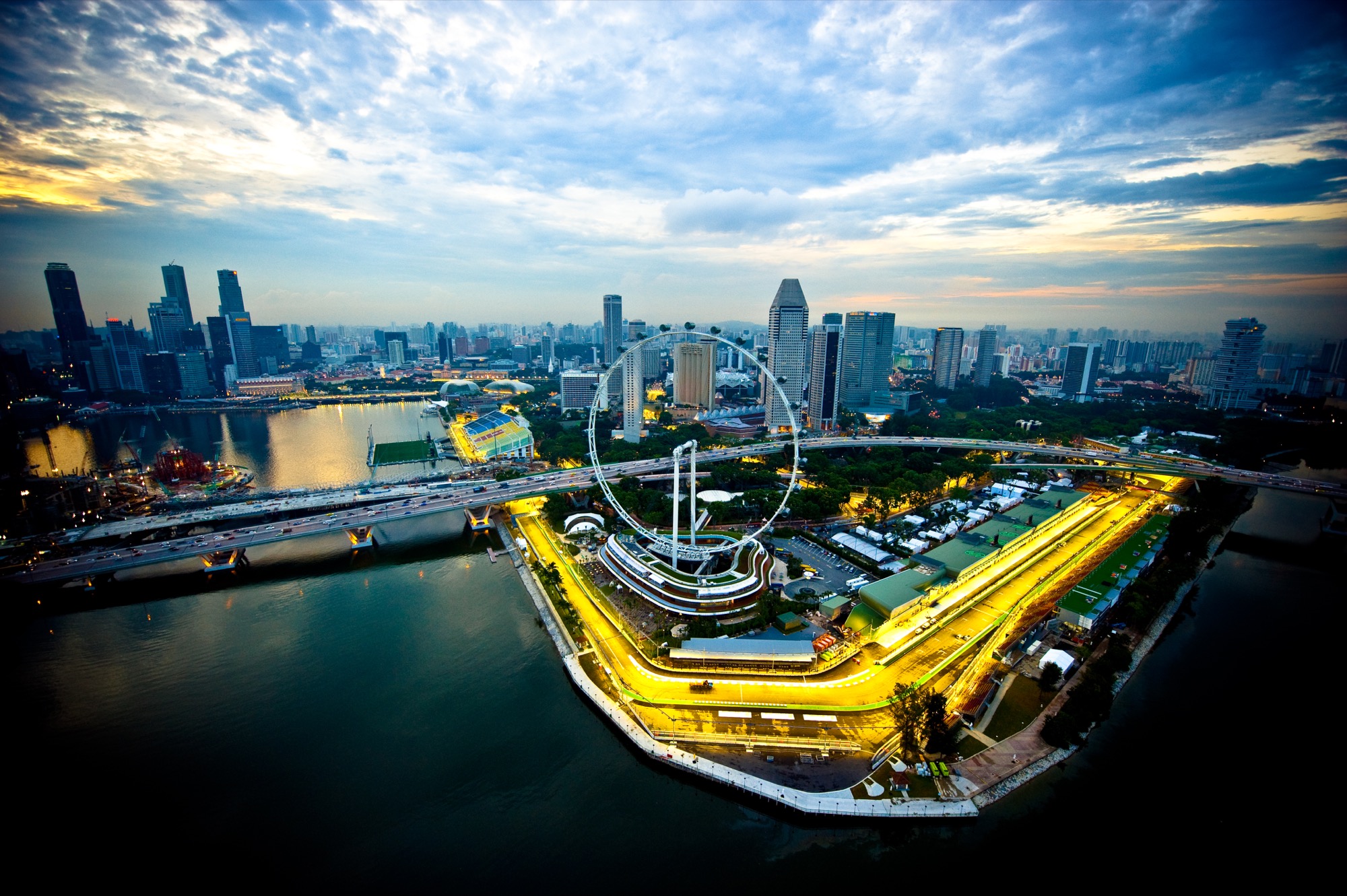
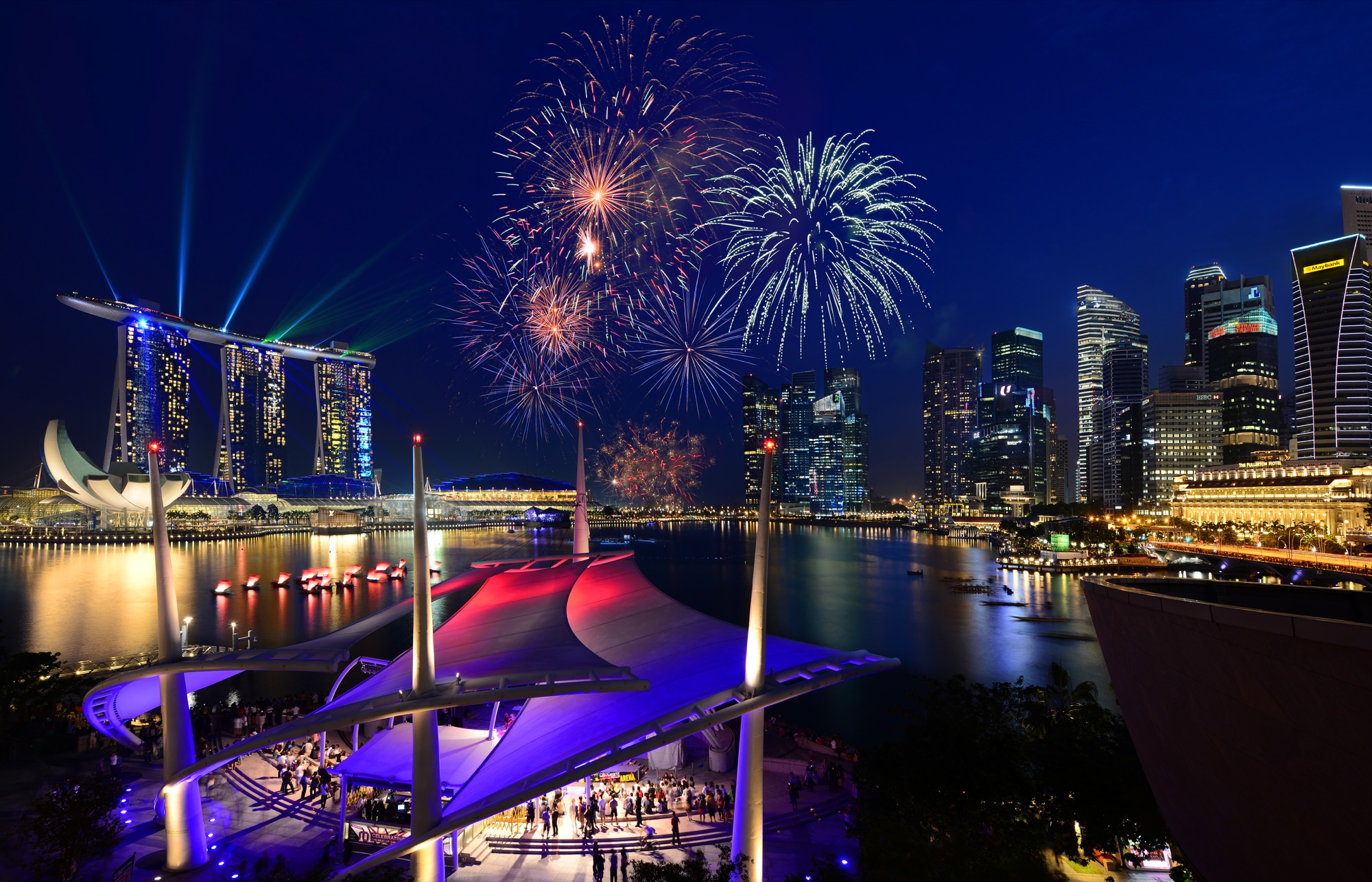
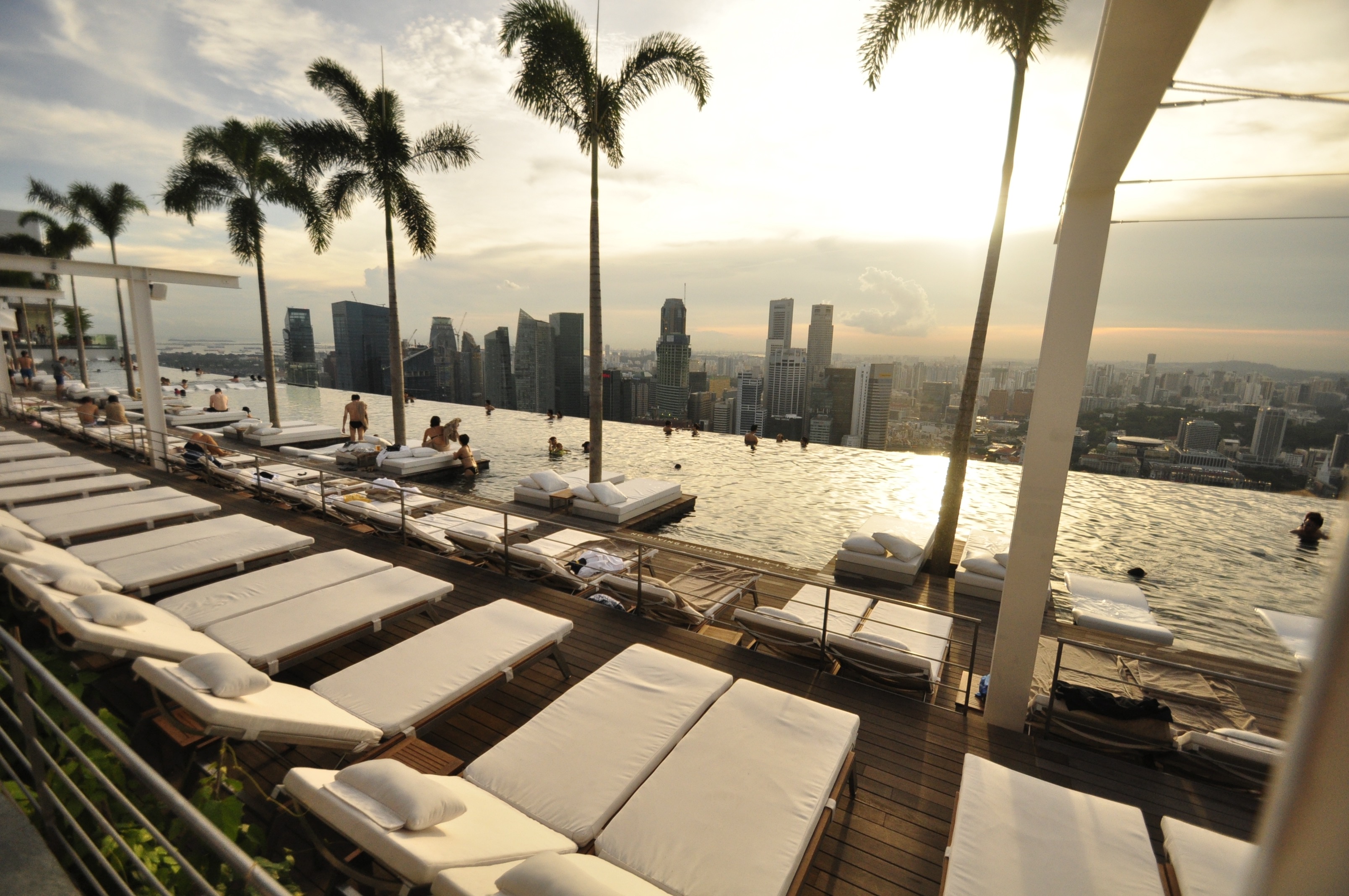
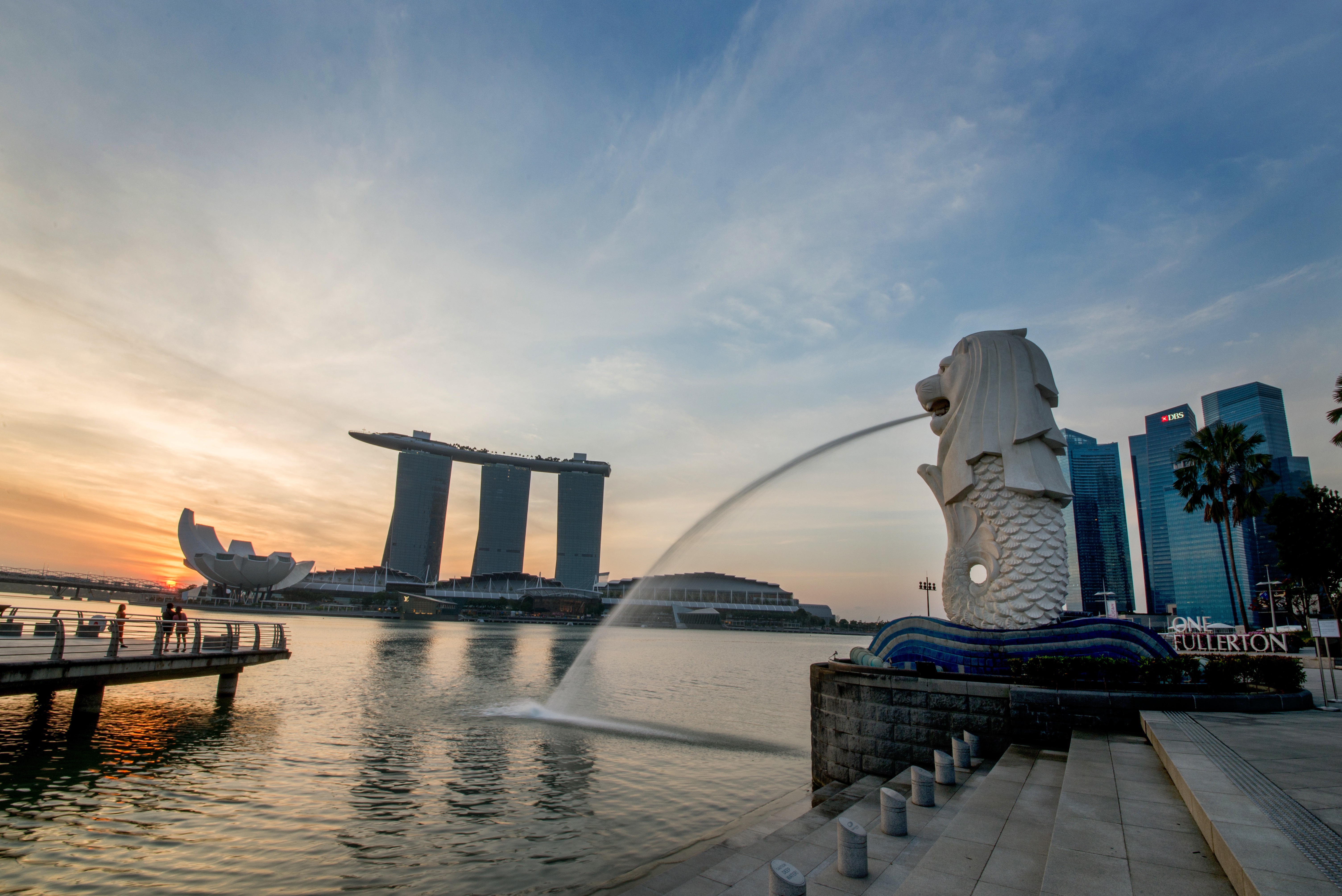
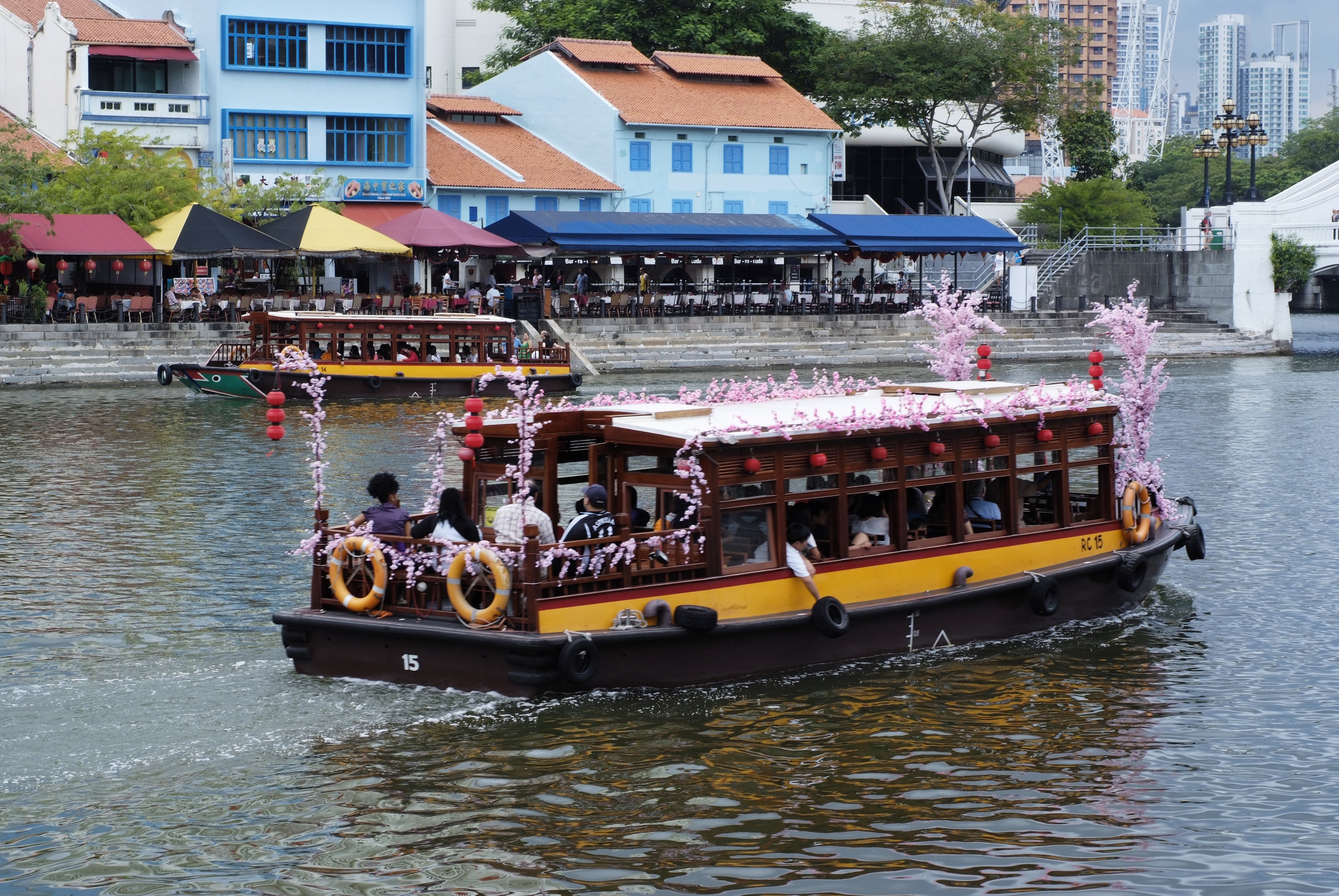
About Singapore
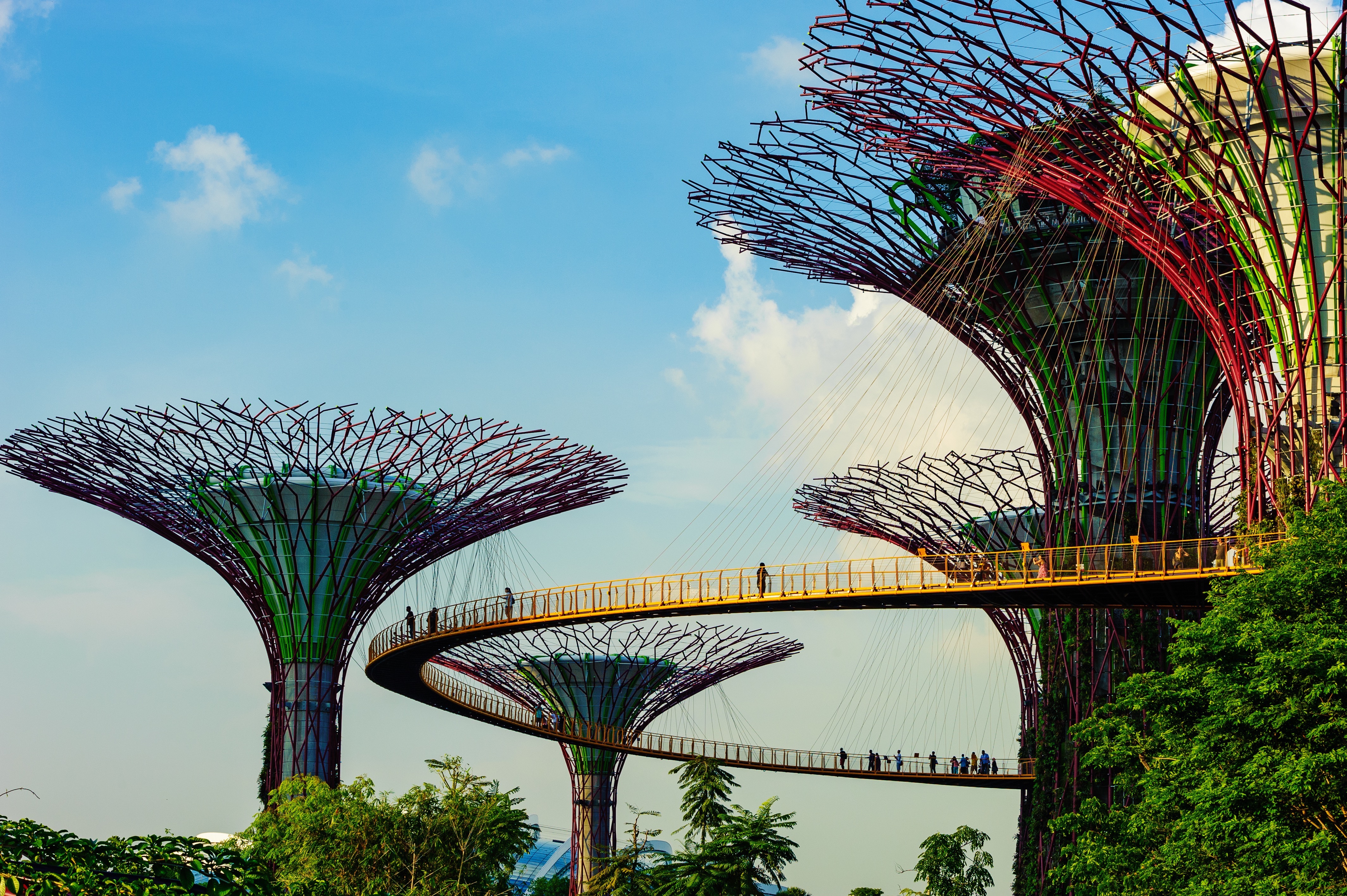
The main island of Singapore is shaped like a flattened diamond, 42 km (26 miles) east to west and 23 km (14 miles) north to south. Near the northern peak is the causeway leading to West Malaysia—Kuala Lumpur is less than four hours away by car. It is at the southern foot where you will find most of the city-state’s action, with its gleaming office towers, working docks, and futuristic "supertrees," which are solar-powered and serve as vertical gardens. Offshore are Sentosa and over 60 smaller islands, most uninhabited, that serve as bases for oil refining or as playgrounds and beach escapes from the city. To the east is Changi International Airport, connected to the city by metro, bus, and a tree-lined parkway. Of the island's total land area, more than half is built up, with the balance made up of parkland, farmland, plantations, swamp areas, and rain forest. Well-paved roads connect all parts of the island, and Singapore city has an excellent, and constantly expanding, public transportation system. The heart of Singapore's history and its modern wealth are in and around the Central Business District. The area includes the skyscrapers in the Central Business District, the 19th-century Raffles Hotel, the convention centers of Marina Square, on up to the top of Ft. Canning. Although most of old Singapore has been knocked down to make way for the modern city, most colonial landmarks have been preserved in the CBD, including early-19th-century buildings designed by the Irish architect George Coleman.












About Singapore
The main island of Singapore is shaped like a flattened diamond, 42 km (26 miles) east to west and 23 km (14 miles) north to south. Near the northern peak is the causeway leading to West Malaysia—Kuala Lumpur is less than four hours away by car. It is at the southern foot where you will find most of the city-state’s action, with its gleaming office towers, working docks, and futuristic "supertrees," which are solar-powered and serve as vertical gardens. Offshore are Sentosa and over 60 smaller islands, most uninhabited, that serve as bases for oil refining or as playgrounds and beach escapes from the city. To the east is Changi International Airport, connected to the city by metro, bus, and a tree-lined parkway. Of the island's total land area, more than half is built up, with the balance made up of parkland, farmland, plantations, swamp areas, and rain forest. Well-paved roads connect all parts of the island, and Singapore city has an excellent, and constantly expanding, public transportation system. The heart of Singapore's history and its modern wealth are in and around the Central Business District. The area includes the skyscrapers in the Central Business District, the 19th-century Raffles Hotel, the convention centers of Marina Square, on up to the top of Ft. Canning. Although most of old Singapore has been knocked down to make way for the modern city, most colonial landmarks have been preserved in the CBD, including early-19th-century buildings designed by the Irish architect George Coleman.












About Singapore
The main island of Singapore is shaped like a flattened diamond, 42 km (26 miles) east to west and 23 km (14 miles) north to south. Near the northern peak is the causeway leading to West Malaysia—Kuala Lumpur is less than four hours away by car. It is at the southern foot where you will find most of the city-state’s action, with its gleaming office towers, working docks, and futuristic "supertrees," which are solar-powered and serve as vertical gardens. Offshore are Sentosa and over 60 smaller islands, most uninhabited, that serve as bases for oil refining or as playgrounds and beach escapes from the city. To the east is Changi International Airport, connected to the city by metro, bus, and a tree-lined parkway. Of the island's total land area, more than half is built up, with the balance made up of parkland, farmland, plantations, swamp areas, and rain forest. Well-paved roads connect all parts of the island, and Singapore city has an excellent, and constantly expanding, public transportation system. The heart of Singapore's history and its modern wealth are in and around the Central Business District. The area includes the skyscrapers in the Central Business District, the 19th-century Raffles Hotel, the convention centers of Marina Square, on up to the top of Ft. Canning. Although most of old Singapore has been knocked down to make way for the modern city, most colonial landmarks have been preserved in the CBD, including early-19th-century buildings designed by the Irish architect George Coleman.












About Muara
The microscopic Sultanate of Brunei lays claim to one of the most dramatic rags-to-riches stories. Thanks to oil, the Sultan of Brunei is one of the richest men in the world, and the Sultanate is often dubbed a Shell-fare-state. Brunei's citizens do not pay income tax; they enjoy free education, medical care and old-age pensions. The government employs a third of the workforce, who are probably the best-paid bureaucrats in the world. Brunei Darussalam, as the country is officially called, is the rump of what was once a sprawling empire that occupied a land area of about twice the size of Luxembourg. On January 1, 1984, after nearly 100 years as a British Protectorate, Brunei became a fully independent sovereign nation. In August of 1967, Hassanal Bolkiah was crowned the 29th Sultan of Brunei. He succeeded his father, Sir Omar Ali Saifuddien III, who started to modernize the capital and is known as the architect of modern Brunei. Bandar Seri Begawan is the capital and the only town of any size in the country. It is a neat, modern city, split into three main areas. The "old" sector, built in the 1950s, is being redeveloped with new buildings around the Omar Ali Saifuddien Mosque; the Seri Complex, a commercial area dates from the 1970s, and Gadong boasts a recently shopping center and numerous restaurants: Bandar or, simply BSB, as the capital is commonly called, still features a sprawling maze of wooden houses built on stilts along the Brunei River.
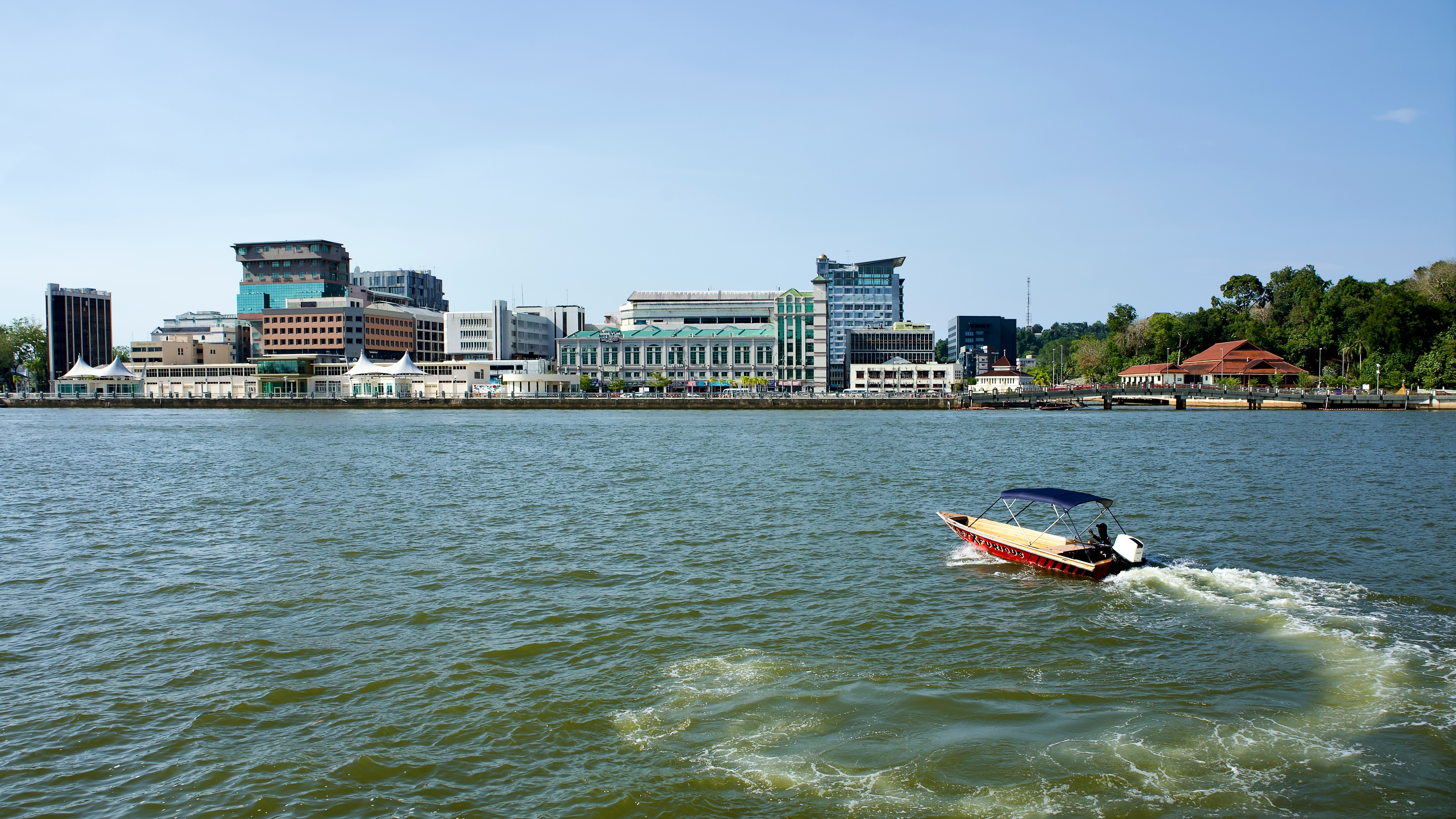

About Kota Kinabalu, Sabah
The capital of Sabah, Borneo's northernmost state, Kota Kinabalu is wedged between a tropical rainforest and the South China Sea. Many explorers use it as a launching point to venture off and see the surrounding jungle and marine life. Mt. Kinabalu challenges climbers daily, and top diving spots reel in underwater adventurers. The city is made up of a dense grid of concrete buildings built over reclaimed land along the coast. Several waterfront seafood restaurants and a diverse mix of hotels appeal to the travelers passing through, mostly off to explore the region.

About Puerto Princesa, Palawan
The Spanish arrived at this beautiful corner of the world in March of 1872, founding the city, that would eventually become the Capital of Palawan. In 2011, the area received a huge boost, when New7 announced its list of the 7 Wonders of Nature – counting 500 million votes in the process. Puerto Princesa’s stunning underground river - complete with a cavernous, sunken lagoon - beat off wonderful sites like the Great Barrier Reef, to claim a spot on the final, prestigious list. Set sail across the glowing green water, on a journey into the gaping mouth of the limestone caves at Puerto Princesa. Known for being one of the least densely populated, cleanest and most environmentally friendly cities in the Philippines, there’s a raft of natural wonders to explore - from diving hotspots to towering limestone cliffs, and the entrancing underworld of the underground river.

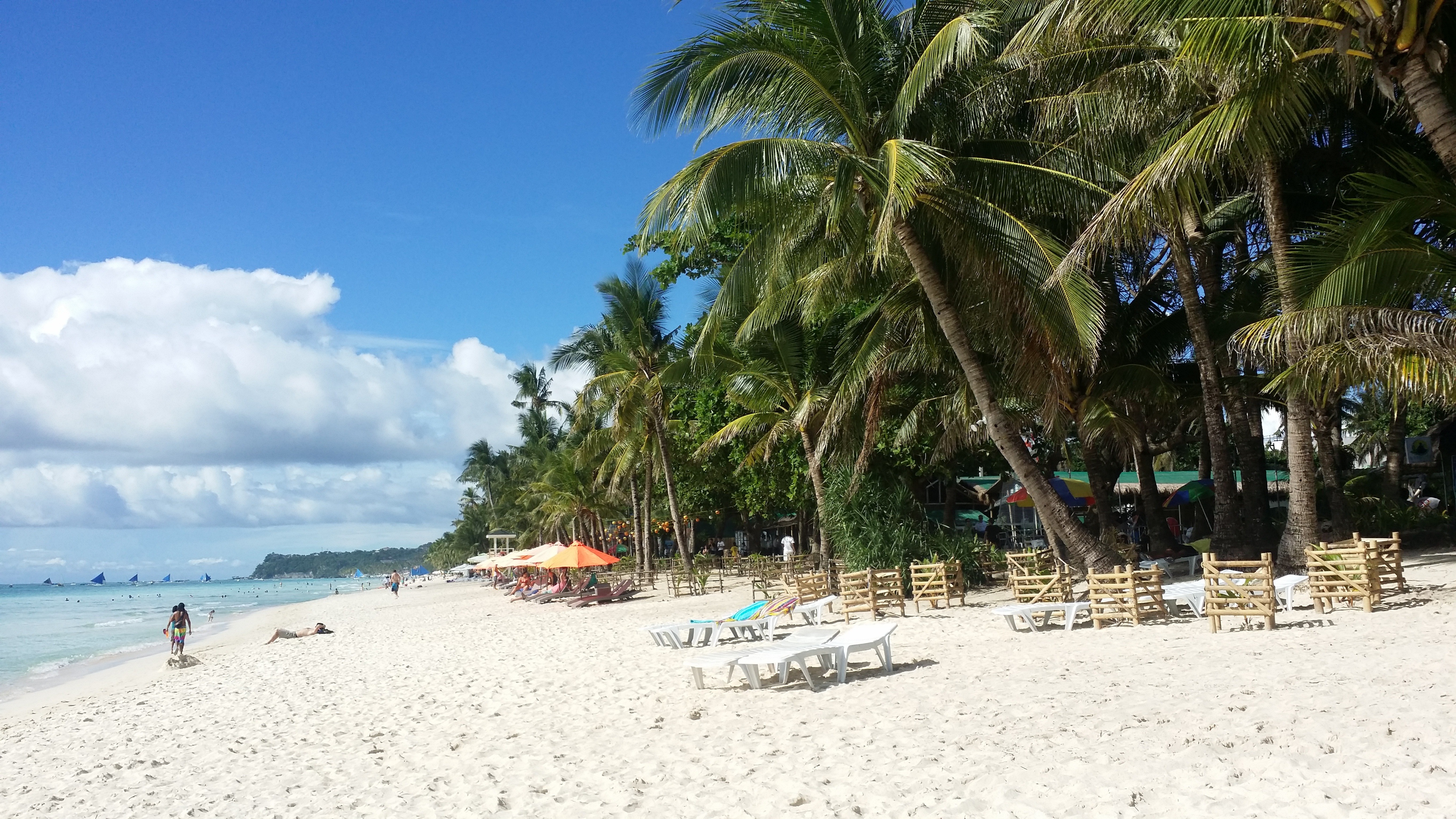
About Boracay Island

About Manila
MANILA, the capital city of the Philippines, was founded in, 1571 by Spanish conquistador Miguel López de Legazpi. It is one of the oldest cities in the country and was the seat of power for most of the colonial rules of the Philippines. It is situated on the eastern shore of Manila Bay and contains a multitude of landmarks, some of which date back to the 16th century. It is home to the baroque 16th-century San Agustin Church as well as Fort Santiago, a storied citadel and military prison. In the 19th century Manila became one of the most modern cities in Asia. Before the Spanish–American War, Manila saw the rise of the Philippine Revolution. Under the American rule following the Spanish-American War, the United States changed the official language from Spanish to English. Towards the end of World War II, during the Battle of Manila, most of the city was flattened by intensive aerial bombardment. Today, tourism is a vital industry in Manila. Major shopping malls and bazaars thrive around Manila.

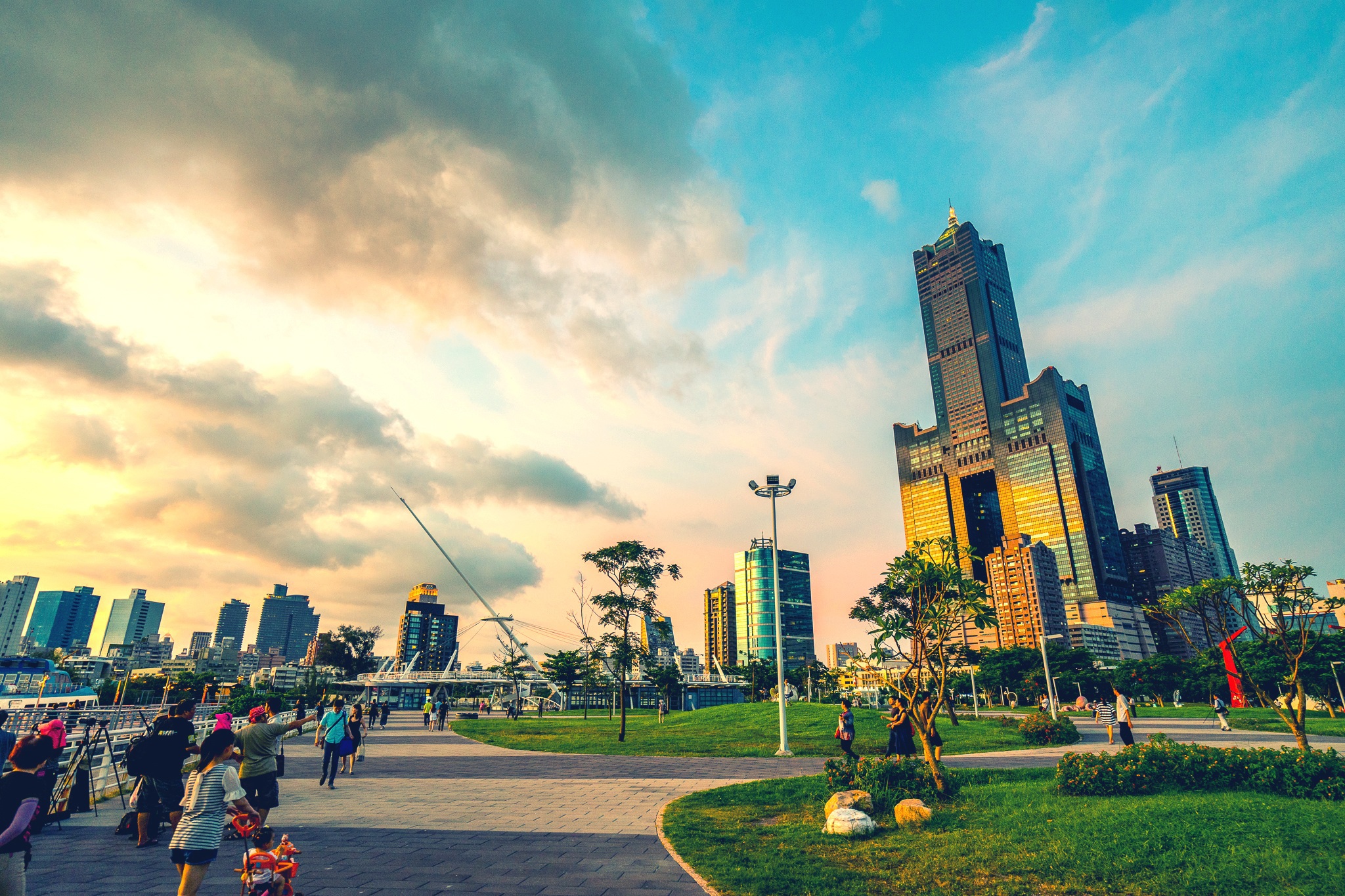
About Kaohsiung
Kaohsiung is Taiwan’s second largest city, its biggest seaport, and the world’s fourth largest container port. It entered the 21st century as a newly emerging international metropolis. In the forefront of Taiwan’s expansion and modernisation efforts are the China Steel Corporation and China Shipbuilding. They are perfect examples of what Taiwan’s export-oriented economy is all about. The Love River, which has seen some recent landscaping, adds to the beauty of the city. Coffee shops along its banks offer good opportunities to view the river’s activities and enjoy a nice breeze. A 495-feet (150 metres)-long urban corridor of light, known as Urban Spotlight, was designed by local artists who wanted to make light and shadows the theme of the hall. The result is an urban space in the Central Park area teeming with artistic vision. A very important event in Taiwan’s recent history occurred here in 1979, and is known as the Kaohsiung Incident. It was the day of the first major human rights celebration on the island. Until that time, the authorities had never allowed any expression of discontent. When the day came, however, the celebration ended in chaos when police encircled the peaceful crowd and started using teargas, and pro-government instigators incited violence. Kuomintang (KMT) authorities used this as an excuse to round up all well-known opposition leaders and imprison them. Although it was hardly noticed internationally, it is recognised locally as an important turning point in the island’s transition to democracy, and it galvanised the Taiwanese people into action.

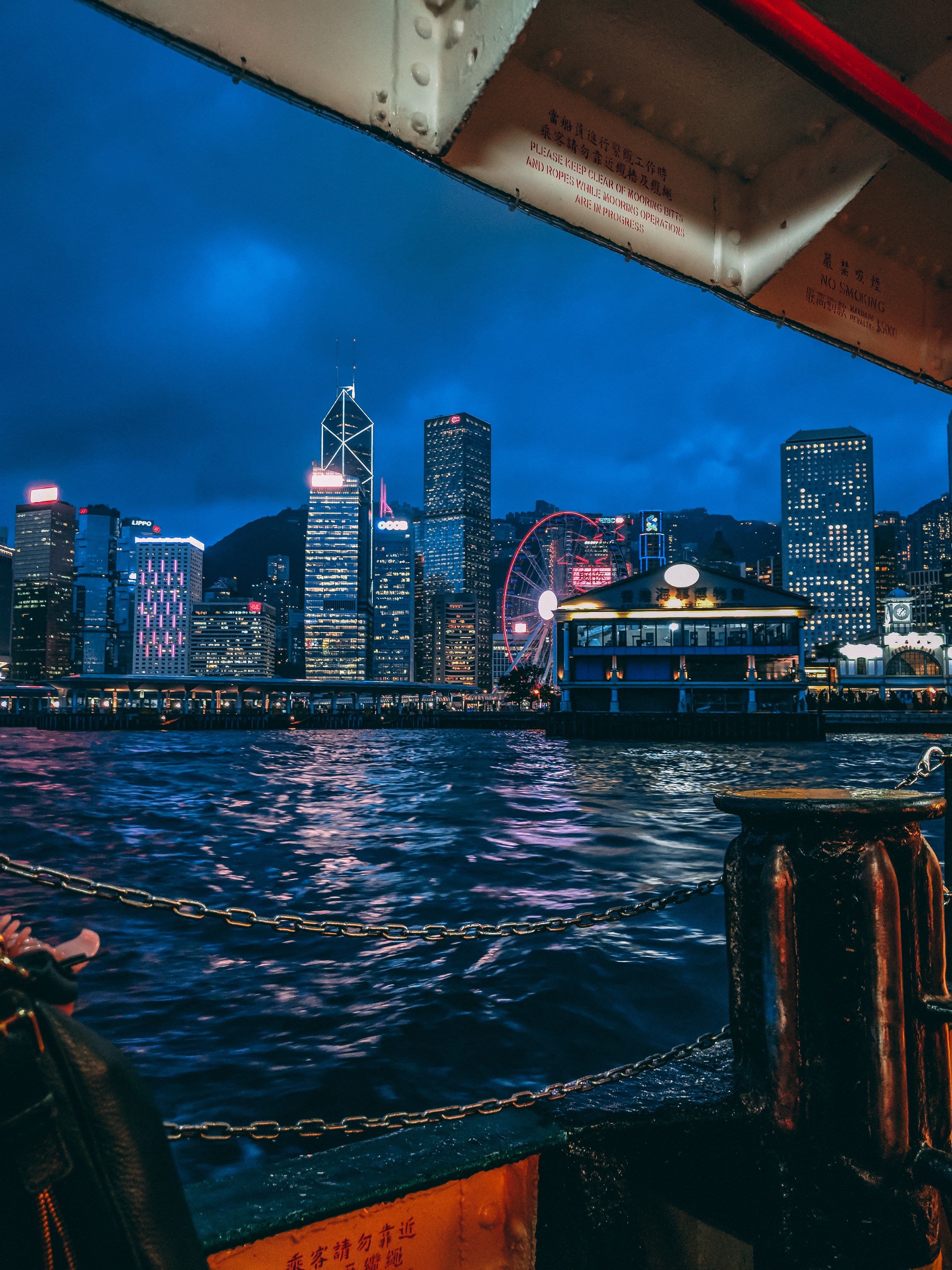
About Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Island skyline, with its ever-growing number of skyscrapers, speaks to ambition and money. Paris, London, even New York were centuries in the making, while Hong Kong's towers, bright lights, and glitzy shopping emporia weren't yet part of the urban scene when many of the young investment bankers who fuel one of the world's leading financial centers were born. Commerce is concentrated in the glittering high-rises of Central, tucked between Victoria Harbor and forested peaks on Hong Kong Island's north shore. While it's easy to think all the bright lights are the sum of today's Hong Kong, you need only walk or board a tram for the short jaunt west into Western to discover a side of Hong Kong that is more traditionally Chinese but no less high-energy. You'll discover the real Hong Kong to the east of Central, too, in Wan Chai, Causeway Bay, and beyond. Amid the residential towers are restaurants, shopping malls, bars, convention centers, a nice smattering of museums, and—depending on fate and the horse you wager on—one of Hong Kong's luckiest or unluckiest spots, the Happy Valley Racecourse. Kowloon sprawls across a generous swath of the Chinese mainland across Victoria Harbour from Central. Tsim Sha Tsui, at the tip of Kowloon peninsula, is packed with glitzy shops, first-rate museums, and eye-popping views of the skyline across the water. Just to the north are the teeming market streets of Mong Kok and in the dense residential neighborhoods beyond, two of Hong Kong's most enchanting spiritual sights, Wong Tai Sin Temple and Chi Lin Nunnery. As you navigate this huge metropolis (easy to do on the excellent transportation network), keep in mind that streets are usually numbered odd on one side, even on the other. There's no baseline for street numbers and no block-based numbering system, but street signs indicate building numbers for any given block.
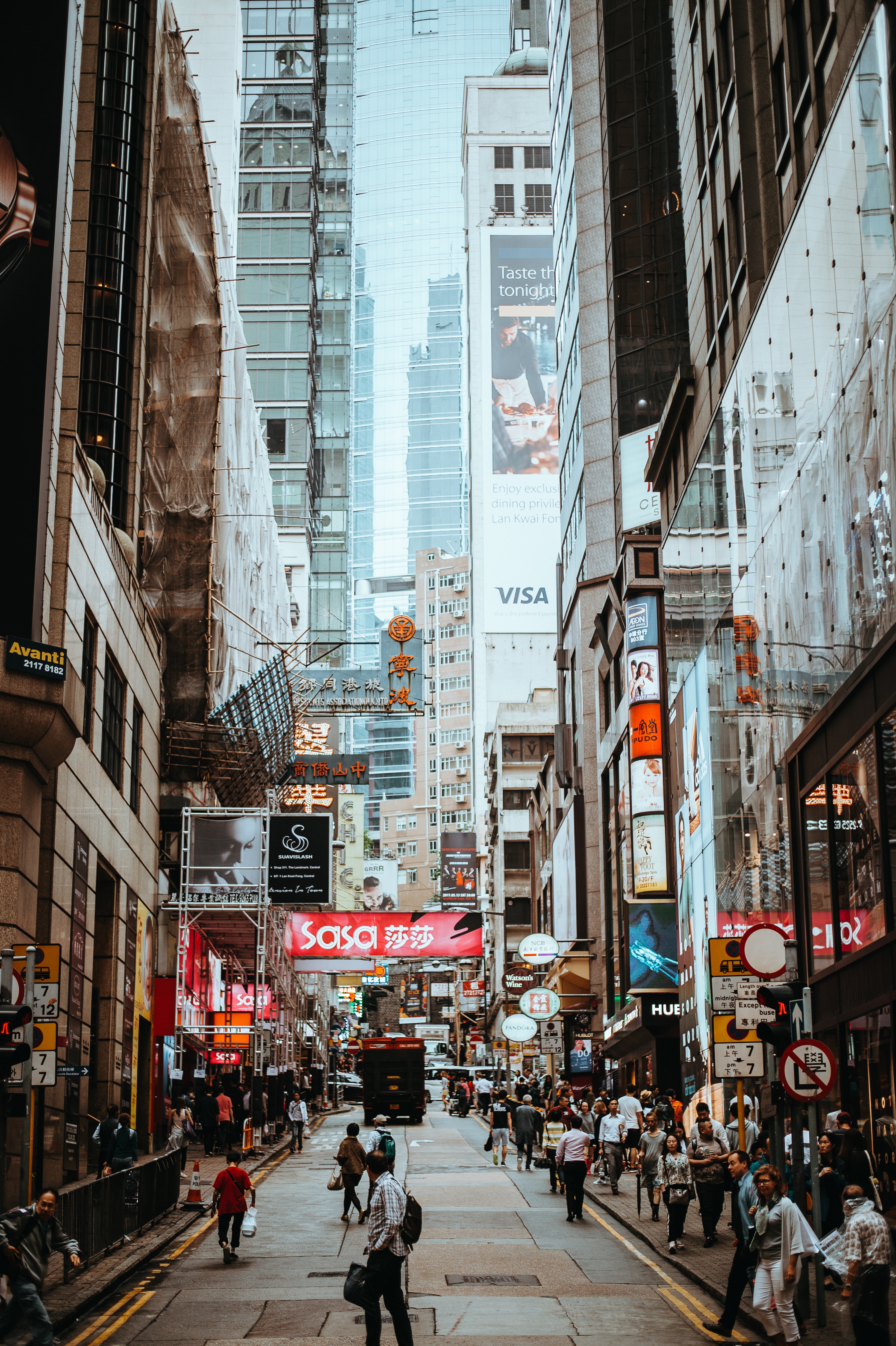
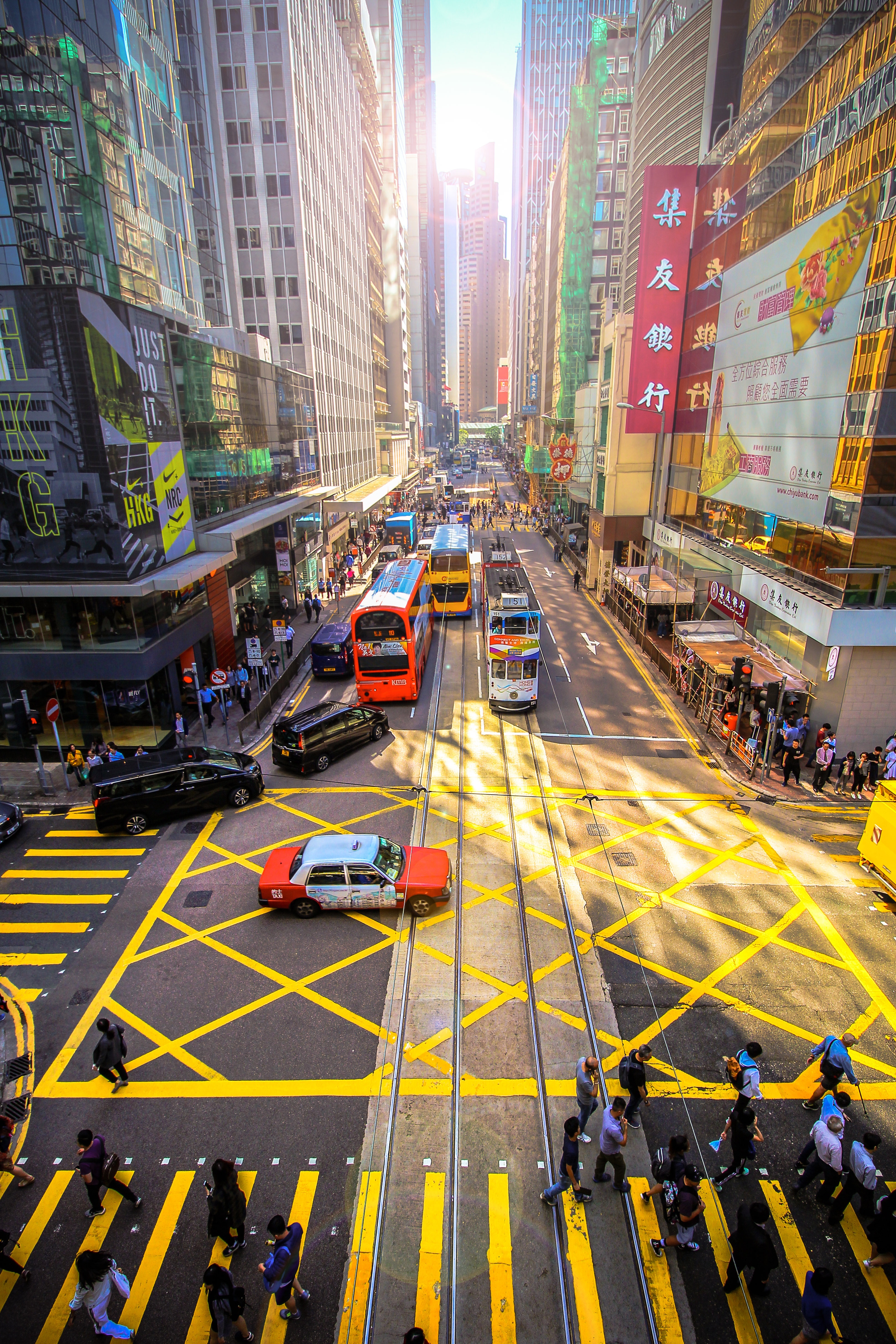



About Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Island skyline, with its ever-growing number of skyscrapers, speaks to ambition and money. Paris, London, even New York were centuries in the making, while Hong Kong's towers, bright lights, and glitzy shopping emporia weren't yet part of the urban scene when many of the young investment bankers who fuel one of the world's leading financial centers were born. Commerce is concentrated in the glittering high-rises of Central, tucked between Victoria Harbor and forested peaks on Hong Kong Island's north shore. While it's easy to think all the bright lights are the sum of today's Hong Kong, you need only walk or board a tram for the short jaunt west into Western to discover a side of Hong Kong that is more traditionally Chinese but no less high-energy. You'll discover the real Hong Kong to the east of Central, too, in Wan Chai, Causeway Bay, and beyond. Amid the residential towers are restaurants, shopping malls, bars, convention centers, a nice smattering of museums, and—depending on fate and the horse you wager on—one of Hong Kong's luckiest or unluckiest spots, the Happy Valley Racecourse. Kowloon sprawls across a generous swath of the Chinese mainland across Victoria Harbour from Central. Tsim Sha Tsui, at the tip of Kowloon peninsula, is packed with glitzy shops, first-rate museums, and eye-popping views of the skyline across the water. Just to the north are the teeming market streets of Mong Kok and in the dense residential neighborhoods beyond, two of Hong Kong's most enchanting spiritual sights, Wong Tai Sin Temple and Chi Lin Nunnery. As you navigate this huge metropolis (easy to do on the excellent transportation network), keep in mind that streets are usually numbered odd on one side, even on the other. There's no baseline for street numbers and no block-based numbering system, but street signs indicate building numbers for any given block.



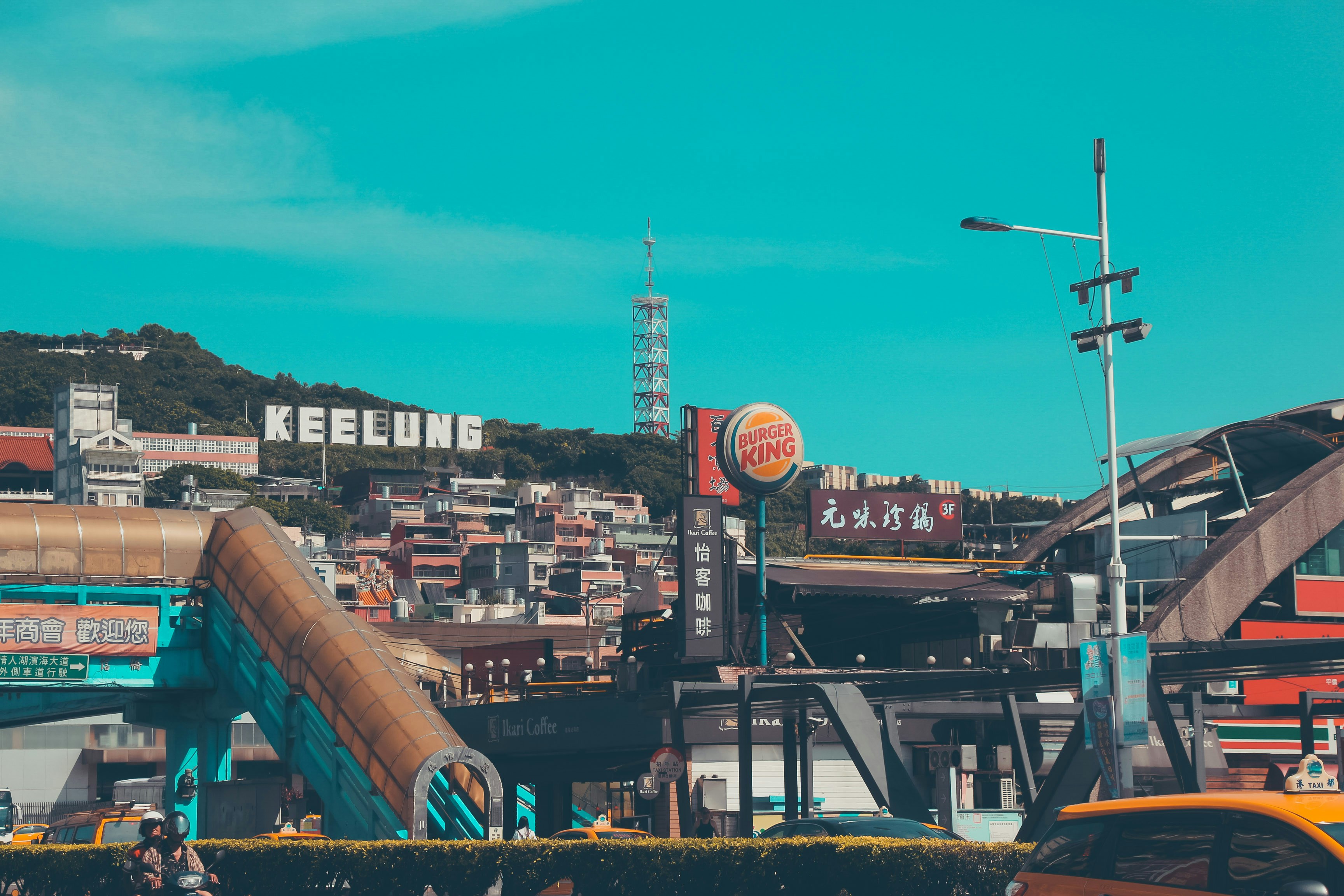
About Keelung (Chilung)
With the glittering lights of Taipei - a futuristic metropolis of culture and ideas - sparkling nearby, Keelung is the first calling point for many visitors arriving in Taiwan. While this port city essentially serves as Taipei's ocean gateway, you shouldn’t be too hasty in dashing off to Taipei's neon-lit magic – first it’s well worth spending some time exploring the famous glowing night market, which hums with life each evening and is famous for its local seafood.
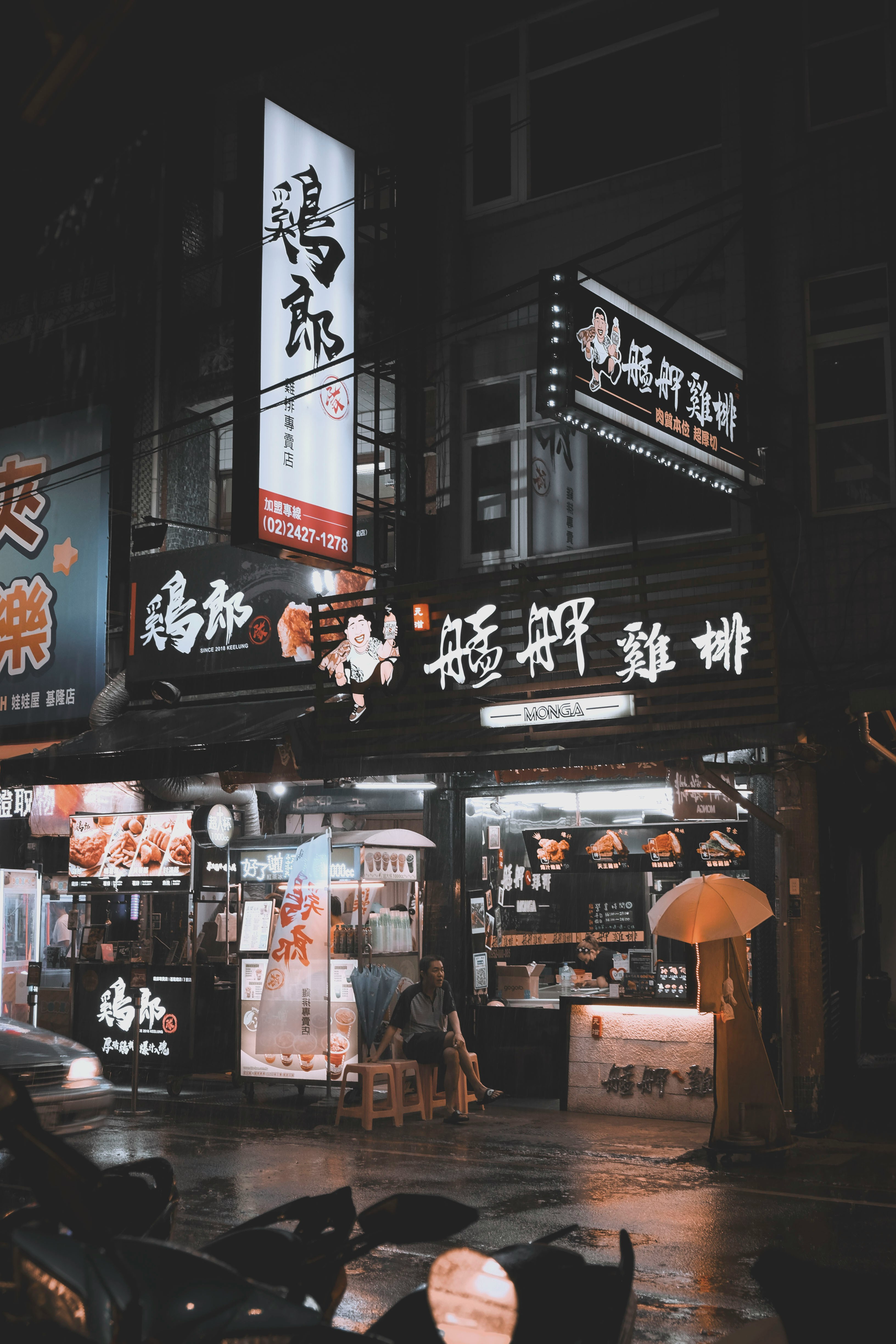






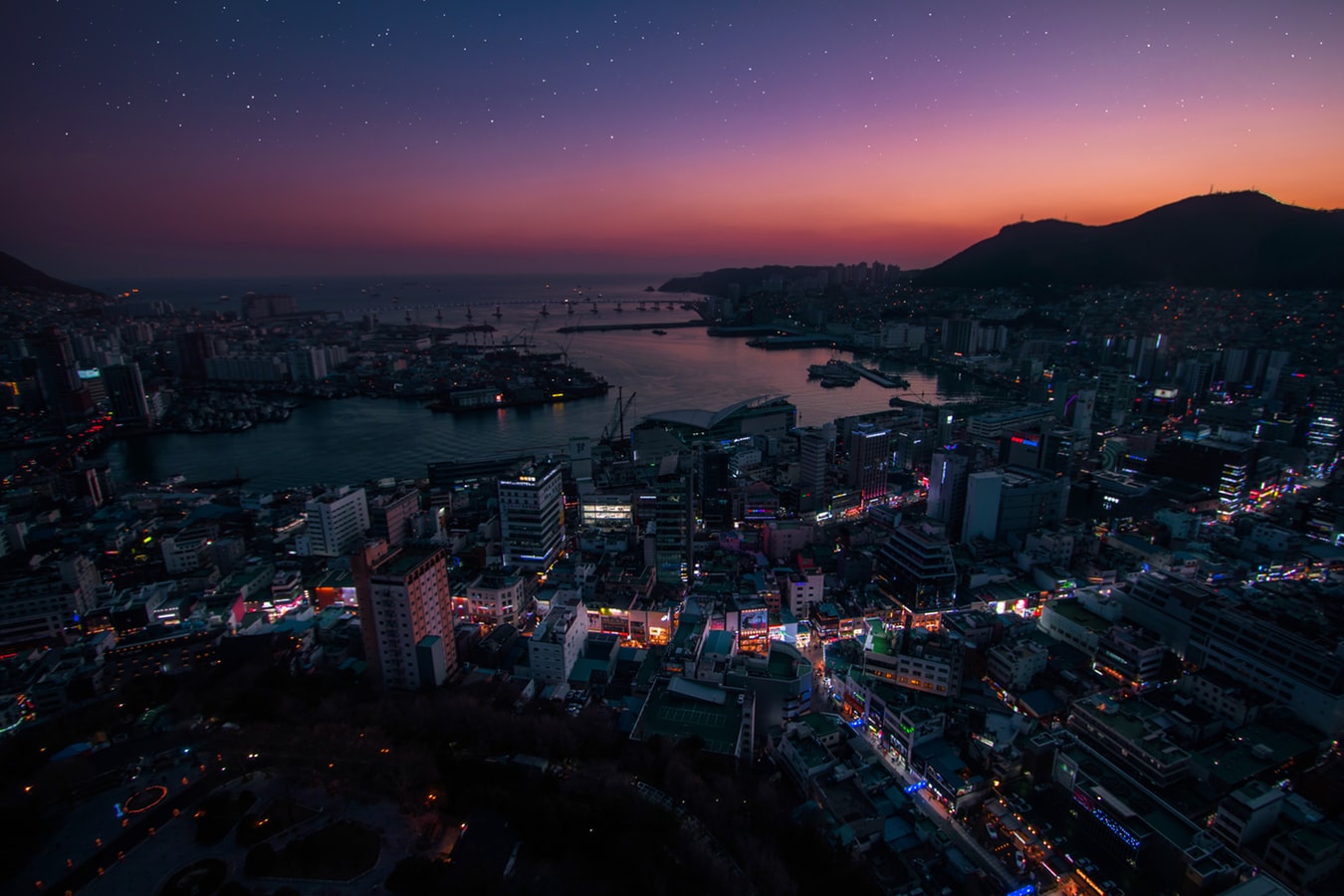
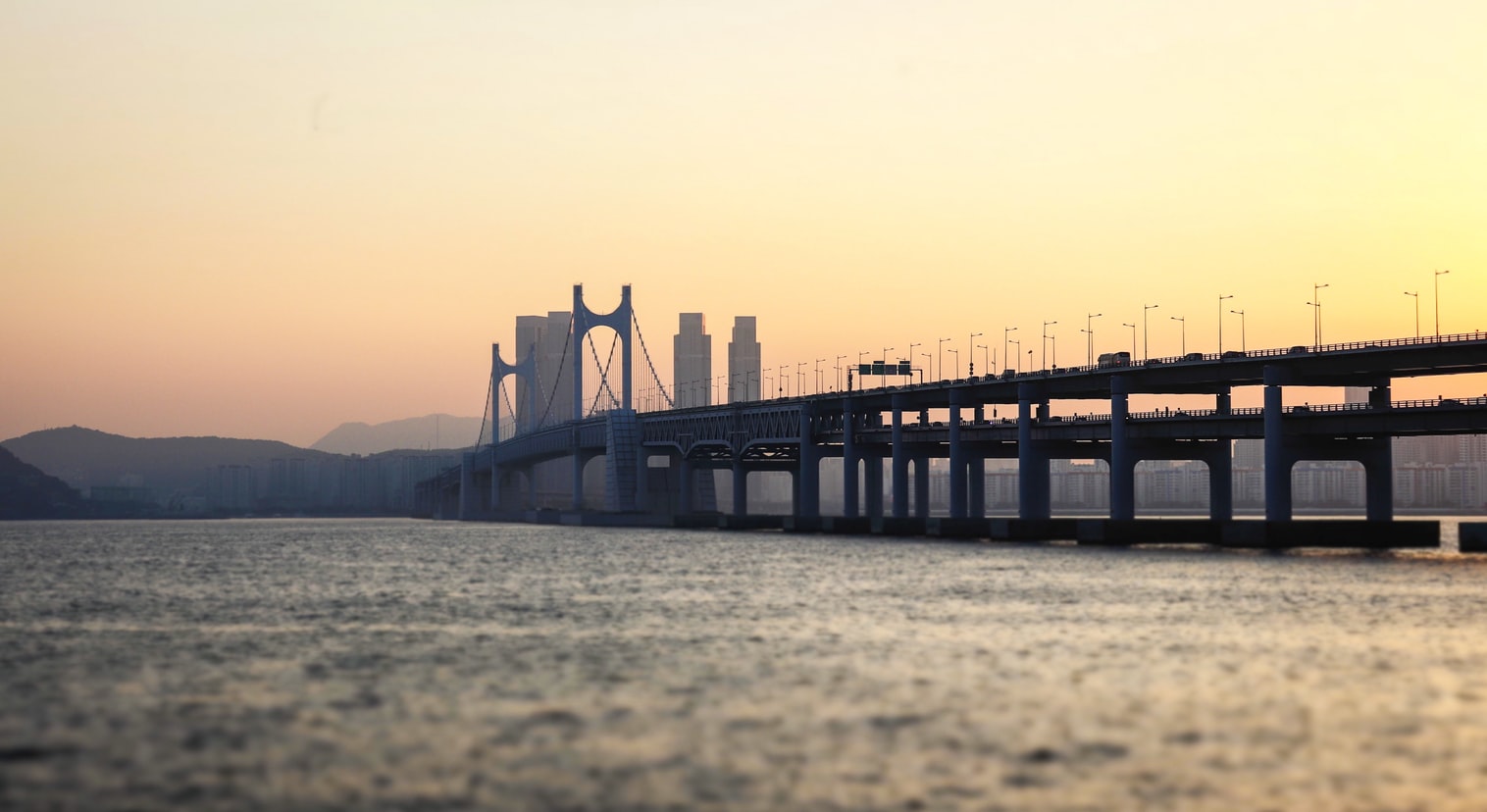
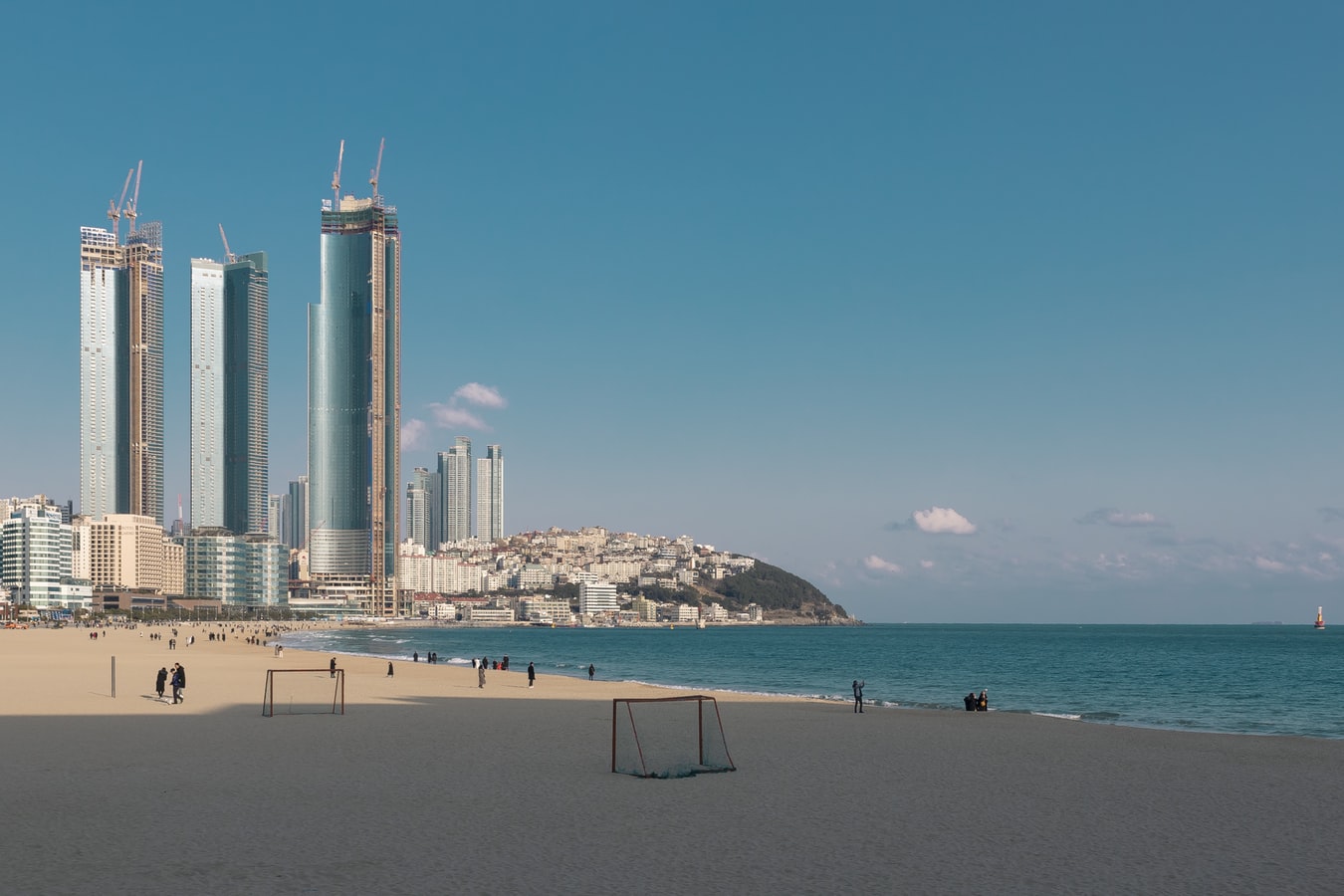
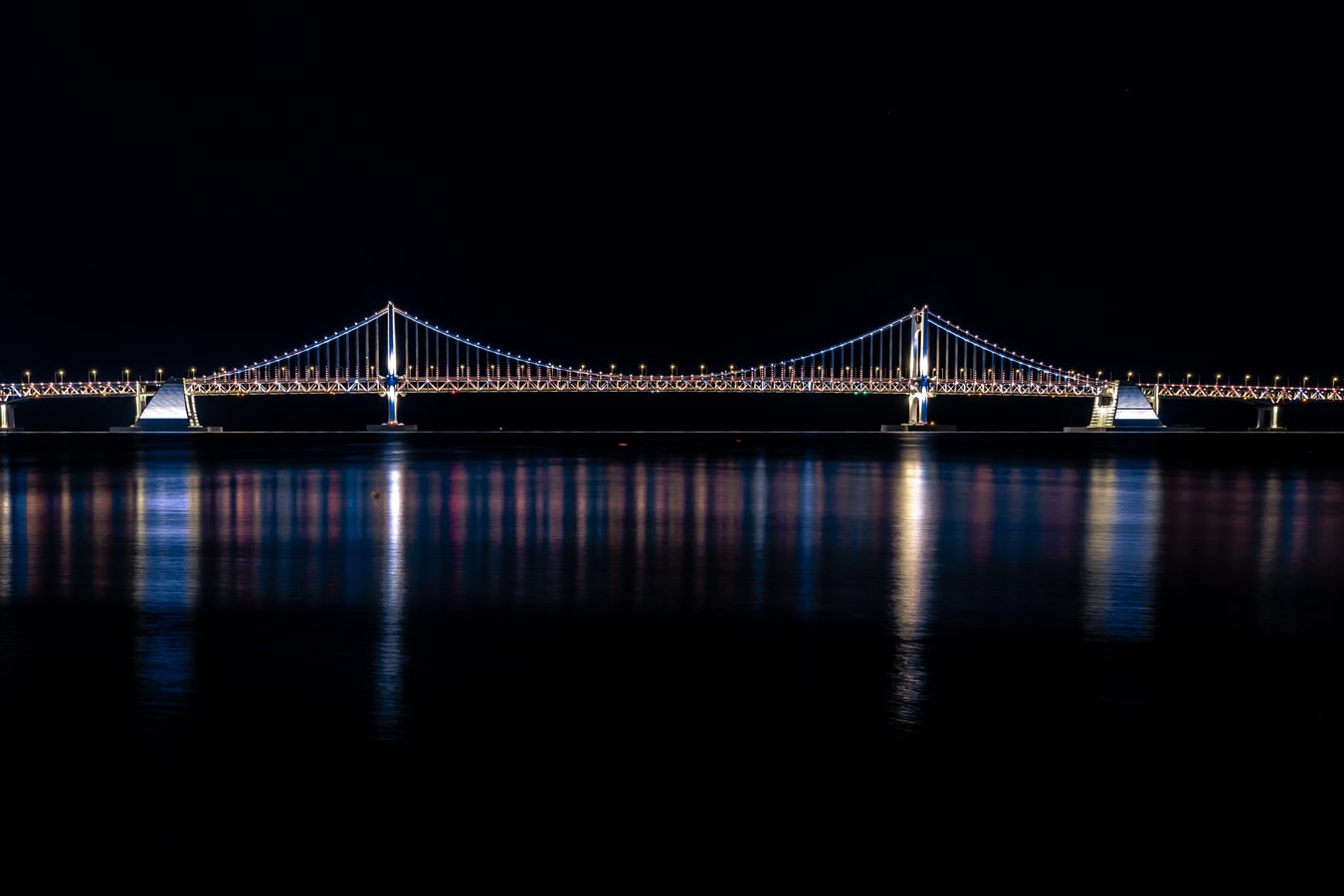
About Busan
White-sand city beaches and hot-spring resorts may not be everyone's first image of Korea, but these are what Koreans flock to Busan for all year. And there are plenty of opportunities for rest, relaxation, retail therapy, and even a touch of glamour every October with the Busan International Film Festival. Busan's beaches are the big summertime draw but there is plenty to be seen year round. Quintessential experiences include taking some rest and relaxation at a local spa and exploring the Beomeosa temple complex.




About Nagasaki
Nagasaki city has developed into one of the most important port cities in Japan. During Japan’s period of isolation in the 17th century, Nagasaki played a prominent role in foreign trade relation and only a very few ports were open to restricted numbers of foreign traders. Even though Holland was a major country who conducted trading during this period, Dutch people were only allowed to stay in Dejima Island and were not allowed to have contact with the Japanese people. Today, you will still find the strong influence of Dutch and Chinese culture in the city which is very different from all other cities in Japan. In the more recent history, Nagasaki became the second city after Hiroshima to be destroyed by an atomic bomb towards the end of World War II. From the visit to Atomic bomb museum and peace memorial park, people could understand how chaotic the situation was and the agony that the people in the days have experienced from the damage inflicted by the atomic bomb. It continues to appeal to the world with their wish for world peace.
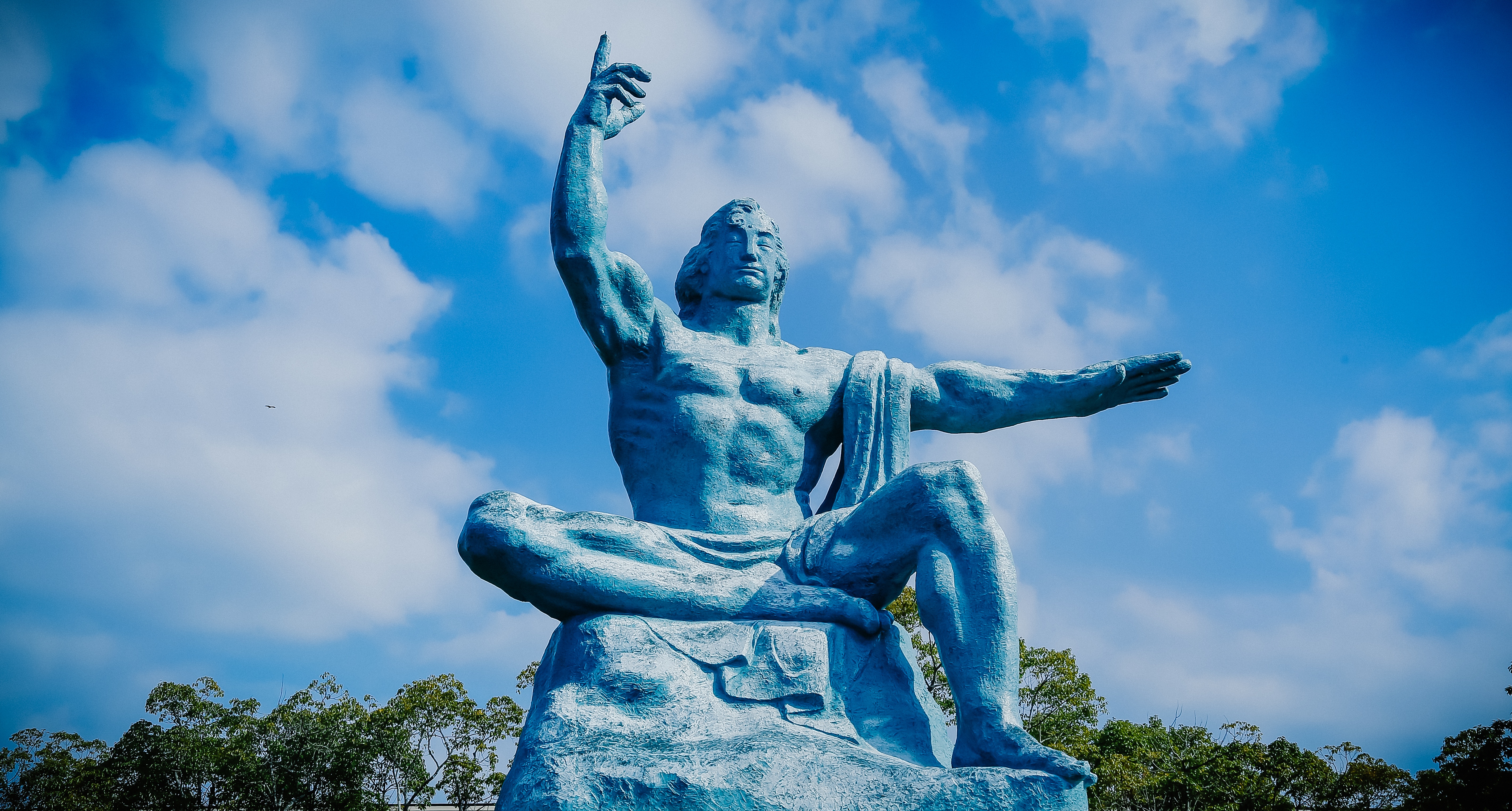
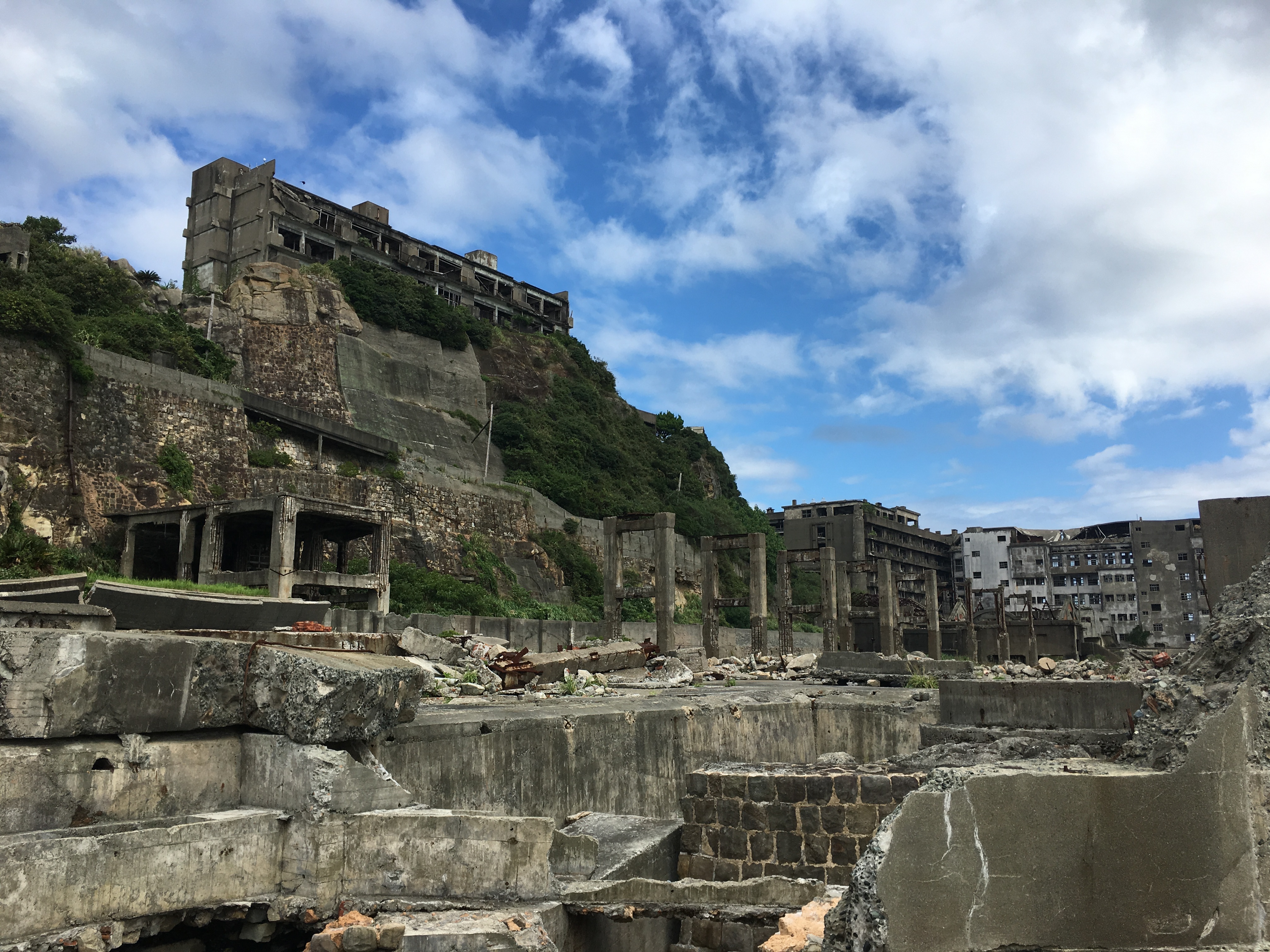
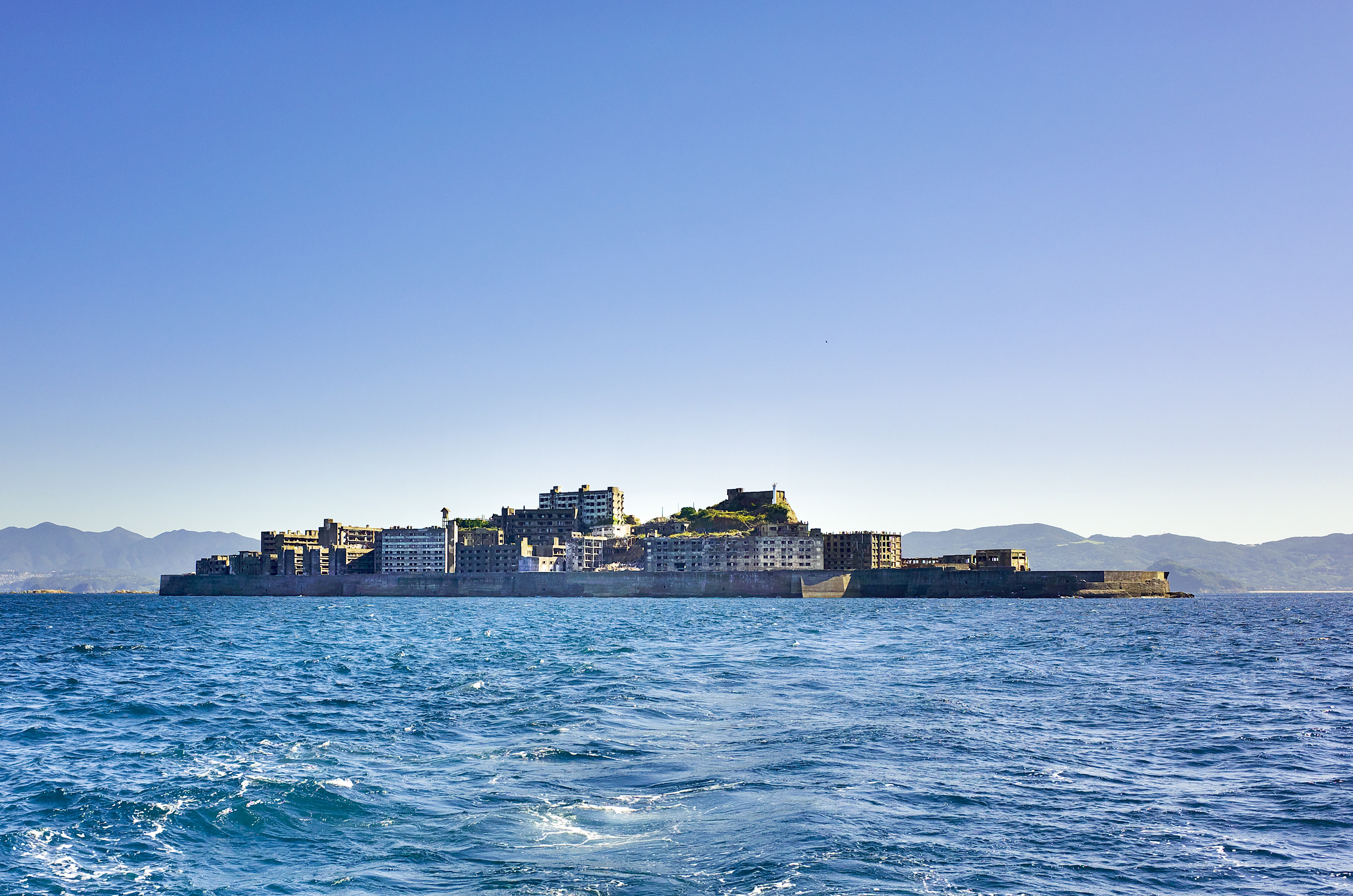






About Beppu, Kyushu Island, Oita
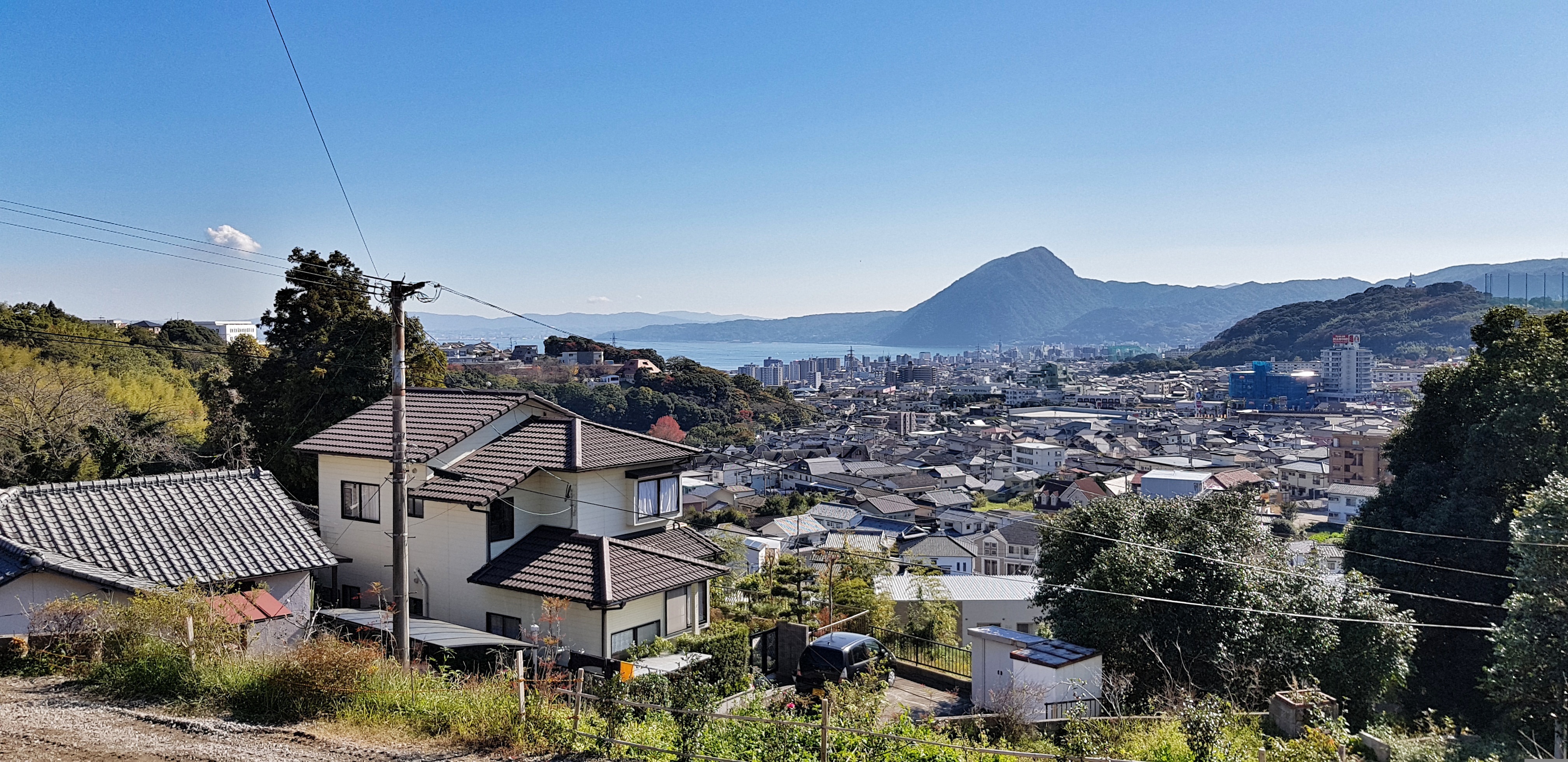

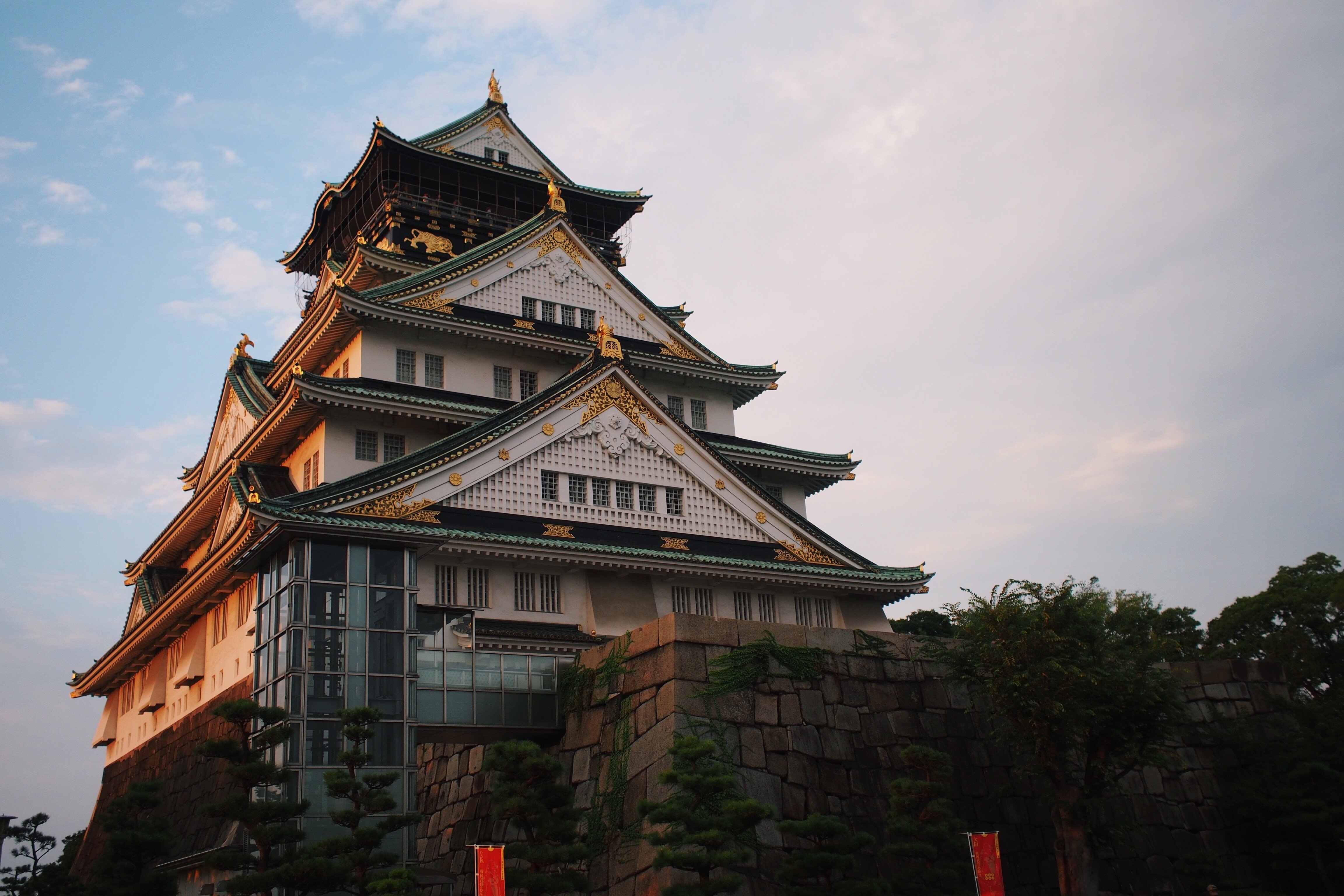
About Osaka
From Minami's neon-lighted Dotombori and historic Tenno-ji to the high-rise class and underground shopping labyrinths of Kita, Osaka is a city that pulses with its own unique rhythm. Though Osaka has no shortage of tourist sites, it is the city itself that is the greatest attraction. Home to some of Japan's best food, most unique fashions, and warmest locals, Osaka does not beg to be explored—it demands it. More than anywhere else in Japan, it rewards the impulsive turn down an interesting side street or the chat with a random stranger. People do not come here to see the city, they come to experience it.Excluded from the formal circles of power and aristocratic culture in 16th-century Edo (Tokyo), Osaka took advantage of its position as Japan's trading center, developing its own art forms such as Bunraku puppet theater and Rakugo comic storytelling. It was in Osaka that feudal Japan's famed Floating World—the dining, theater, and pleasure district—was at its strongest and most inventive. Wealthy merchants and common laborers alike squandered fortunes on culinary delights, turning Osaka into "Japan's Kitchen," a moniker the city still has today. Though the city suffered a blow when the Meiji government canceled all of the samurai class's outstanding debts to the merchants, it was quick to recover. At the turn of the 20th century, it had become Japan's largest and most prosperous city, a center of commerce and manufacturing.Today Osaka remains Japan's iconoclastic metropolis, refusing to fit Tokyo's norms and expectations. Unlike the hordes of Tokyo, Osakans are fiercely independent. As a contrast to the neon and concrete surroundings, the people of Osaka are known as Japan's friendliest and most outgoing. Ask someone on the street for directions in Tokyo and you are lucky to get so much as a glance. Ask someone in Osaka and you get a conversation.The main areas of the city, Kita (north) and Minami (south), are divided by two rivers: the Dojima-gawa and the Tosabori-gawa. Between Kita and Minami is Naka-no-shima, an island and the municipal center of Osaka. Kita (north of Chuo Dori) is Osaka's economic hub and contains Osaka's largest stations: JR Osaka and Hankyu Umeda. The area is crammed with shops, department stores, and restaurants. Nearby are a nightlife district, Kita-shinchi; Naka-no-shima and the Museum of Oriental Ceramics; Osaka-jo (Osaka Castle); and Osaka Koen (Osaka Park). Restaurants, bars, department stores, and boutiques attract Osaka's youth to Minami (south Chuo Dori); theatergoers head to the National Bunraku Theatre and electronics-lovers to Den Den Town. For a glimpse of old Osaka, visit Tenno-ji Temple and Shin Sekai. The main stations are Namba, Shin-sai-bashi, Namba Nankai, and Tenno-ji. There's easy access to the Municipal Museum of Fine Art and Sumiyoshi Taisha (Sumiyoshi Grand Shrine).The bay area, to the west of the city center, is home to the Osaka Aquarium and Universal Studios Japan. The Shinkansen stops at Shin-Osaka, three stops (about five minutes) north of Osaka Station on the Mido-suji subway line. To the north of Shin-Osaka is Senri Expo Park.


About Osaka
From Minami's neon-lighted Dotombori and historic Tenno-ji to the high-rise class and underground shopping labyrinths of Kita, Osaka is a city that pulses with its own unique rhythm. Though Osaka has no shortage of tourist sites, it is the city itself that is the greatest attraction. Home to some of Japan's best food, most unique fashions, and warmest locals, Osaka does not beg to be explored—it demands it. More than anywhere else in Japan, it rewards the impulsive turn down an interesting side street or the chat with a random stranger. People do not come here to see the city, they come to experience it.Excluded from the formal circles of power and aristocratic culture in 16th-century Edo (Tokyo), Osaka took advantage of its position as Japan's trading center, developing its own art forms such as Bunraku puppet theater and Rakugo comic storytelling. It was in Osaka that feudal Japan's famed Floating World—the dining, theater, and pleasure district—was at its strongest and most inventive. Wealthy merchants and common laborers alike squandered fortunes on culinary delights, turning Osaka into "Japan's Kitchen," a moniker the city still has today. Though the city suffered a blow when the Meiji government canceled all of the samurai class's outstanding debts to the merchants, it was quick to recover. At the turn of the 20th century, it had become Japan's largest and most prosperous city, a center of commerce and manufacturing.Today Osaka remains Japan's iconoclastic metropolis, refusing to fit Tokyo's norms and expectations. Unlike the hordes of Tokyo, Osakans are fiercely independent. As a contrast to the neon and concrete surroundings, the people of Osaka are known as Japan's friendliest and most outgoing. Ask someone on the street for directions in Tokyo and you are lucky to get so much as a glance. Ask someone in Osaka and you get a conversation.The main areas of the city, Kita (north) and Minami (south), are divided by two rivers: the Dojima-gawa and the Tosabori-gawa. Between Kita and Minami is Naka-no-shima, an island and the municipal center of Osaka. Kita (north of Chuo Dori) is Osaka's economic hub and contains Osaka's largest stations: JR Osaka and Hankyu Umeda. The area is crammed with shops, department stores, and restaurants. Nearby are a nightlife district, Kita-shinchi; Naka-no-shima and the Museum of Oriental Ceramics; Osaka-jo (Osaka Castle); and Osaka Koen (Osaka Park). Restaurants, bars, department stores, and boutiques attract Osaka's youth to Minami (south Chuo Dori); theatergoers head to the National Bunraku Theatre and electronics-lovers to Den Den Town. For a glimpse of old Osaka, visit Tenno-ji Temple and Shin Sekai. The main stations are Namba, Shin-sai-bashi, Namba Nankai, and Tenno-ji. There's easy access to the Municipal Museum of Fine Art and Sumiyoshi Taisha (Sumiyoshi Grand Shrine).The bay area, to the west of the city center, is home to the Osaka Aquarium and Universal Studios Japan. The Shinkansen stops at Shin-Osaka, three stops (about five minutes) north of Osaka Station on the Mido-suji subway line. To the north of Shin-Osaka is Senri Expo Park.


About Nagoya
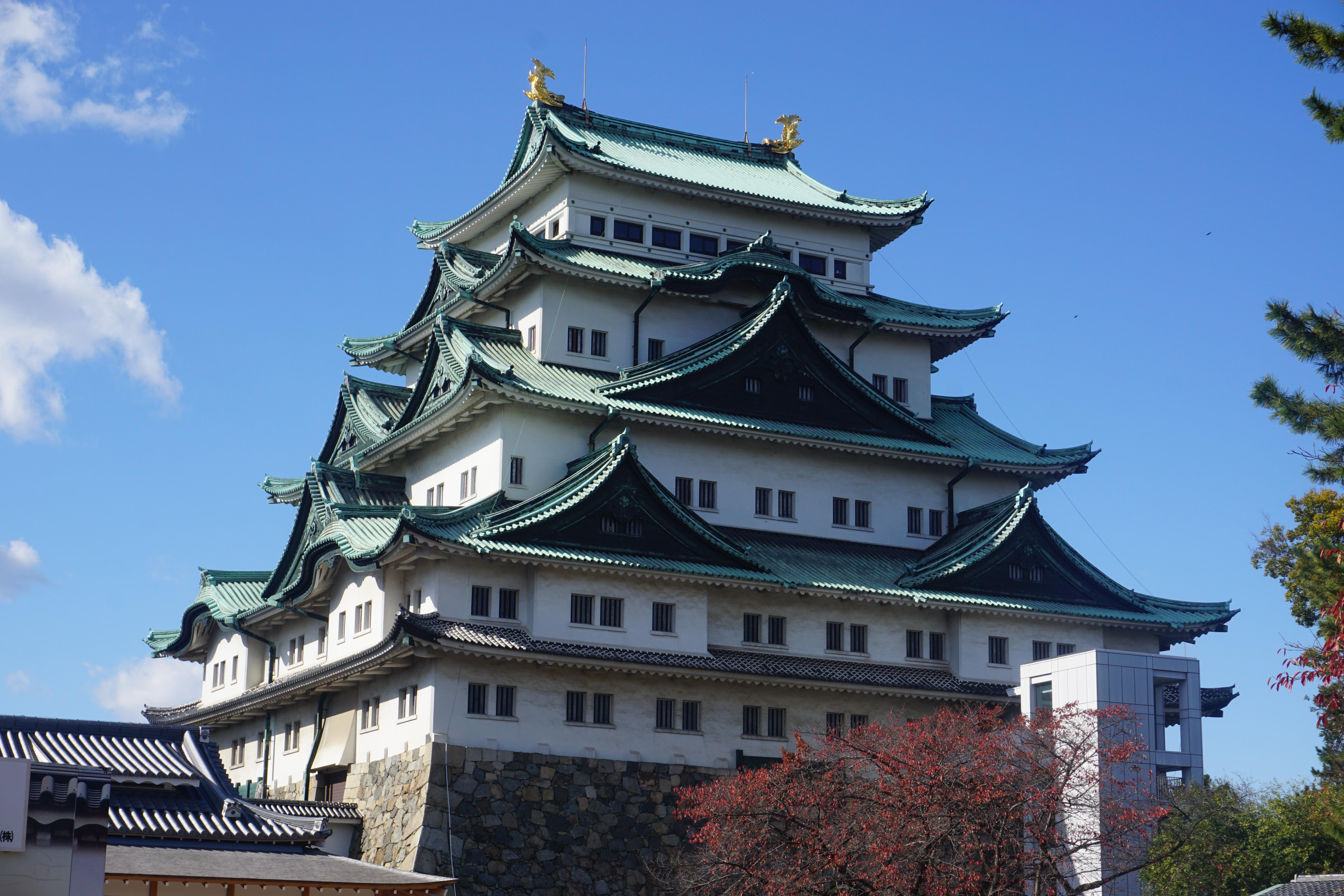

About Yokohama
In 1853, a fleet of four American warships under Commodore Matthew Perry sailed into the bay of Tokyo (then Edo) and presented the reluctant Japanese with the demands of the U.S. government for the opening of diplomatic and commercial relations. The following year Perry returned and first set foot on Japanese soil at Yokohama—then a small fishing village on the mudflats of Tokyo bay. Two years later New York businessman Townsend Harris became America's first diplomatic representative to Japan. In 1858 he was finally able to negotiate a commercial treaty between the two countries; part of the deal designated four locations—one of them Yokohama—as treaty ports. In 1859 the shogunate created a special settlement in Yokohama for the growing community of merchants, traders, missionaries, and other assorted adventurers drawn to this exotic new land of opportunity. The foreigners (predominantly Chinese and British, plus a few French, Americans, and Dutch) were confined here to a guarded compound about 5 square km (2 square miles)—placed, in effect, in isolation—but not for long. Within a few short years the shogunal government collapsed, and Japan began to modernize. Western ideas were welcomed, as were Western goods, and the little treaty port became Japan's principal gateway to the outside world. In 1872 Japan's first railway was built, linking Yokohama and Tokyo. In 1889 Yokohama became a city; by then the population had grown to some 120,000. As the city prospered, so did the international community and by the early 1900s Yokohama was the busiest and most modern center of international trade in all of East Asia. Then Yokohama came tumbling down. On September 1, 1923, the Great Kanto Earthquake devastated the city. The ensuing fires destroyed some 60,000 homes and took more than 40,000 lives. During the six years it took to rebuild the city, many foreign businesses took up quarters elsewhere, primarily in Kobe and Osaka, and did not return. Over the next 20 years Yokohama continued to grow as an industrial center—until May 29, 1945, when in a span of four hours, some 500 American B-29 bombers leveled nearly half the city and left more than half a million people homeless. When the war ended, what remained became—in effect—the center of the Allied occupation. General Douglas MacArthur set up headquarters here, briefly, before moving to Tokyo; the entire port facility and about a quarter of the city remained in the hands of the U.S. military throughout the 1950s. By the 1970s Yokohama was once more rising from the debris; in 1978 it surpassed Osaka as the nation's second-largest city, and the population is now inching up to the 3.5 million mark. Boosted by Japan's postwar economic miracle, Yokohama has extended its urban sprawl north to Tokyo and south to Kamakura—in the process creating a whole new subcenter around the Shinkansen Station at Shin-Yokohama. The development of air travel and the competition from other ports have changed the city's role in Japan's economy. The great liners that once docked at Yokohama's piers are now but a memory, kept alive by a museum ship and the occasional visit of a luxury vessel on a Pacific cruise. Modern Large as Yokohama is, the central area is very negotiable. As with any other port city, much of what it has to offer centers on the waterfront—in this case, on the west side of Tokyo Bay. The downtown area is called Kannai (literally, "within the checkpoint"); this is where the international community was originally confined by the shogunate. Though the center of interest has expanded to include the waterfront and Ishikawa-cho, to the south, Kannai remains the heart of town. Think of that heart as two adjacent areas. One is the old district of Kannai, bounded by Basha-michi on the northwest and Nippon-odori on the southeast, the Keihin Tohoku Line tracks on the southwest, and the waterfront on the northeast. This area contains the business offices of modern Yokohama. The other area extends southeast from Nippon-odori to the Moto-machi shopping street and the International Cemetery, bordered by Yamashita Koen and the waterfront to the northeast; in the center is Chinatown, with Ishikawa-cho Station to the southwest. This is the most interesting part of town for tourists. Whether you're coming from Tokyo, Nagoya, or Kamakura, make Ishikawa-cho Station your starting point. Take the South Exit from the station and head in the direction of the waterfront.
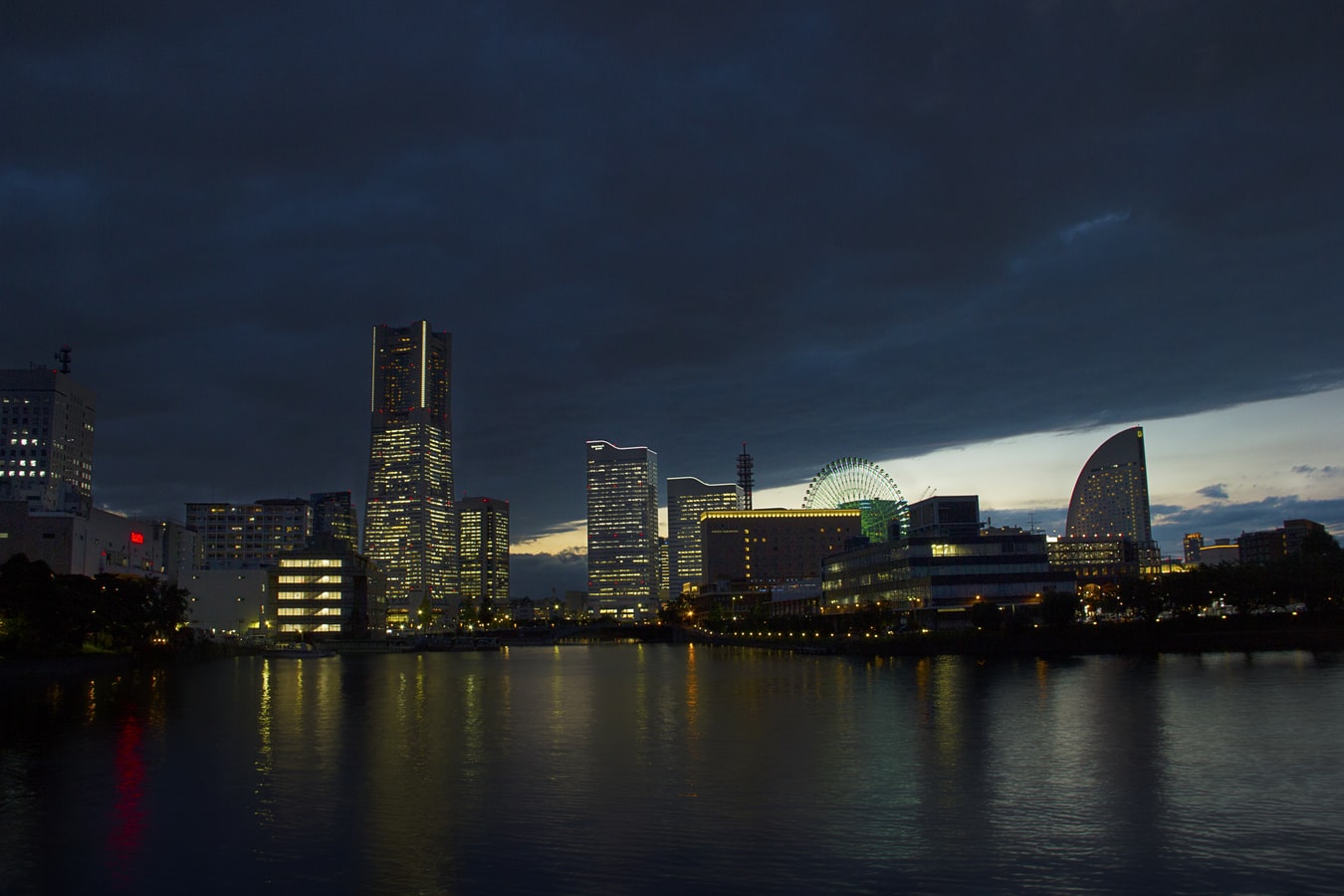
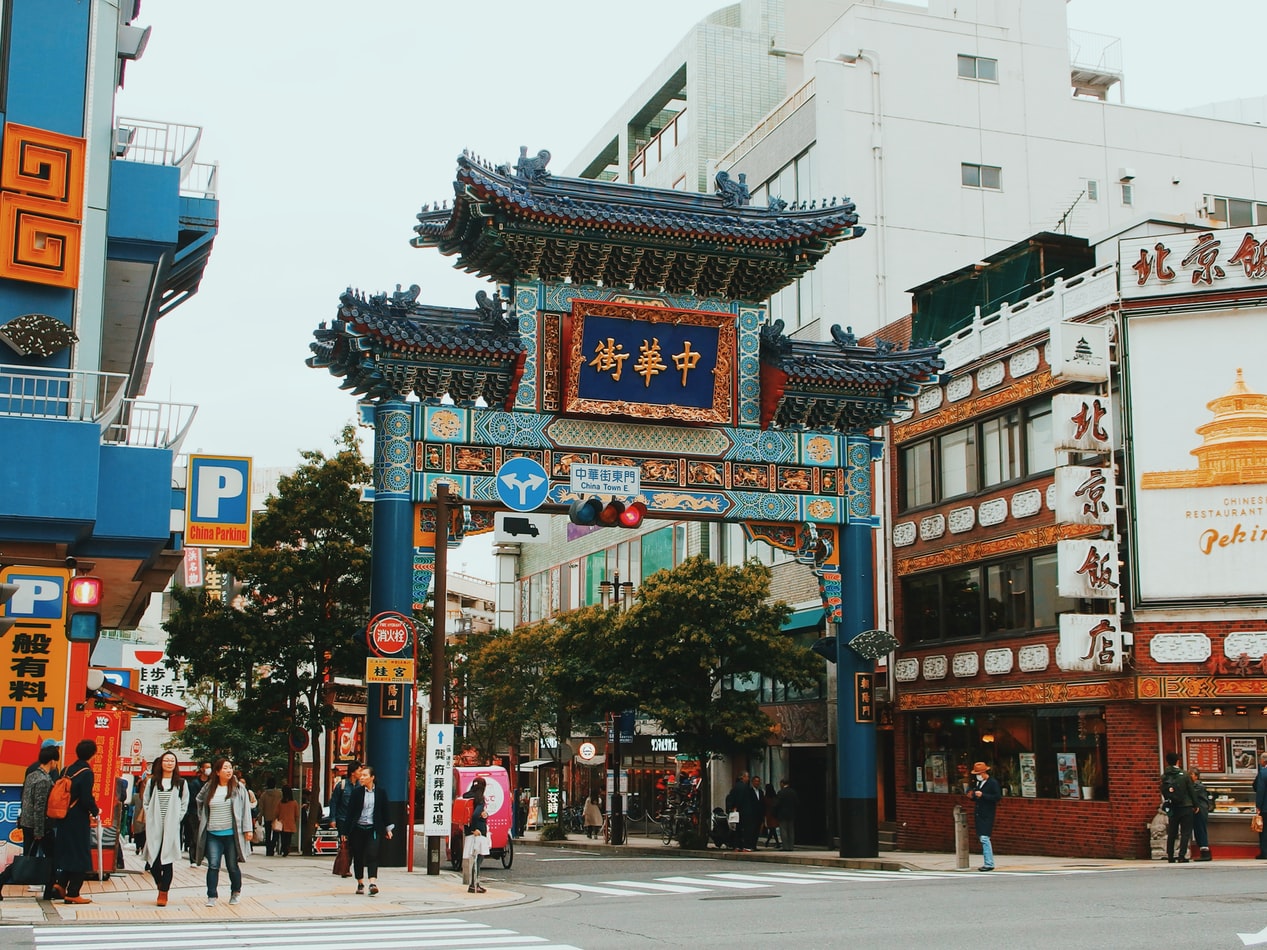
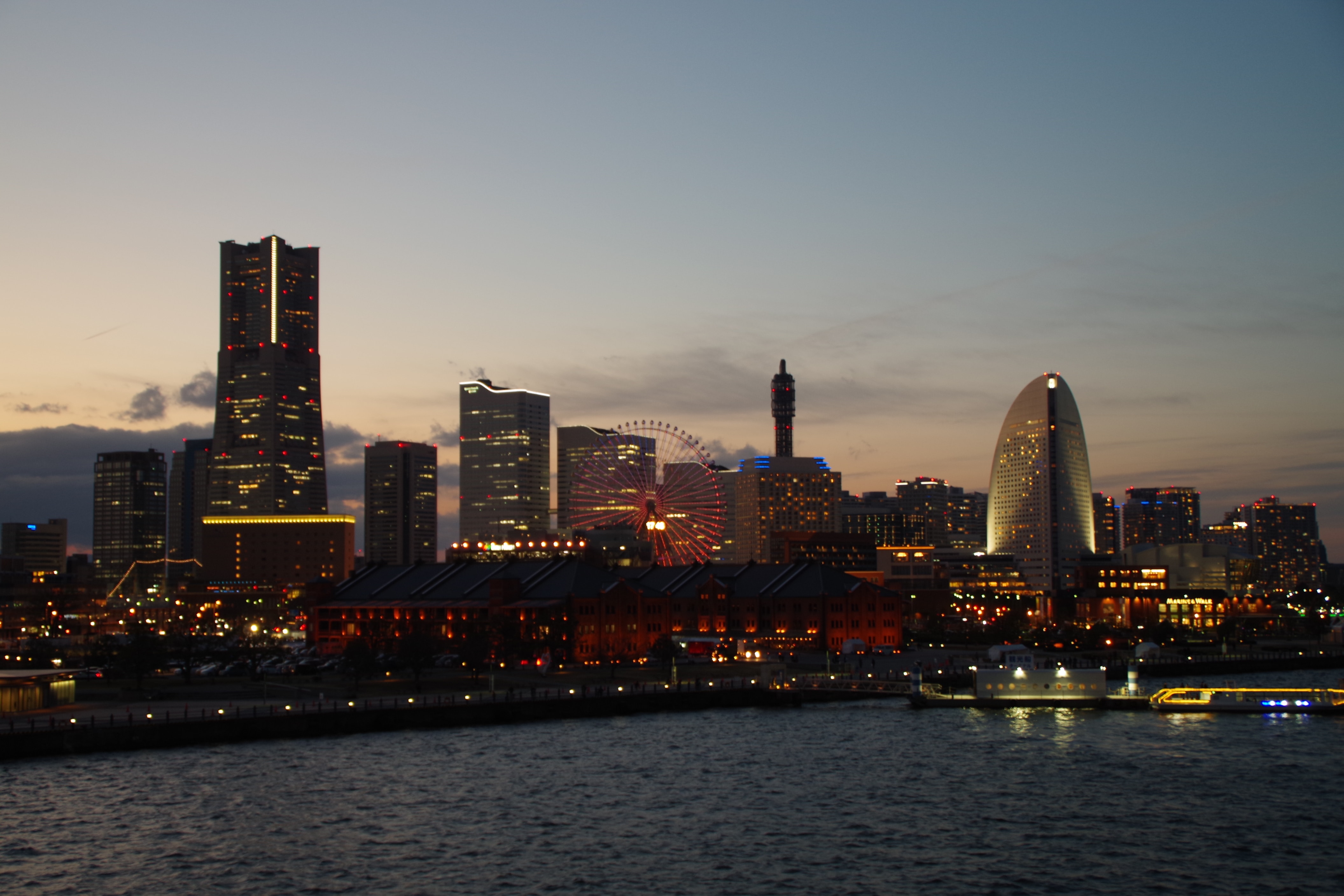



About Yokohama
In 1853, a fleet of four American warships under Commodore Matthew Perry sailed into the bay of Tokyo (then Edo) and presented the reluctant Japanese with the demands of the U.S. government for the opening of diplomatic and commercial relations. The following year Perry returned and first set foot on Japanese soil at Yokohama—then a small fishing village on the mudflats of Tokyo bay. Two years later New York businessman Townsend Harris became America's first diplomatic representative to Japan. In 1858 he was finally able to negotiate a commercial treaty between the two countries; part of the deal designated four locations—one of them Yokohama—as treaty ports. In 1859 the shogunate created a special settlement in Yokohama for the growing community of merchants, traders, missionaries, and other assorted adventurers drawn to this exotic new land of opportunity. The foreigners (predominantly Chinese and British, plus a few French, Americans, and Dutch) were confined here to a guarded compound about 5 square km (2 square miles)—placed, in effect, in isolation—but not for long. Within a few short years the shogunal government collapsed, and Japan began to modernize. Western ideas were welcomed, as were Western goods, and the little treaty port became Japan's principal gateway to the outside world. In 1872 Japan's first railway was built, linking Yokohama and Tokyo. In 1889 Yokohama became a city; by then the population had grown to some 120,000. As the city prospered, so did the international community and by the early 1900s Yokohama was the busiest and most modern center of international trade in all of East Asia. Then Yokohama came tumbling down. On September 1, 1923, the Great Kanto Earthquake devastated the city. The ensuing fires destroyed some 60,000 homes and took more than 40,000 lives. During the six years it took to rebuild the city, many foreign businesses took up quarters elsewhere, primarily in Kobe and Osaka, and did not return. Over the next 20 years Yokohama continued to grow as an industrial center—until May 29, 1945, when in a span of four hours, some 500 American B-29 bombers leveled nearly half the city and left more than half a million people homeless. When the war ended, what remained became—in effect—the center of the Allied occupation. General Douglas MacArthur set up headquarters here, briefly, before moving to Tokyo; the entire port facility and about a quarter of the city remained in the hands of the U.S. military throughout the 1950s. By the 1970s Yokohama was once more rising from the debris; in 1978 it surpassed Osaka as the nation's second-largest city, and the population is now inching up to the 3.5 million mark. Boosted by Japan's postwar economic miracle, Yokohama has extended its urban sprawl north to Tokyo and south to Kamakura—in the process creating a whole new subcenter around the Shinkansen Station at Shin-Yokohama. The development of air travel and the competition from other ports have changed the city's role in Japan's economy. The great liners that once docked at Yokohama's piers are now but a memory, kept alive by a museum ship and the occasional visit of a luxury vessel on a Pacific cruise. Modern Large as Yokohama is, the central area is very negotiable. As with any other port city, much of what it has to offer centers on the waterfront—in this case, on the west side of Tokyo Bay. The downtown area is called Kannai (literally, "within the checkpoint"); this is where the international community was originally confined by the shogunate. Though the center of interest has expanded to include the waterfront and Ishikawa-cho, to the south, Kannai remains the heart of town. Think of that heart as two adjacent areas. One is the old district of Kannai, bounded by Basha-michi on the northwest and Nippon-odori on the southeast, the Keihin Tohoku Line tracks on the southwest, and the waterfront on the northeast. This area contains the business offices of modern Yokohama. The other area extends southeast from Nippon-odori to the Moto-machi shopping street and the International Cemetery, bordered by Yamashita Koen and the waterfront to the northeast; in the center is Chinatown, with Ishikawa-cho Station to the southwest. This is the most interesting part of town for tourists. Whether you're coming from Tokyo, Nagoya, or Kamakura, make Ishikawa-cho Station your starting point. Take the South Exit from the station and head in the direction of the waterfront.



About Sendai
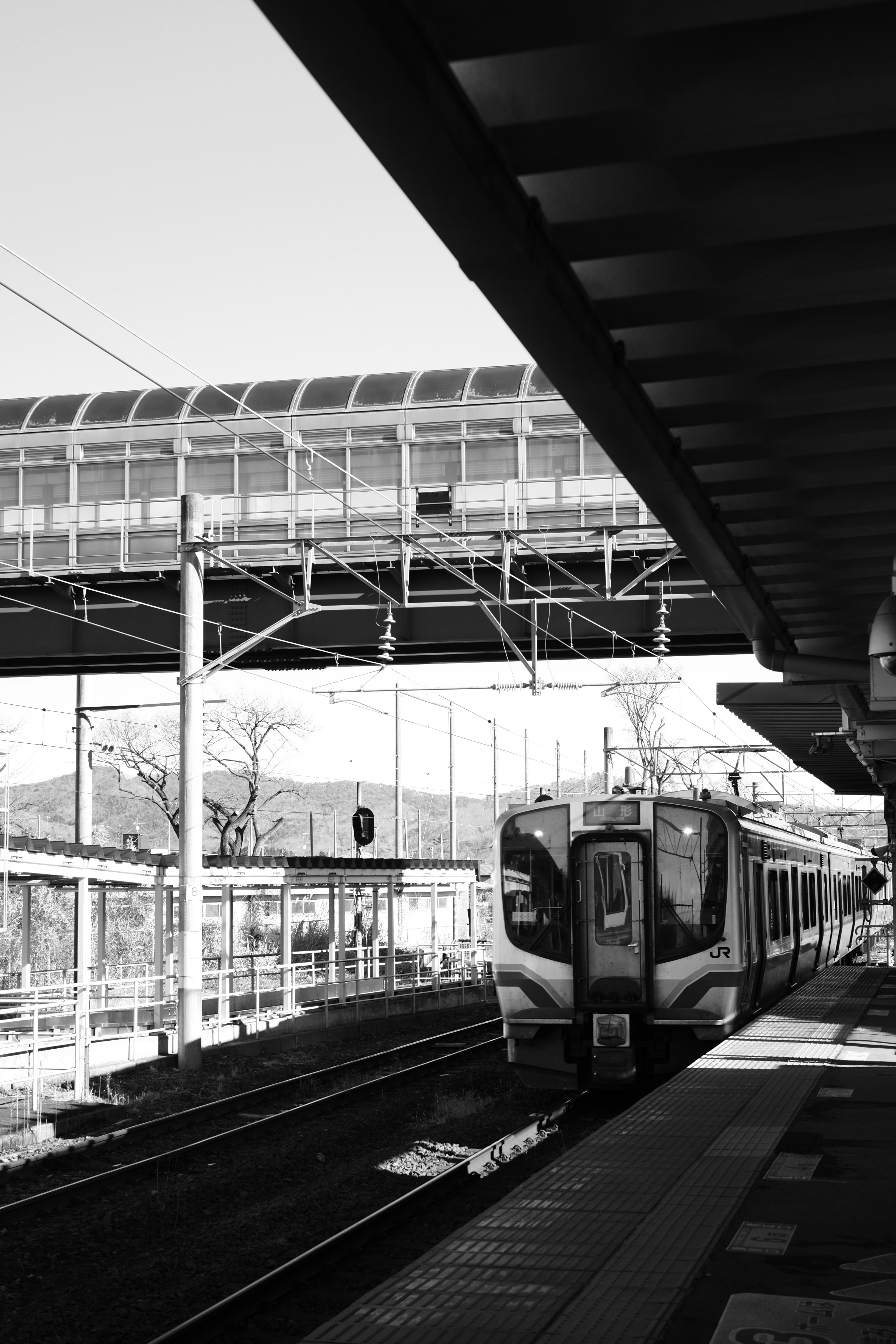
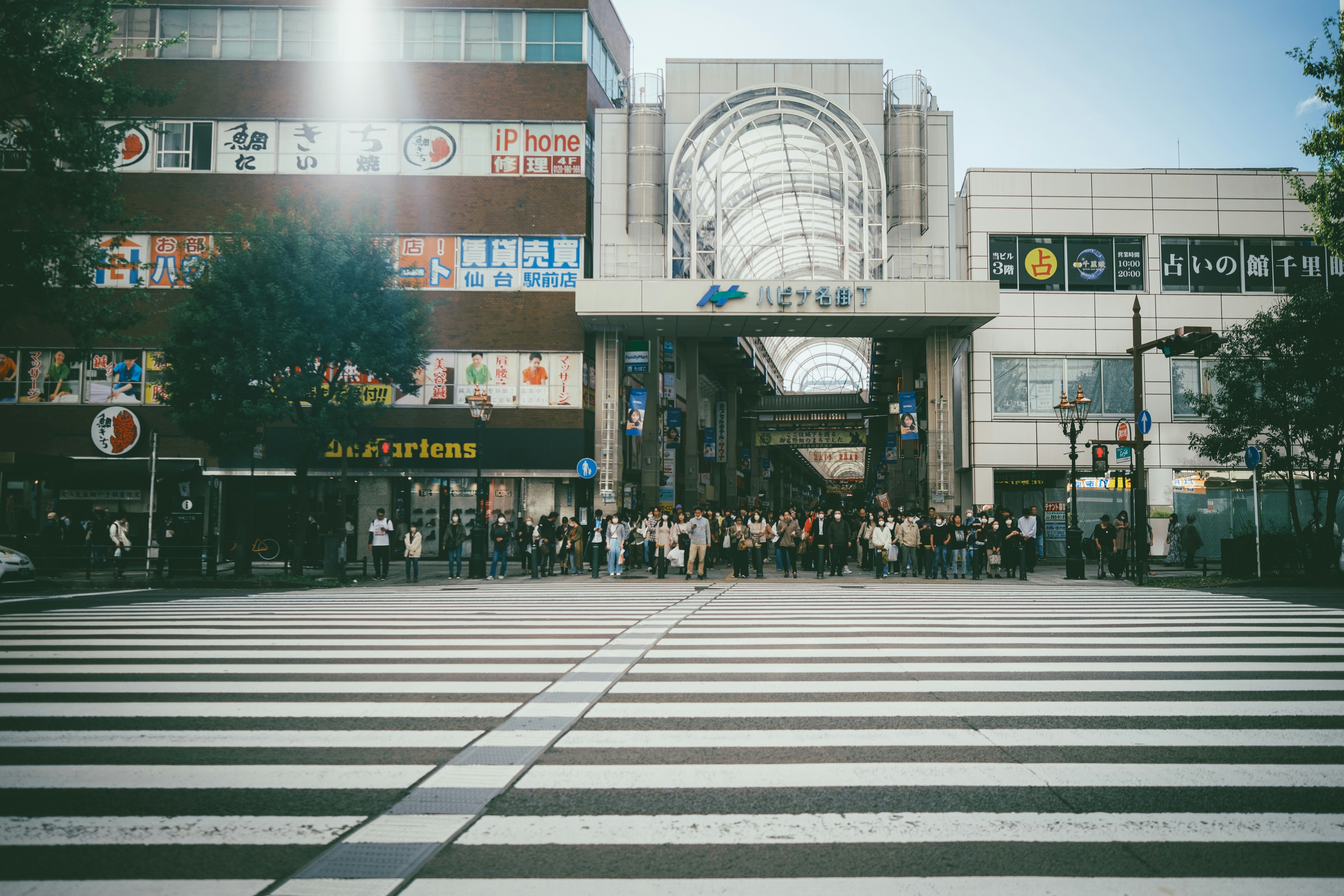
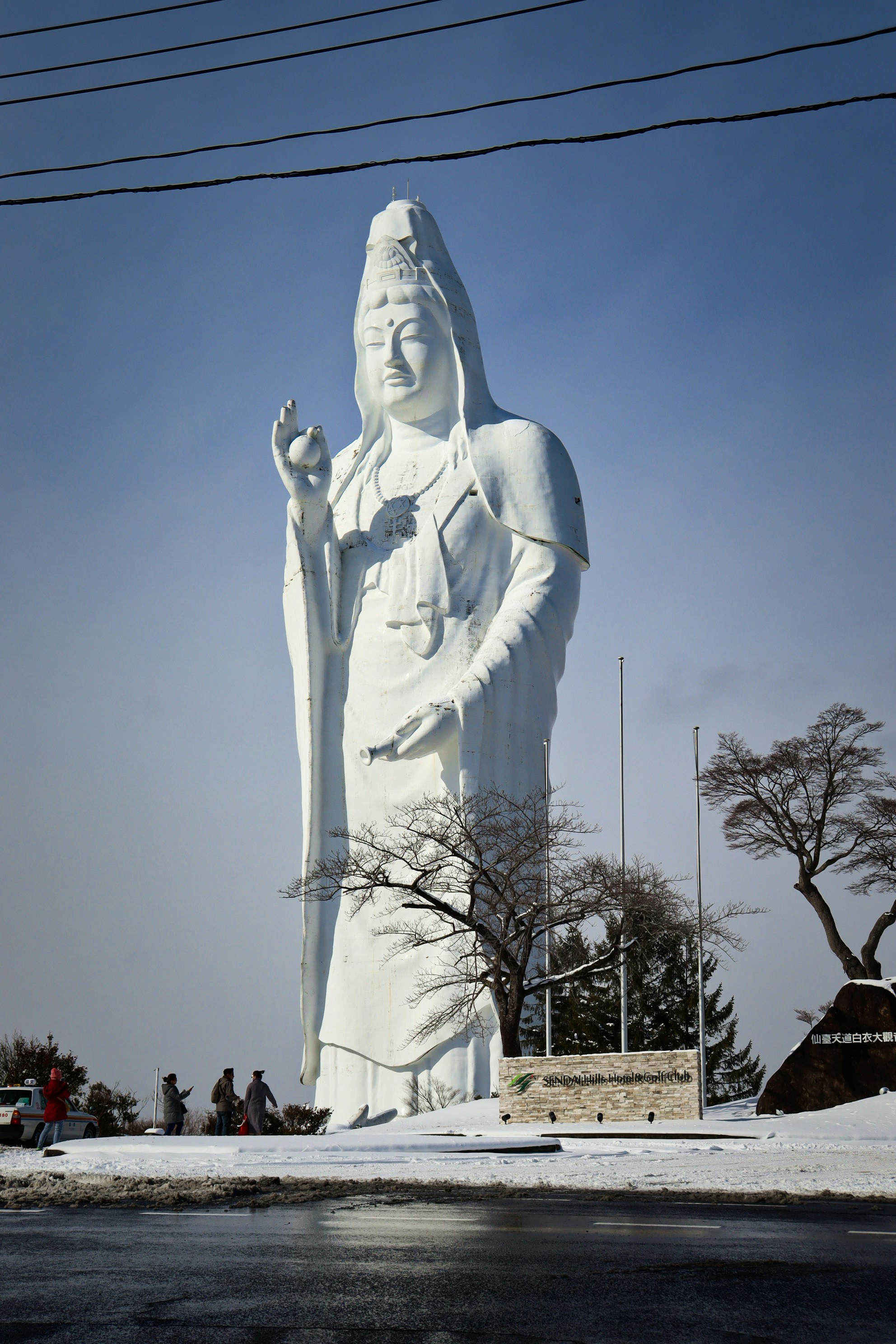










About Miyako, Iwate

About Muroran

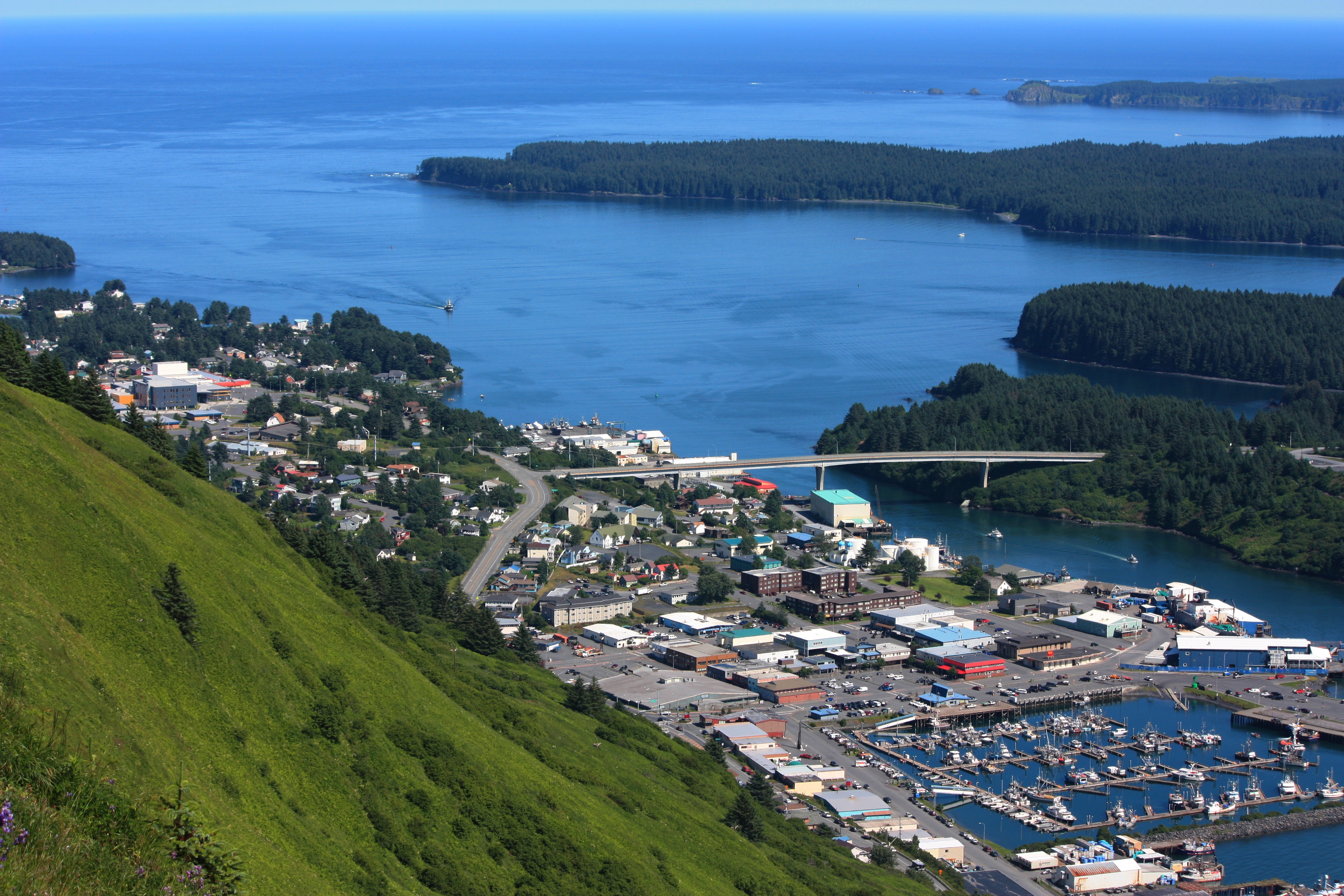
About Kodiak, Alaska
Today, commercial fishing is king in Kodiak. Despite its small population—about 6,475 people scattered among the several islands in the Kodiak group—the city is among the busiest fishing ports in the United States. The harbor is also an important supply point for small communities on the Aleutian Islands and the Alaska Peninsula.Visitors to the island tend to follow one of two agendas: either immediately fly out to a remote lodge for fishing, kayaking, or bear viewing; or stay in town and access whatever pursuits they can reach from the limited road system. If the former is too pricey an option, consider combining the two: drive the road system to see what can be seen inexpensively, then add a fly-out or charter-boat excursion to a remote lodge or wilderness access point.Floatplane and boat charters are available from Kodiak to many remote attractions, chief among them the Kodiak National Wildlife Refuge , which covers four islands in the Gulf of Alaska: Kodiak, Afognak, Ban, and Uganik.

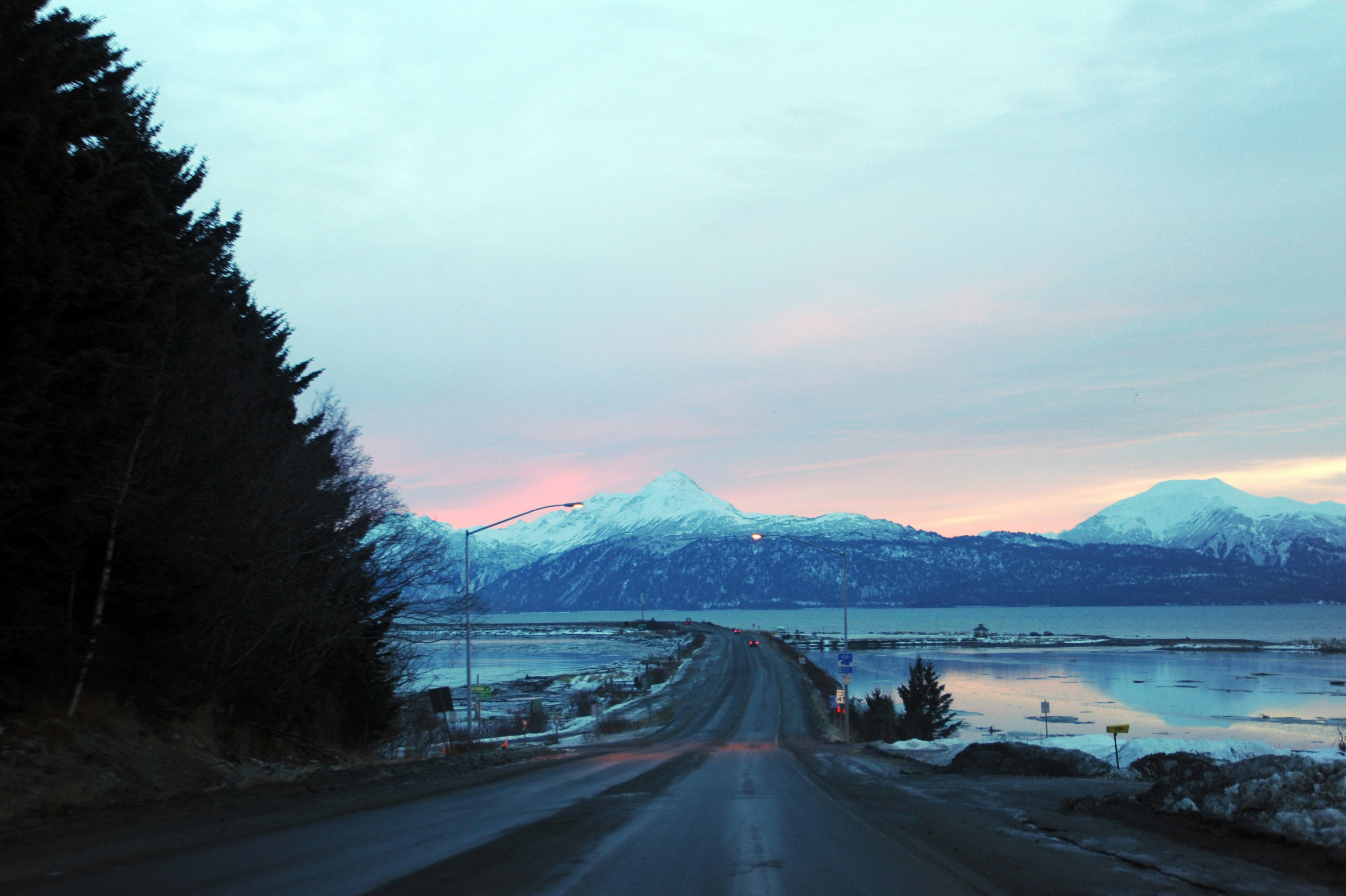
About Homer, Alaska
At the southern end of the Sterling Highway lies the city of Homer, at the base of a narrow spit that juts 4 miles into beautiful Kachemak Bay. Glaciers and snowcapped mountains form a dramatic backdrop across the water. Founded in the late 1800s as a gold-prospecting camp, this community was later used as coal-mining headquarters. Chunks of coal are still common along local beaches; they wash into the bay from nearby slopes where the coal seams are exposed. Today the town of Homer is an eclectic community with most of the tacky tourist paraphernalia relegated to the Spit (though do note the Spit has plenty else to recommend it, not the least of which is the 360-degree view of the surrounding mountains); the rest of the town is full of local merchants and artisans. The community is an interesting mix of fishermen, actors, artists, and writers. Much of the commercial fishing centers on halibut, and the popular Homer Jackpot Halibut Derby is often won by enormous fish weighing more than 300 pounds. The local architecture includes everything from dwellings that are little more than assemblages of driftwood to steel commercial buildings and magnificent homes on the hillside overlooking the surrounding bay, mountains, forests, and glaciers.
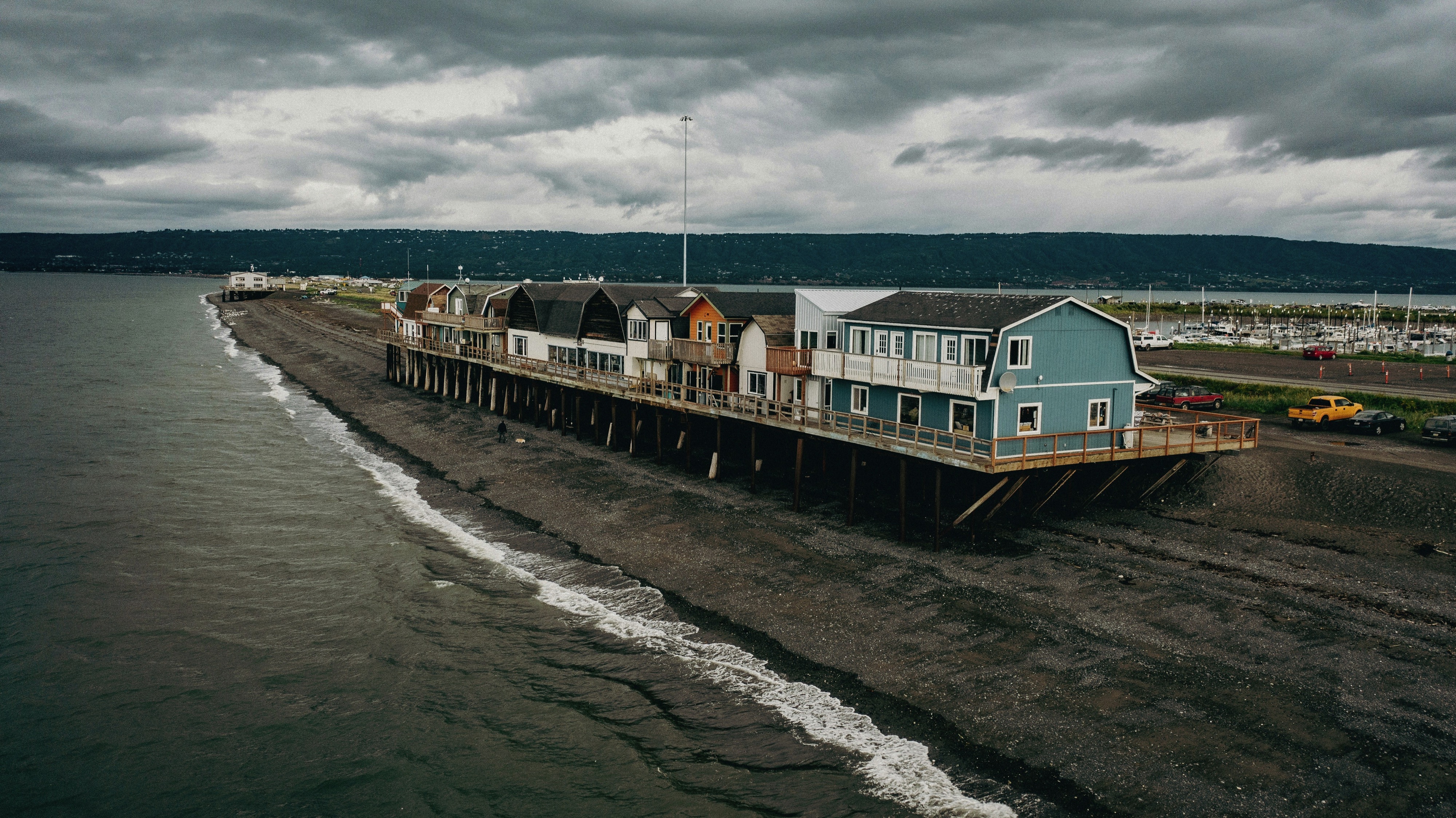
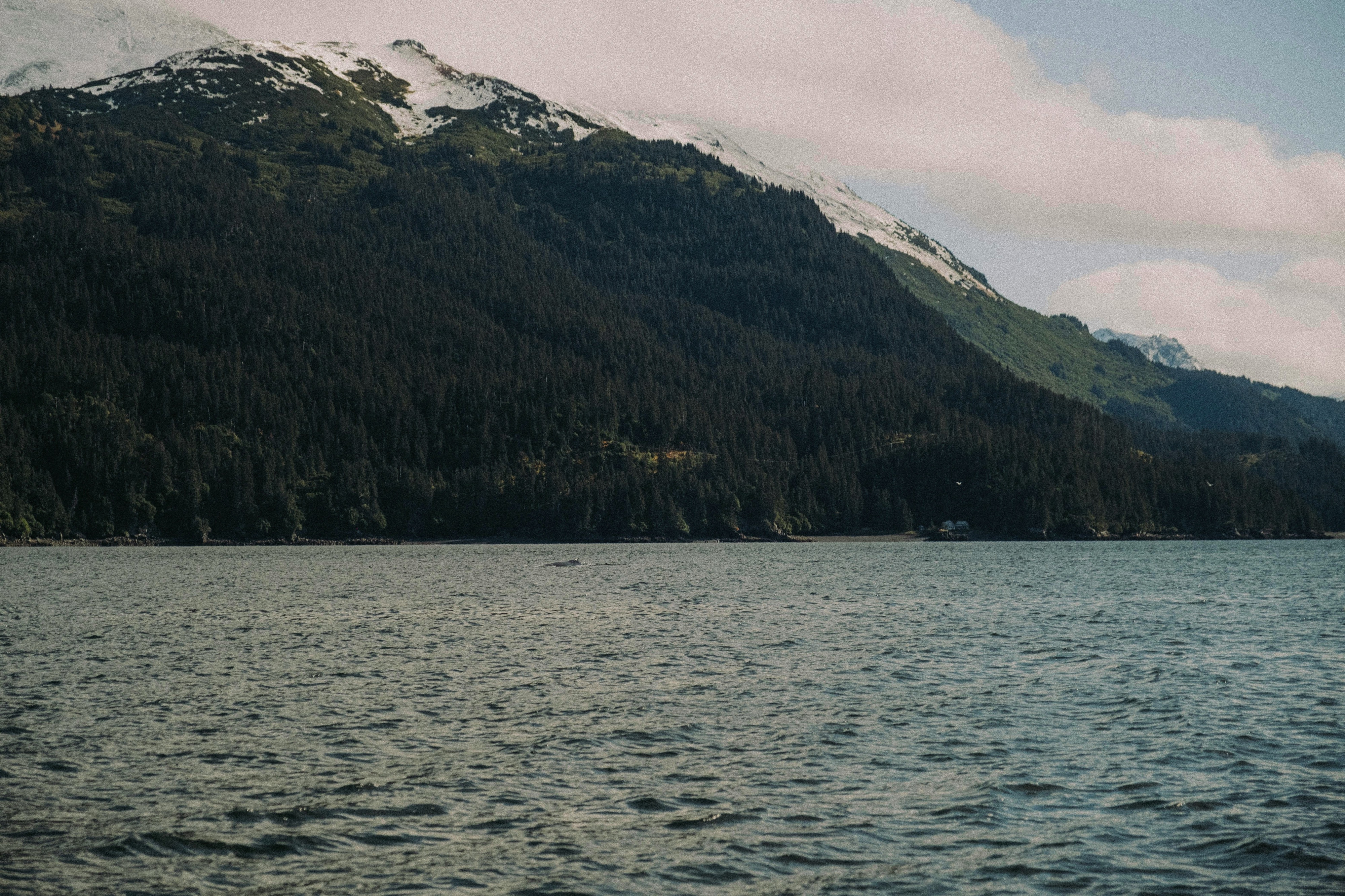



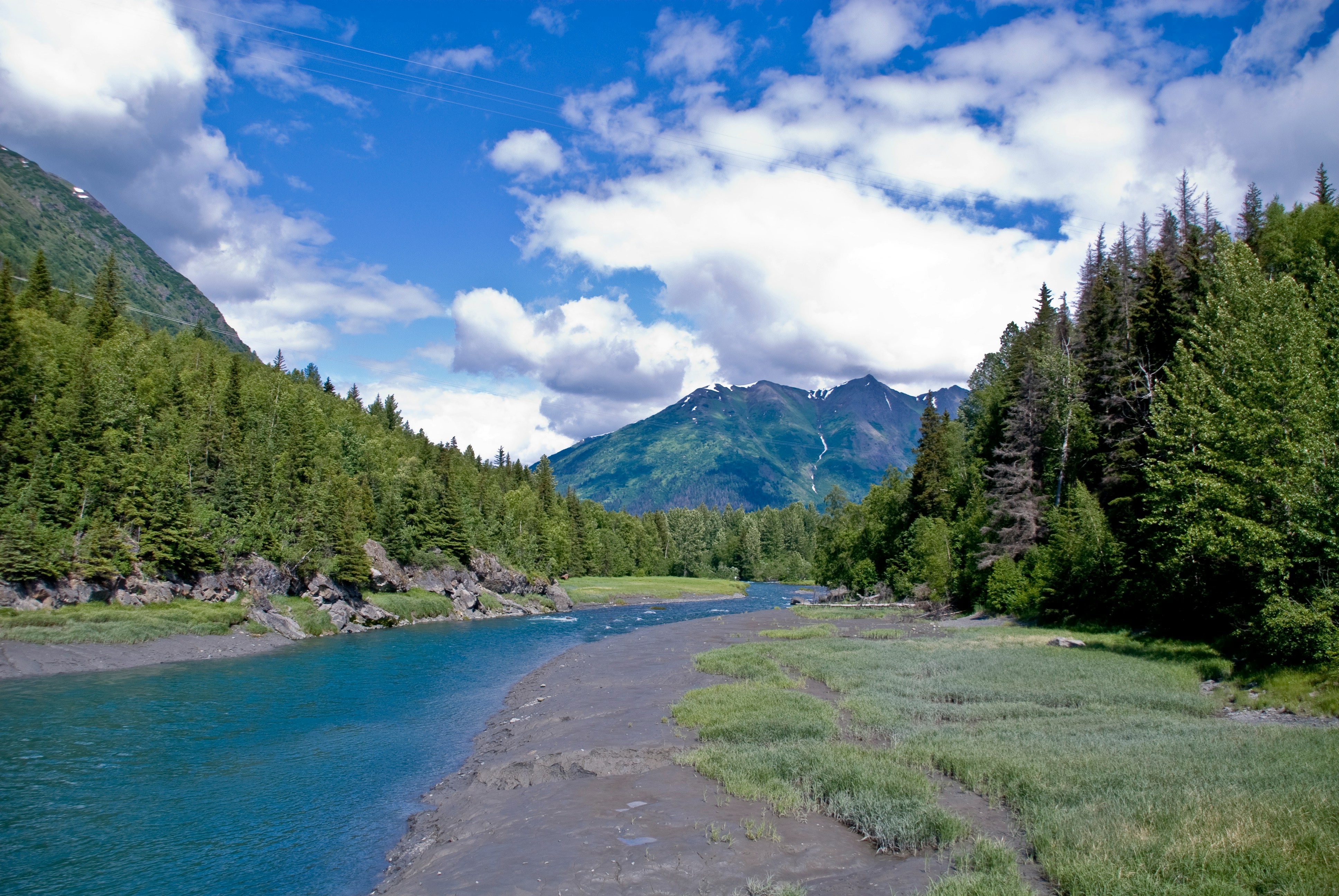
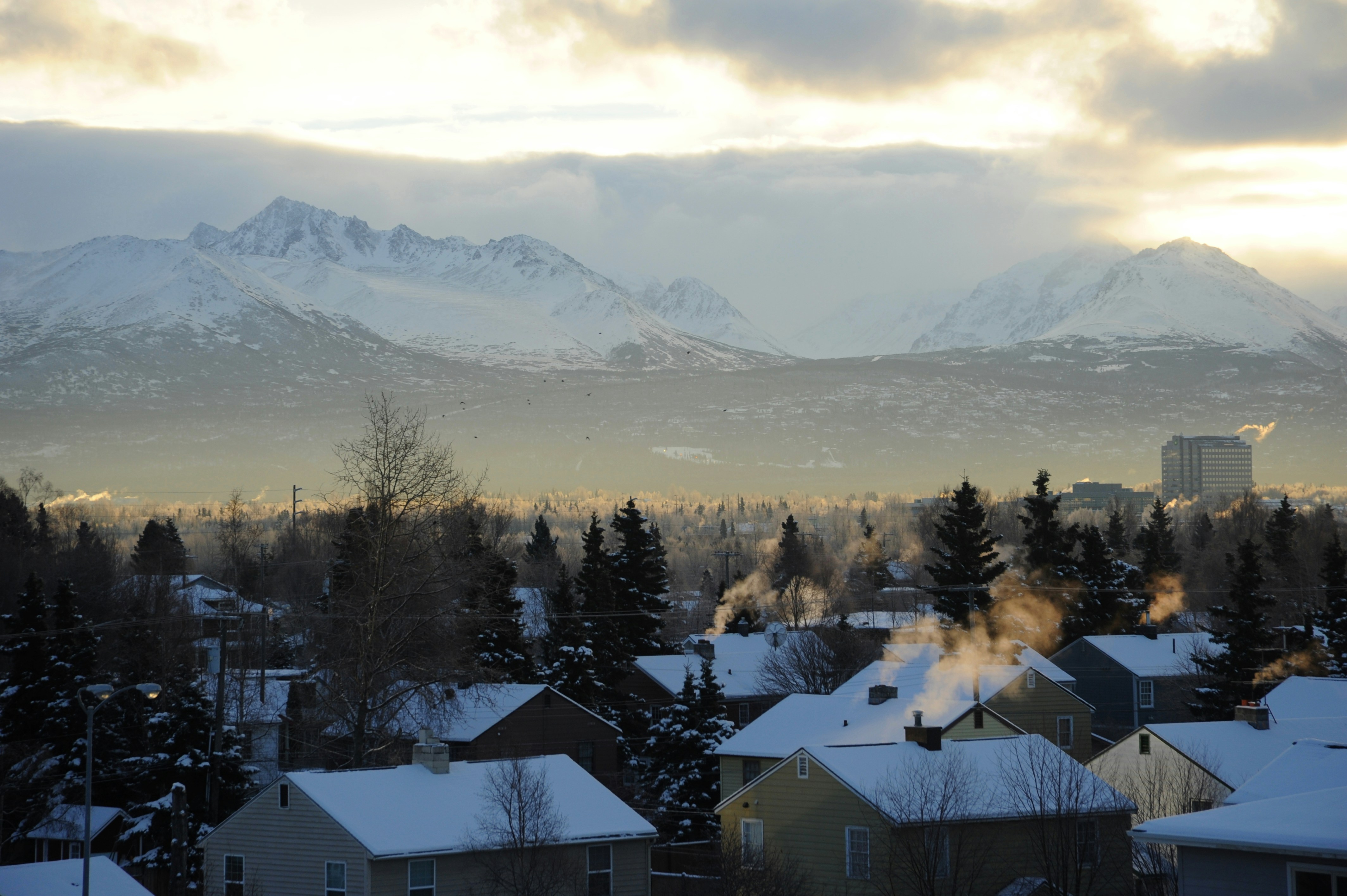
About Anchorage, Alaska
Anchorage is the largest city in Alaska. Located between mountains, it is a beautiful mixture of urban and wilderness. Thanks to its proximity to the Chugach State Park with its 45 species of mammals and the city's rich history, there is so much to be seen in this unique destination.
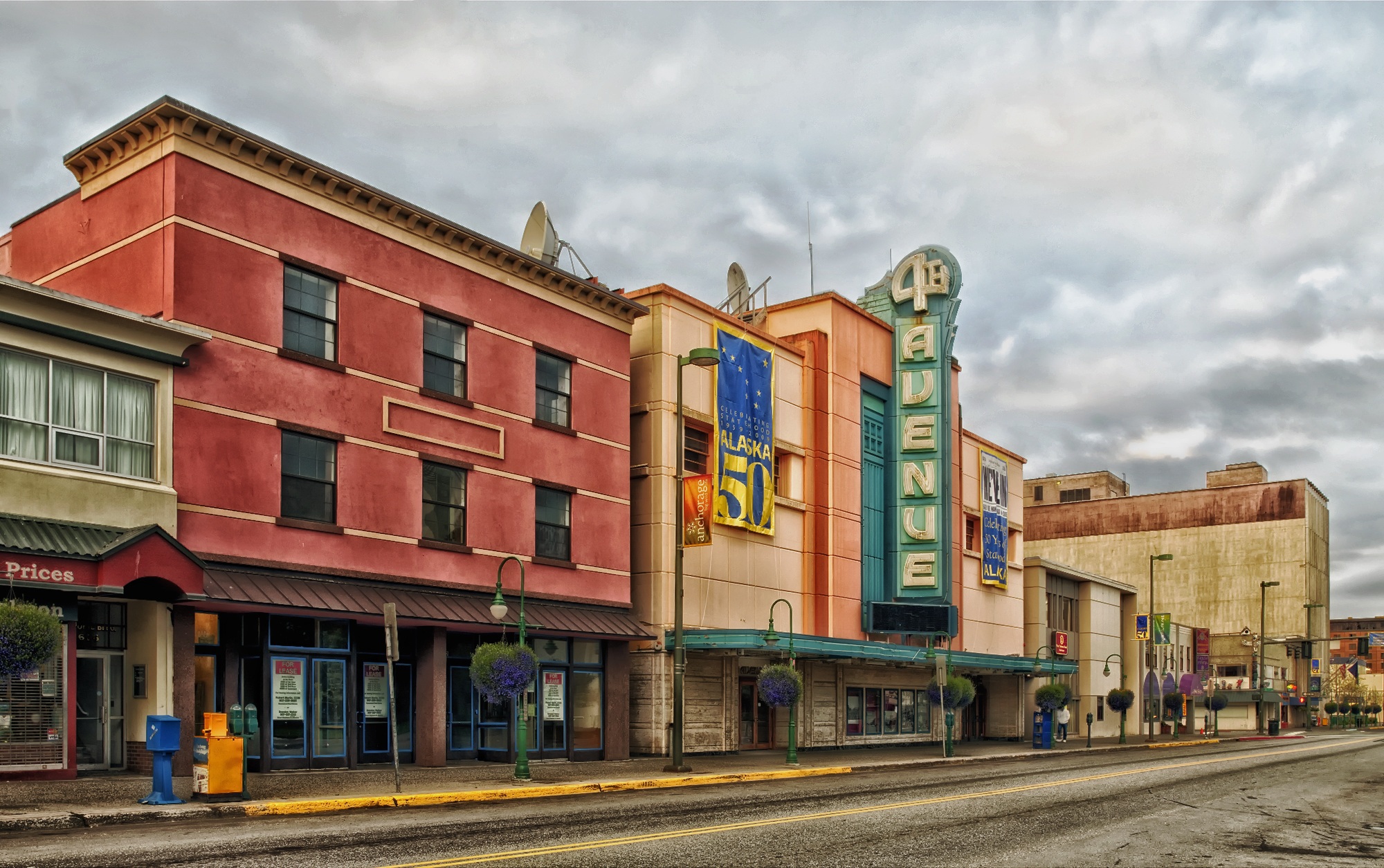
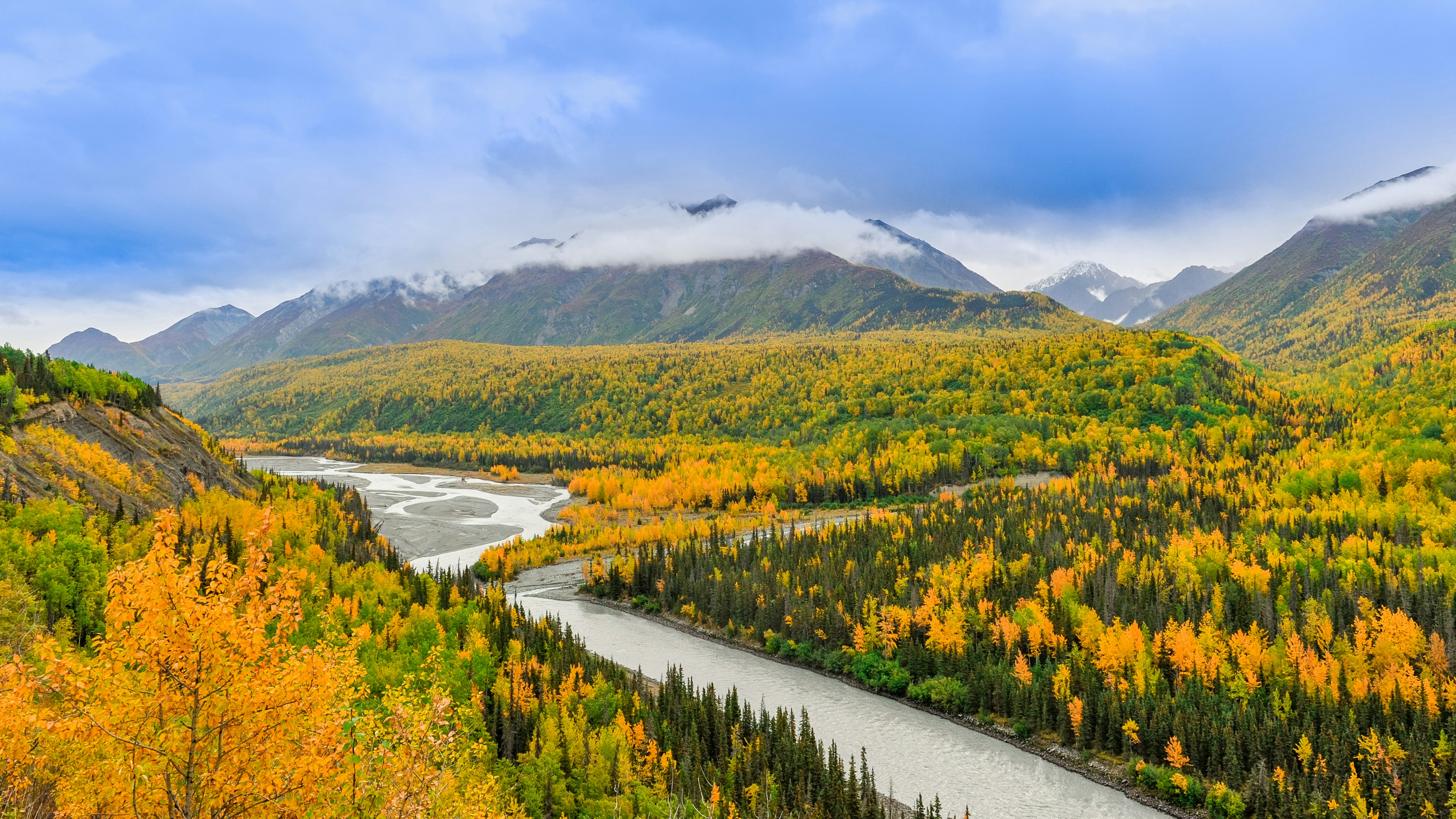
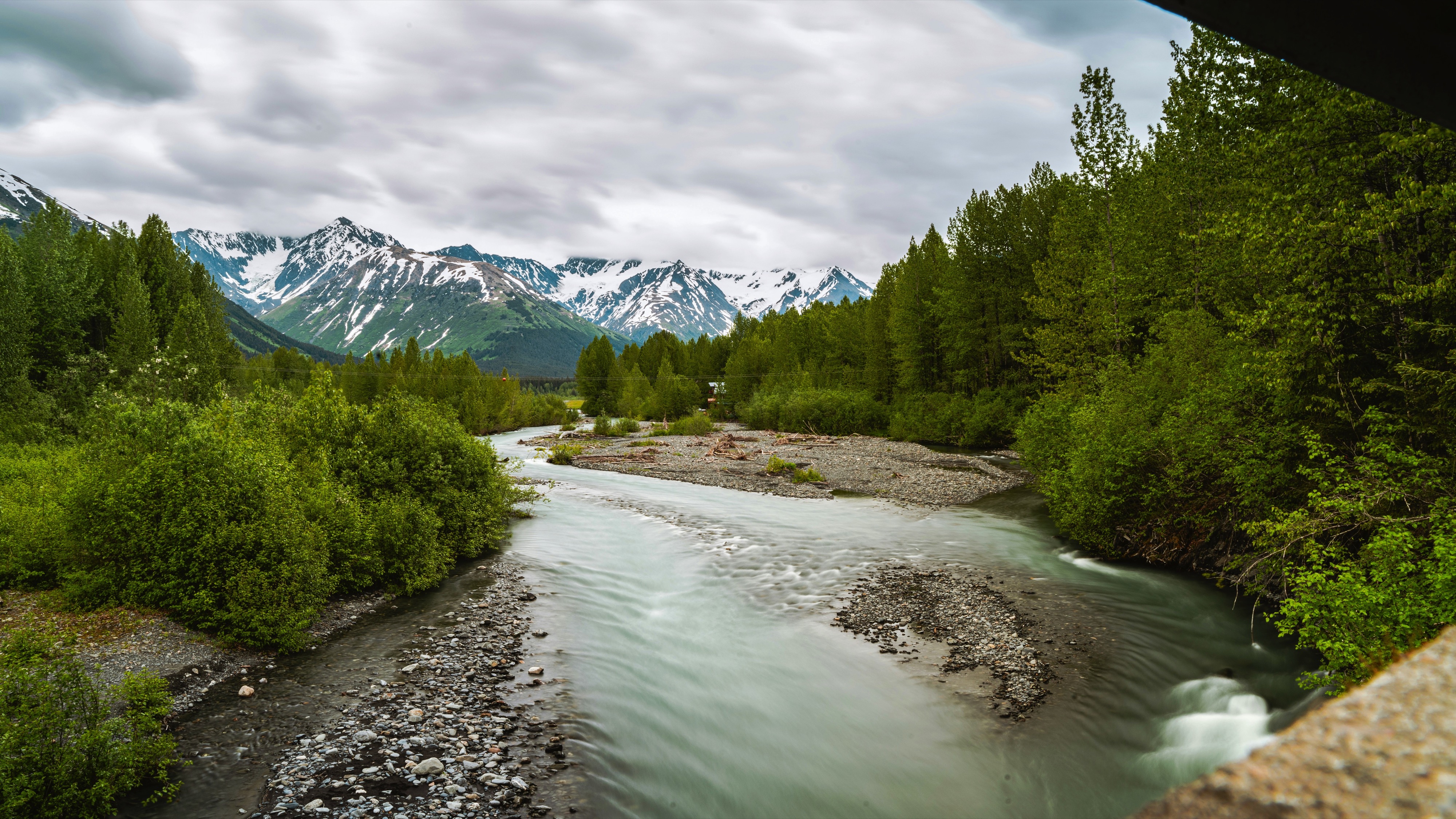
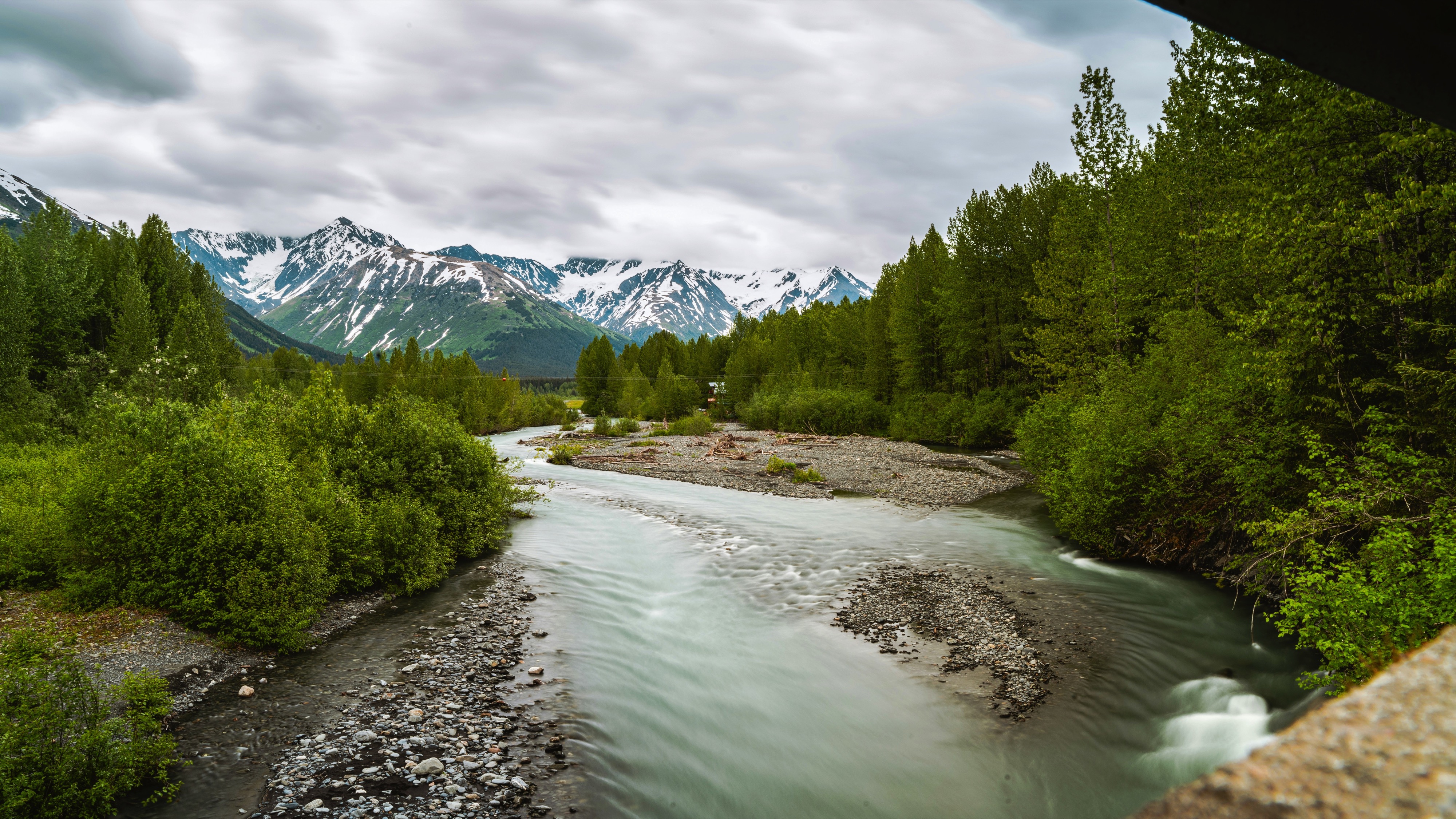






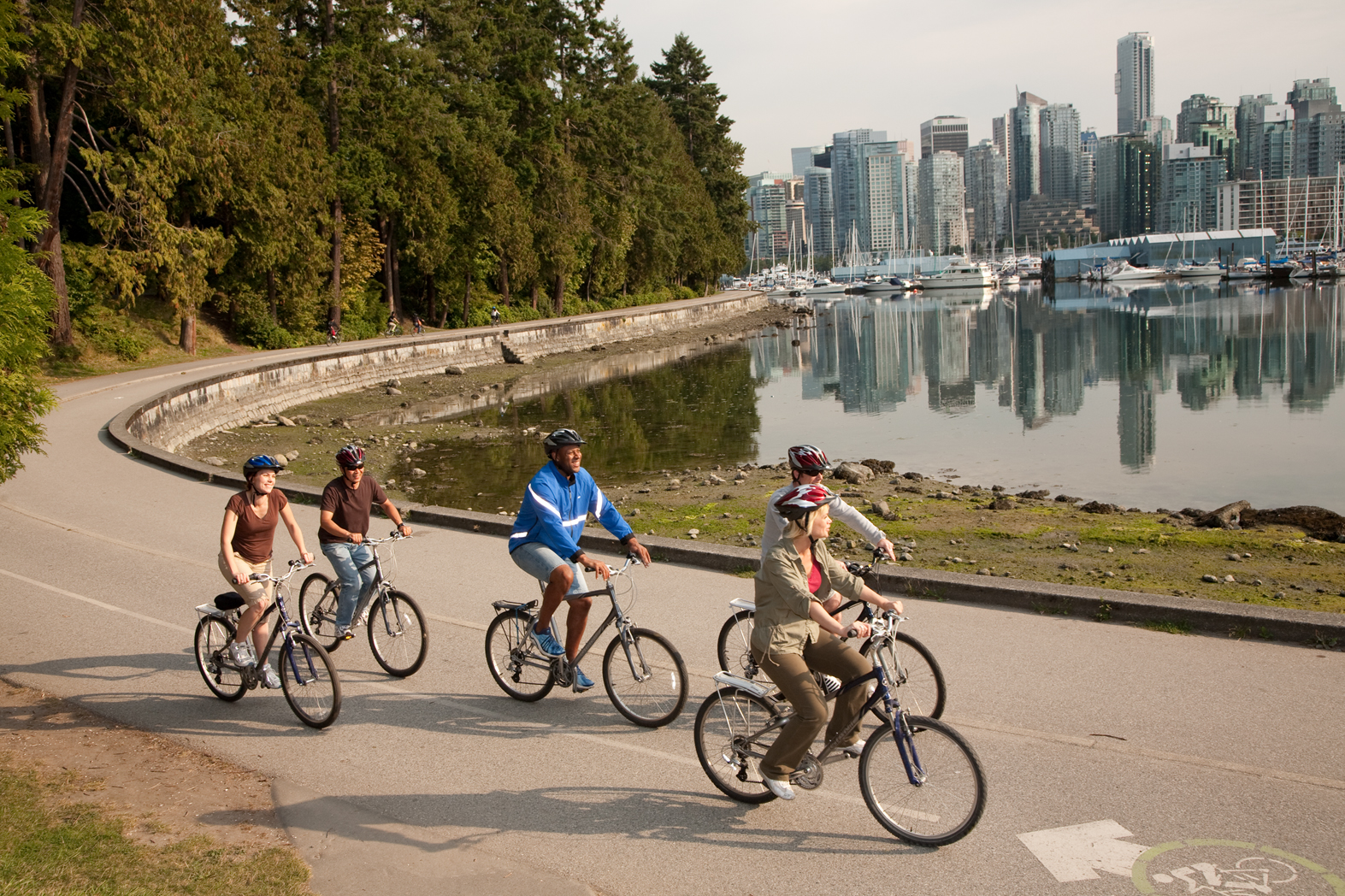
About Vancouver, British Columbia
Vancouver is a delicious juxtaposition of urban sophistication and on-your-doorstep wilderness adventure. The mountains and seascape make the city an outdoor playground for hiking, skiing, kayaking, cycling, and sailing—and so much more—while the cuisine and arts scenes are equally diverse, reflecting the makeup of Vancouver's ethnic (predominantly Asian) mosaic. Vancouver is consistently ranked as one of the world's most livable cities, and it's easy for visitors to see why. It's beautiful, it's outdoorsy, and there's a laidback West Coast vibe. On the one hand, there's easy access to a variety of outdoor activities, a fabulous variety of beaches, and amazing parks. At the same time, the city has a multicultural vitality and cosmopolitan flair. The attraction is as much in the range of food choices—the fresh seafood and local produce are some of North America's best—as it is in the museums, shopping, and nightlife.Vancouver's landscaping also adds to the city's walking appeal. In spring, flowerbeds spill over with tulips and daffodils while sea breezes scatter scented cherry blossoms throughout Downtown; in summer office workers take to the beaches, parks, and urban courtyards for picnic lunches and laptop meetings. More than 8 million visitors each year come to Vancouver, Canada's third-largest metropolitan area. Because of its peninsula location, traffic flow is a contentious issue. Thankfully, Vancouver is wonderfully walkable, especially in the downtown core. The North Shore is a scoot across the harbor, and the rapid-transit system to Richmond and the airport means that staying in the more affordable ’burbs doesn't have to be synonymous with sacrificing convenience. The mild climate, exquisite natural scenery, and relaxed outdoor lifestyle keep attracting residents, and the number of visitors is increasing for the same reasons. People often get their first glimpse of Vancouver when catching an Alaskan cruise, and many return at some point to spend more time here.
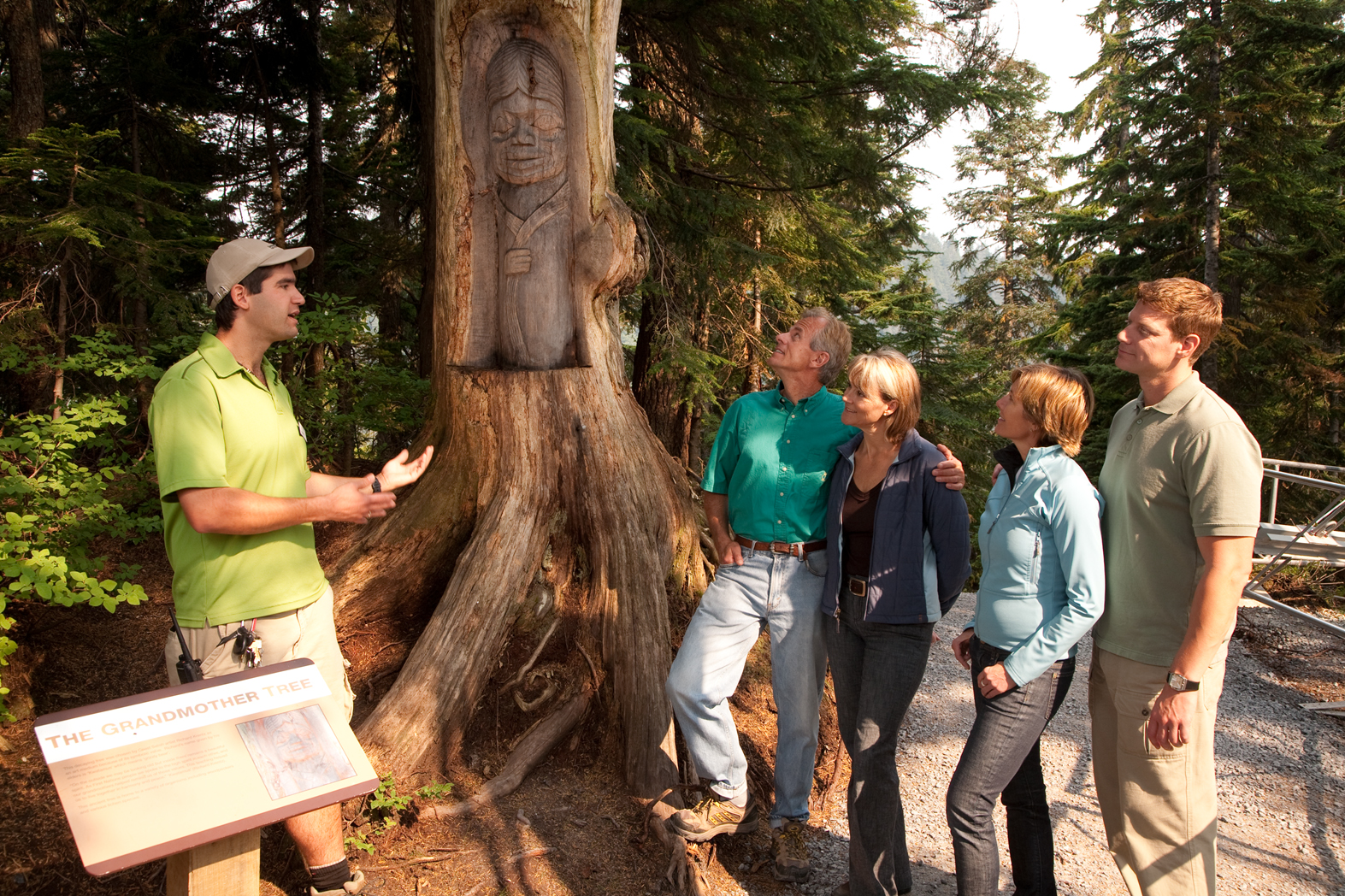



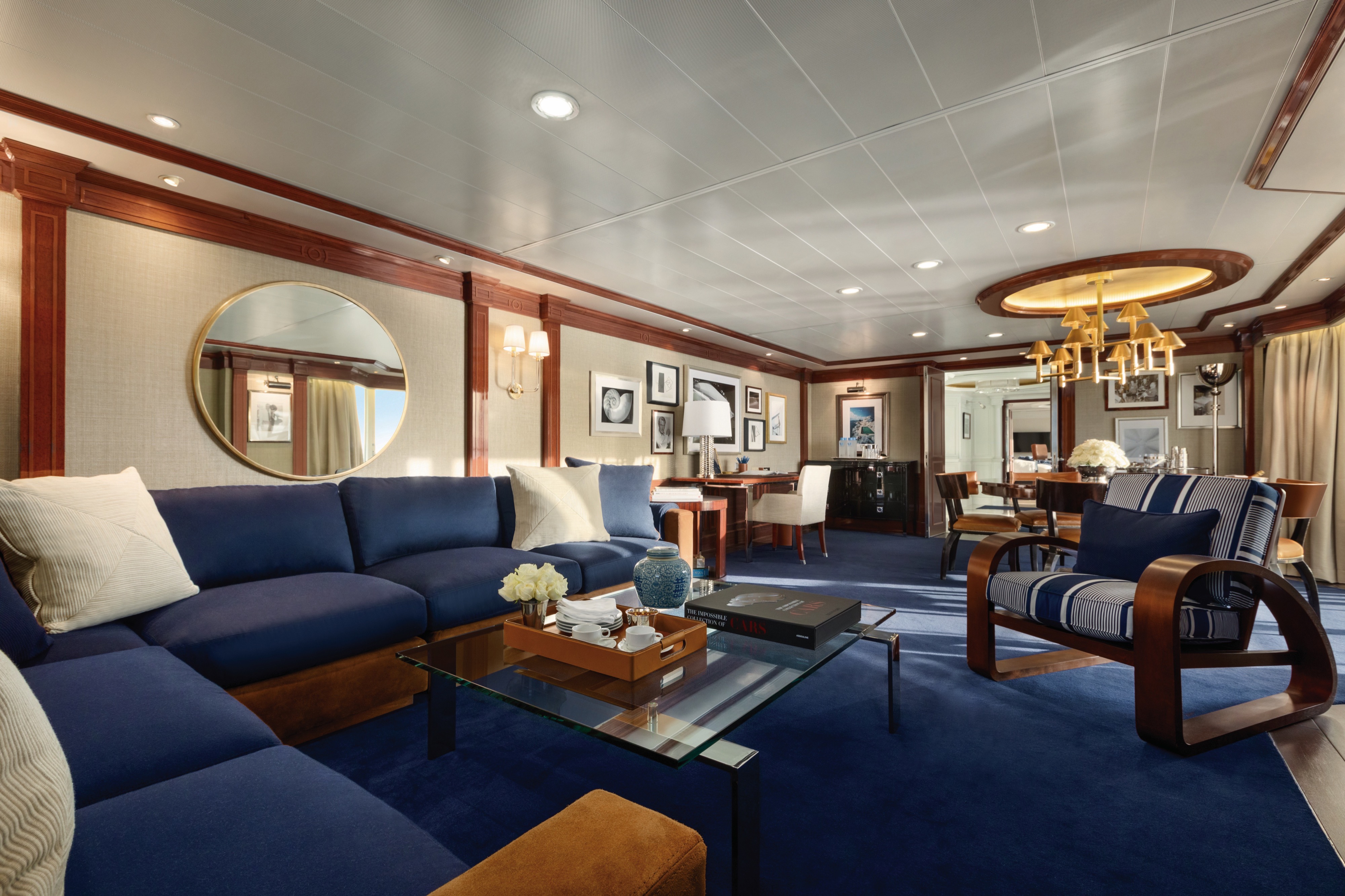
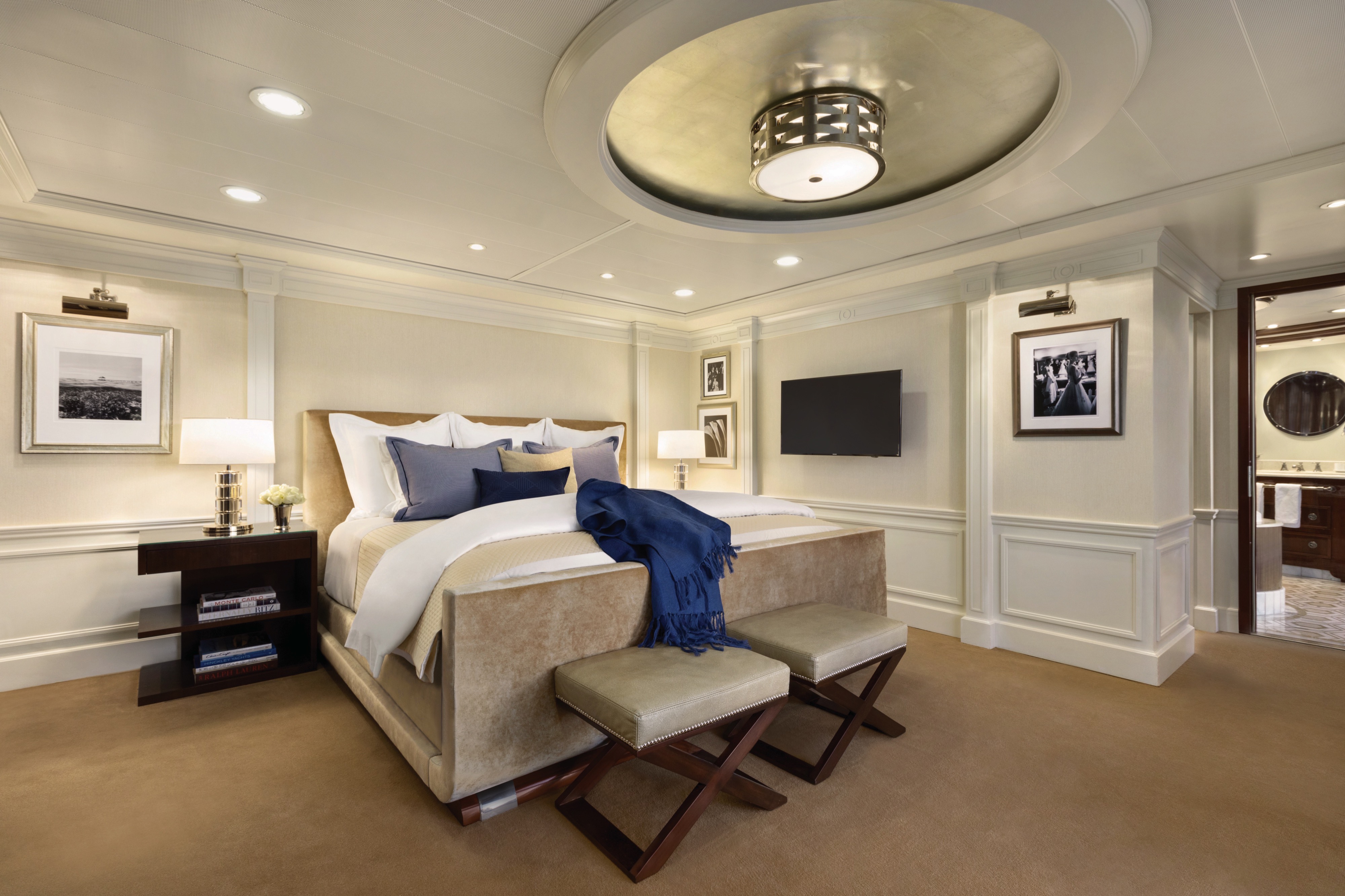
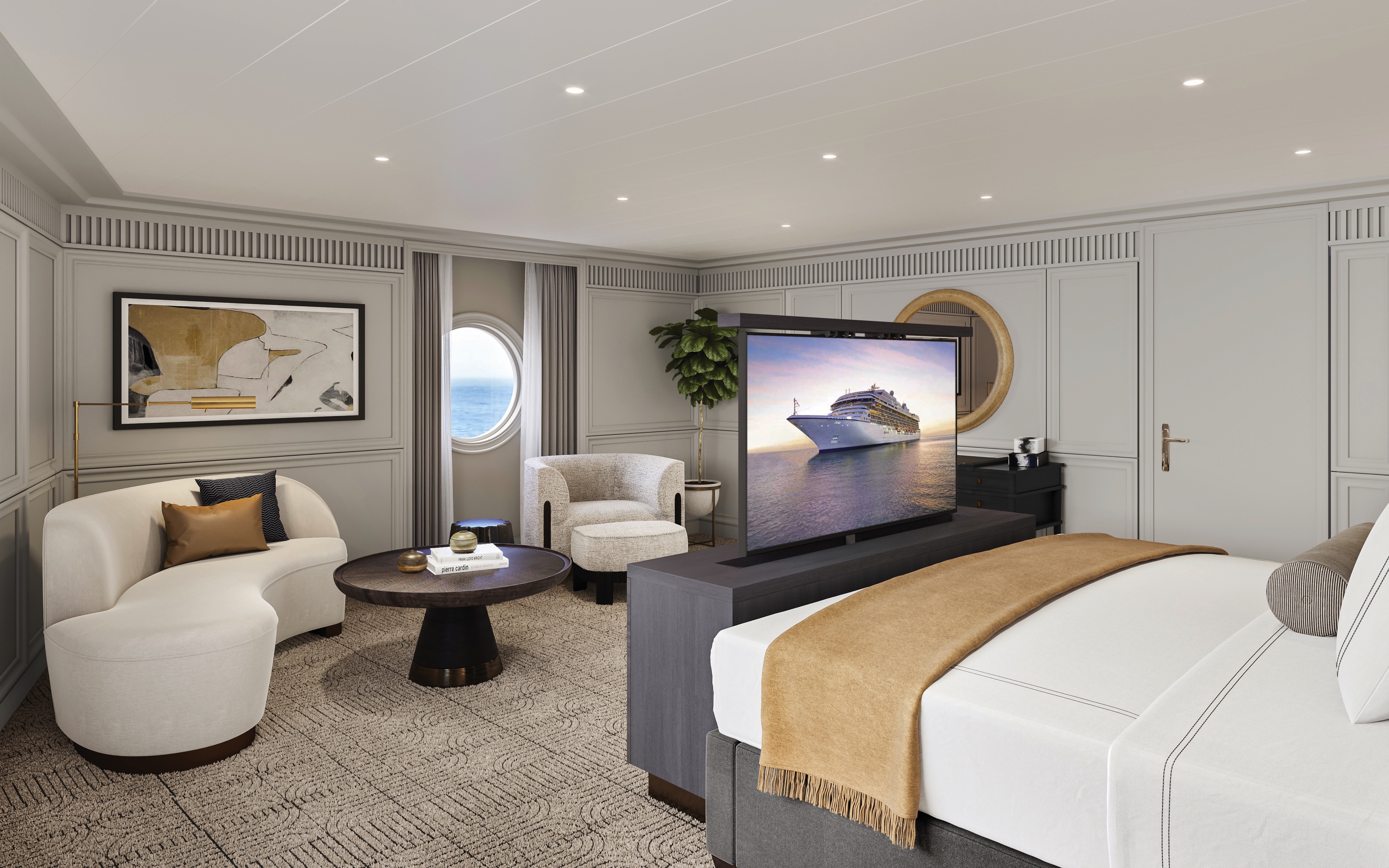
Akin to a dramatic coastal villa, the Owner’s Suites exude a sophisticated and luxurious personality. At more than 2,000 square feet, each features a living room, dining room, master bedroom and two bathrooms. These suites are adorned with designer furnishings and exquisite appointments, creating a blissful enclave at sea. There are separate terraces for the living areas and bedroom and expanses of floor-to-ceiling windows provide captivating vistas and with the stunning backdrop of the sea all around. All of our suites include exclusive 24-hour Butler service and are uncommonly spacious, further adding to the unparalleled suite experience.
Owner's Suite Privileges
In addition to Stateroom Amenities
- Priority luggage delivery
- Exclusive card-only access to private Executive Lounge staffed by a dedicated Concierge featuring complimentary sodas, coffees and snacks throughout the day
- 24-hour Butler service
- Optional private in-suite embarkation day lunch from noon to 2 pm in Owner’s Suites
- Complimentary in-suite bar setup with 6 full-size bottles of your choice of premium spirits and wines from our suite beverage menu
- Complimentary welcome bottle of Champagne
- In-suite illy® coffee maker and pods
- Fresh fruit basket upon request
- Choice of daily newspaper
- Exclusive pillow menu
- Course-by-course in-suite dining*
- Order in from any of our specialty restaurants*
- Coordination of shoreside dinner and entertainment reservations
- Last-minute luggage collection
- Packing and unpacking upon request
- Complimentary garment pressing*
- Complimentary shoeshine service
- Gourmet evening canapés upon request
- Special services upon request
+Up to 20 garments per laundry bag; additional restrictions apply.++Certain limitations apply.Smoking in suites, staterooms and on verandas is strictly prohibited.
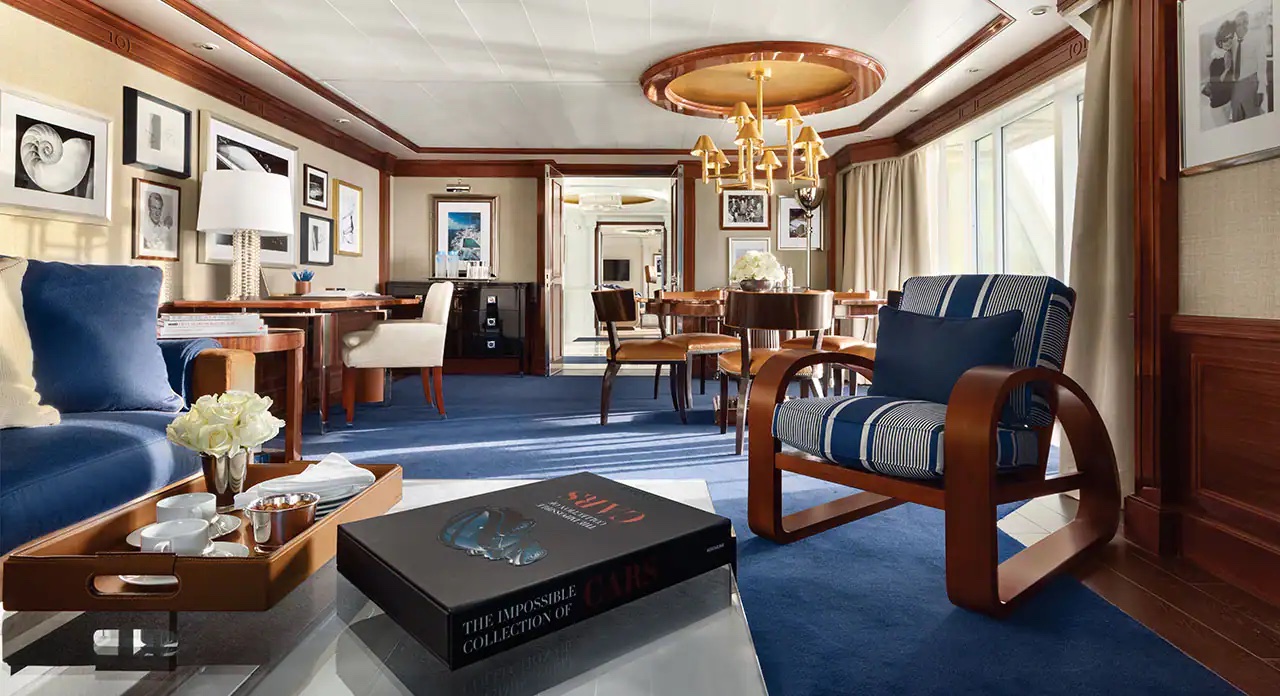
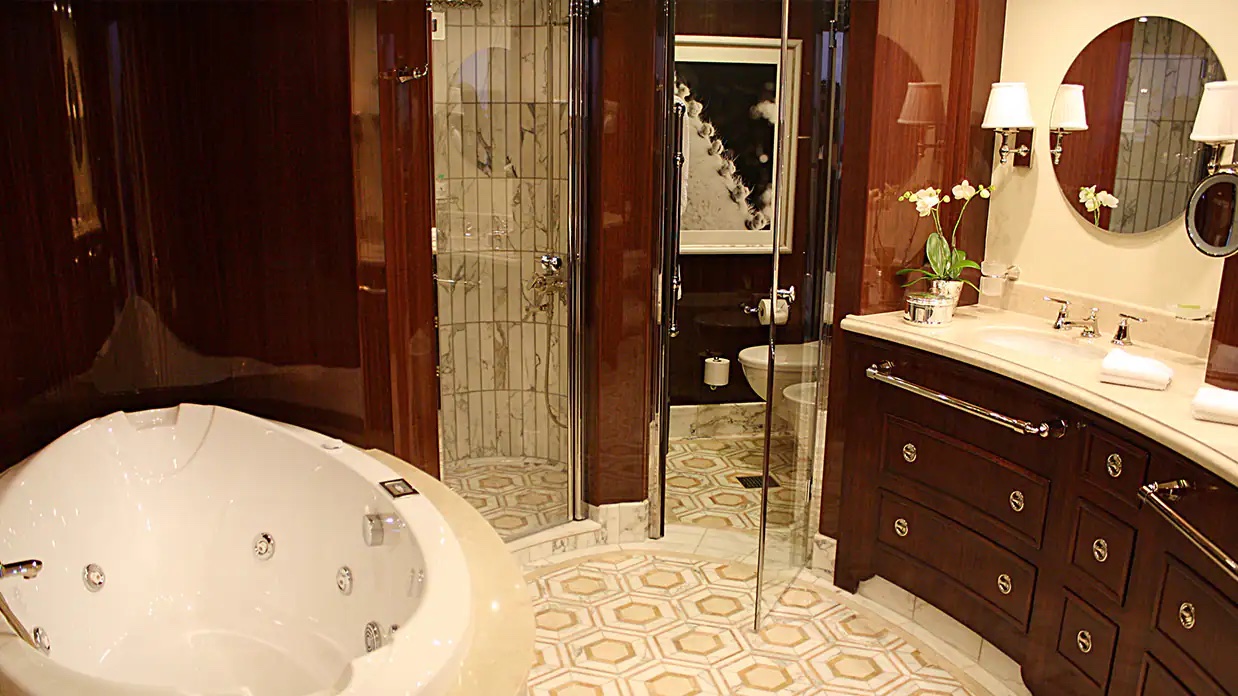










Given their lavish interior design that resembles an elegant and luxurious Park Avenue home along with their premier location overlooking the bow of the ship, the eight Vista Suites are in high demand. These 1,200- to 1,500-square-foot suites include access to the exclusive Executive Lounge as well as every imaginable amenity, such as a large walk-in closet, king-size bed, second bathroom for guests, whirlpool spa and your own private fitness room.
Vista Suite Privileges
+In addition to Concierge Level privileges
- Priority luggage delivery
- Exclusive card-only access to private Executive Lounge staffed by a dedicated Concierge featuring complimentary sodas, coffees and snacks throughout the day
- 24-hour Butler service
- Complimentary in-suite bar setup with 6 full-size bottles of your choice of premium spirits and wines from our suite beverage menu
- Complimentary welcome bottle of Champagne
- Fresh fruit basket upon request
- Choice of daily newspaper
- Exclusive pillow menu
- Course-by-course in-suite dining*
- Order in from any of our specialty restaurants*
- Coordination of shoreside dinner and entertainment reservations
- Last-minute luggage collection
- Packing and unpacking upon request
- Complimentary garment pressing*
- Complimentary shoeshine service
- Gourmet evening canapés upon request
- Special services upon request
++Certain limitations apply.
Smoking in suites, staterooms and on verandas is strictly prohibited.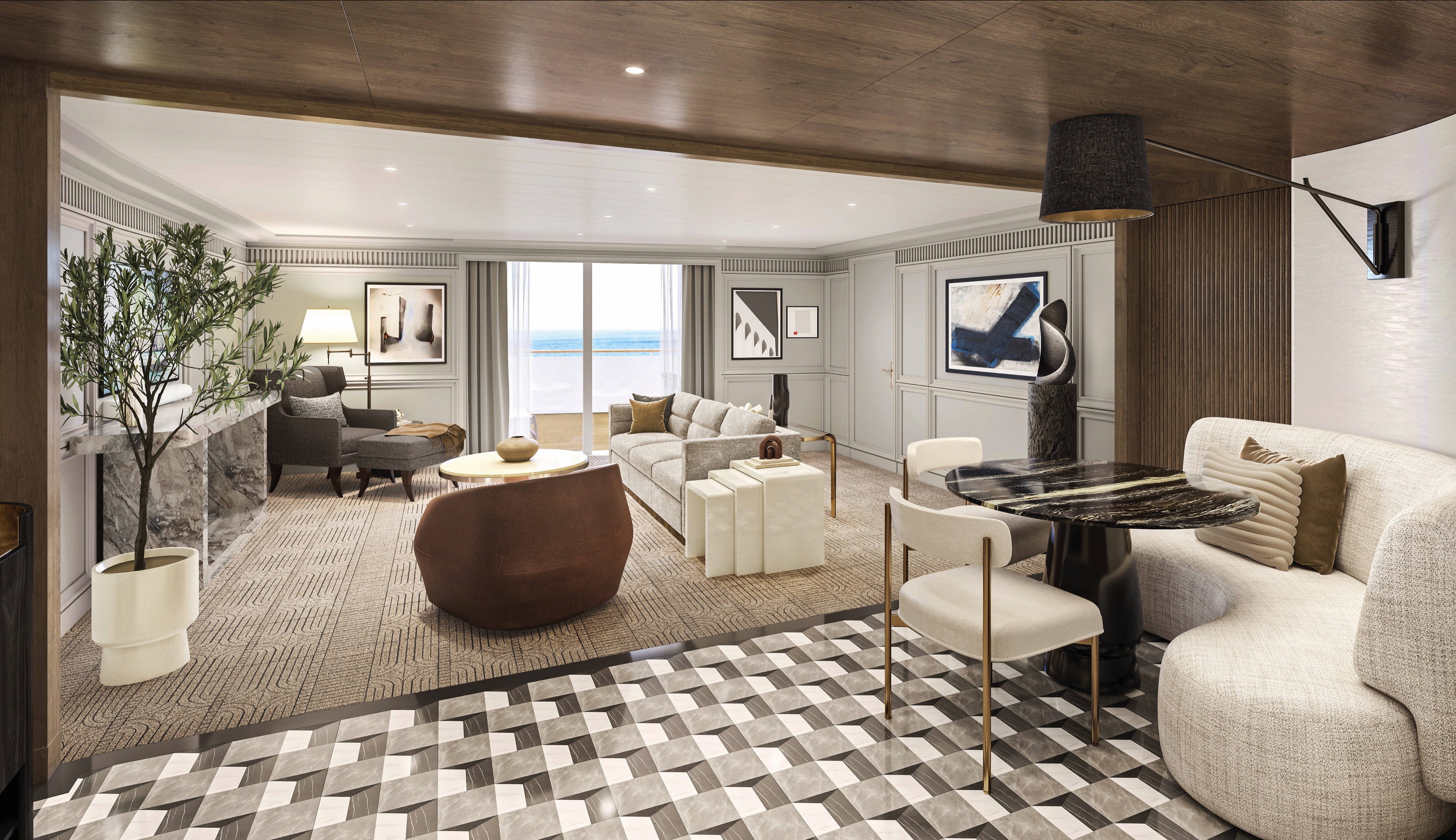
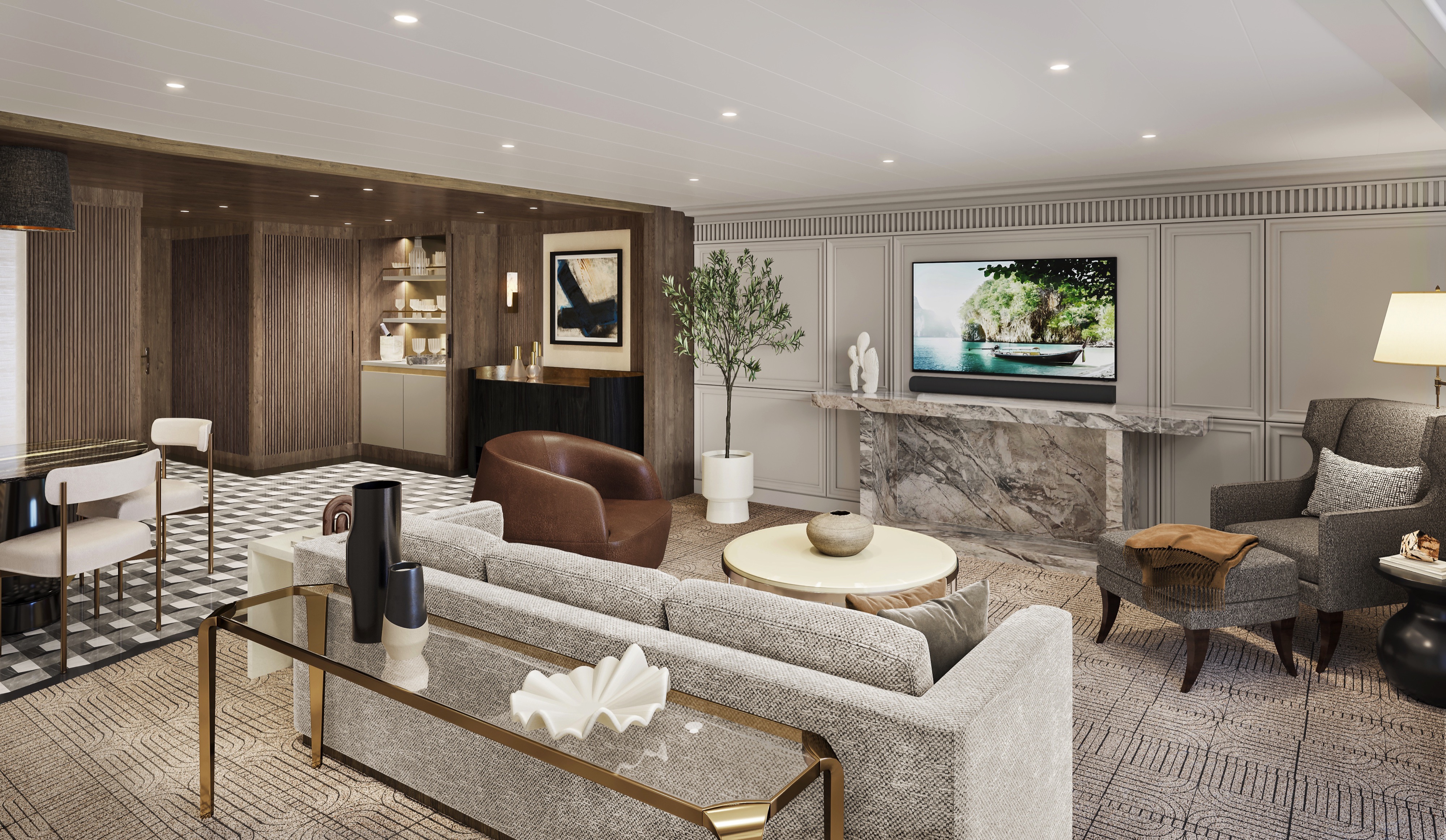
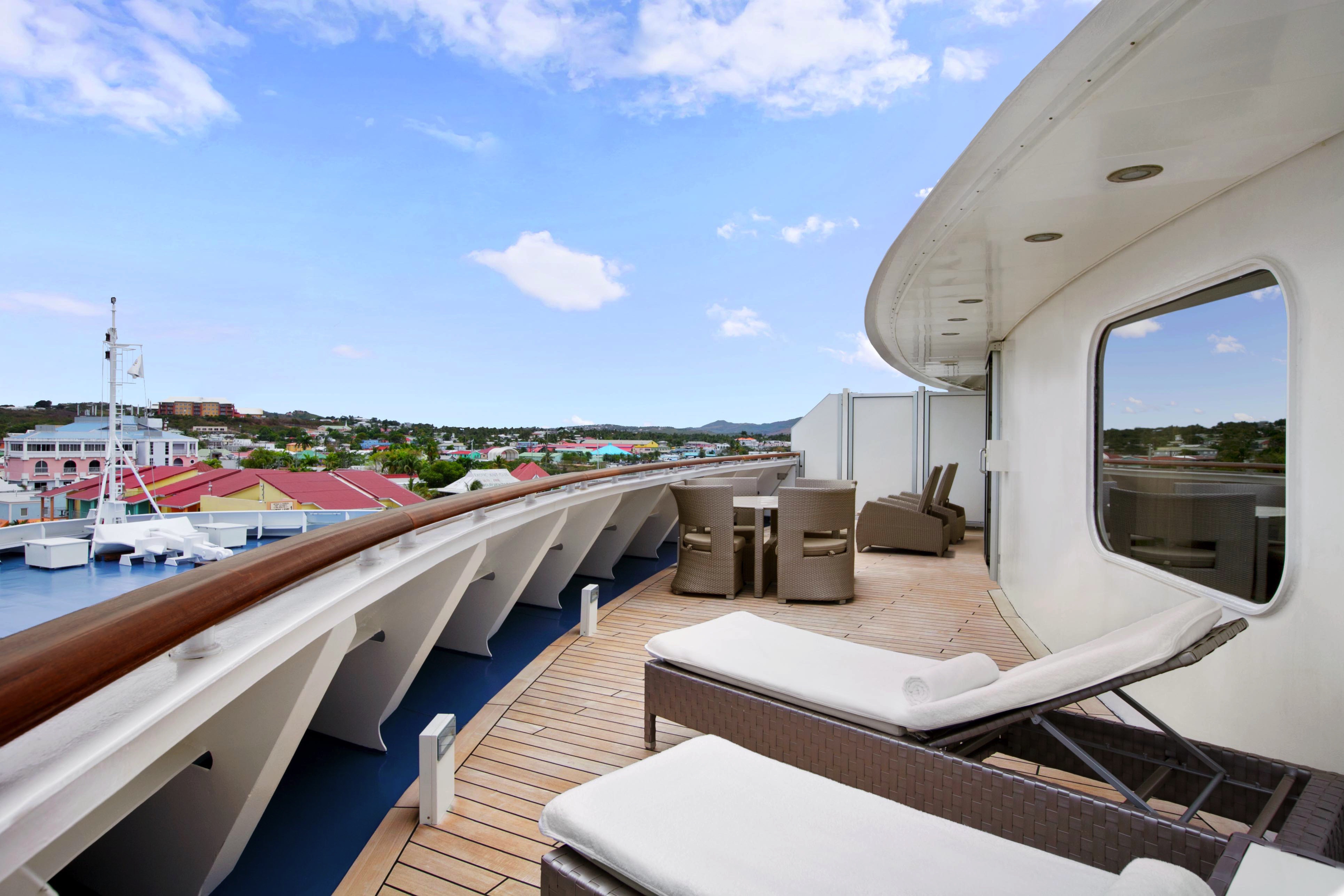









Featuring a luxurious residential design and stylish furnishings, each of the twelve Oceania Suites offers more than 1,000 square feet of luxury. These stylish suites feature a living room, dining room, fully equipped media room, large walk-in closet, king-size bed, indoor whirlpool spa, expansive private veranda and a second bathroom for guests. Also included is access to the private Executive Lounge with magazines, daily newspapers, beverages and snacks.Oceania Suite Privileges
+In addition to Concierge Level privileges
- Priority luggage delivery
- Exclusive card-only access to private Executive Lounge staffed by a dedicated Concierge featuring complimentary sodas, coffees and snacks throughout the day
- 24-hour Butler service
- Complimentary in-suite bar setup with 6 full-size bottles of your choice of premium spirits and wines from our suite beverage menu
- Complimentary welcome bottle of Champagne
- Fresh fruit basket upon request
- Choice of daily newspaper
- Exclusive pillow menu
- Course-by-course in-suite dining*
- Order in from any of our specialty restaurants*
- Coordination of shoreside dinner and entertainment reservations
- Last-minute luggage collection
- Packing and unpacking upon request
- Complimentary garment pressing*
- Complimentary shoeshine service
- Gourmet evening canapés upon request
- Special services upon request
+Up to 20 garments per laundry bag. 3 day turnaround time and laundry will not be accepted 3 days prior to disembarkation.
++Certain limitations apply
Smoking in suites, staterooms and on verandas is strictly prohibited.
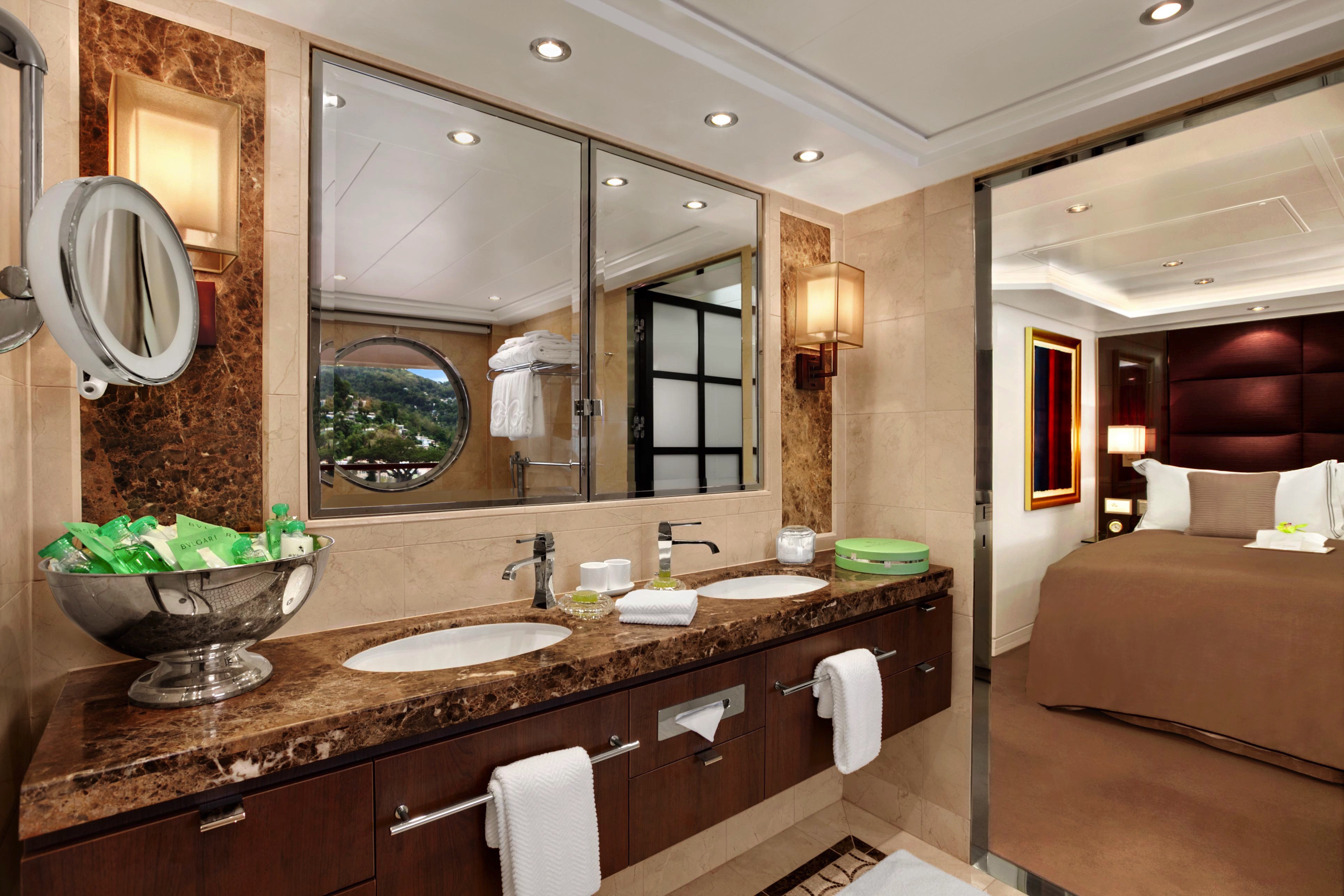
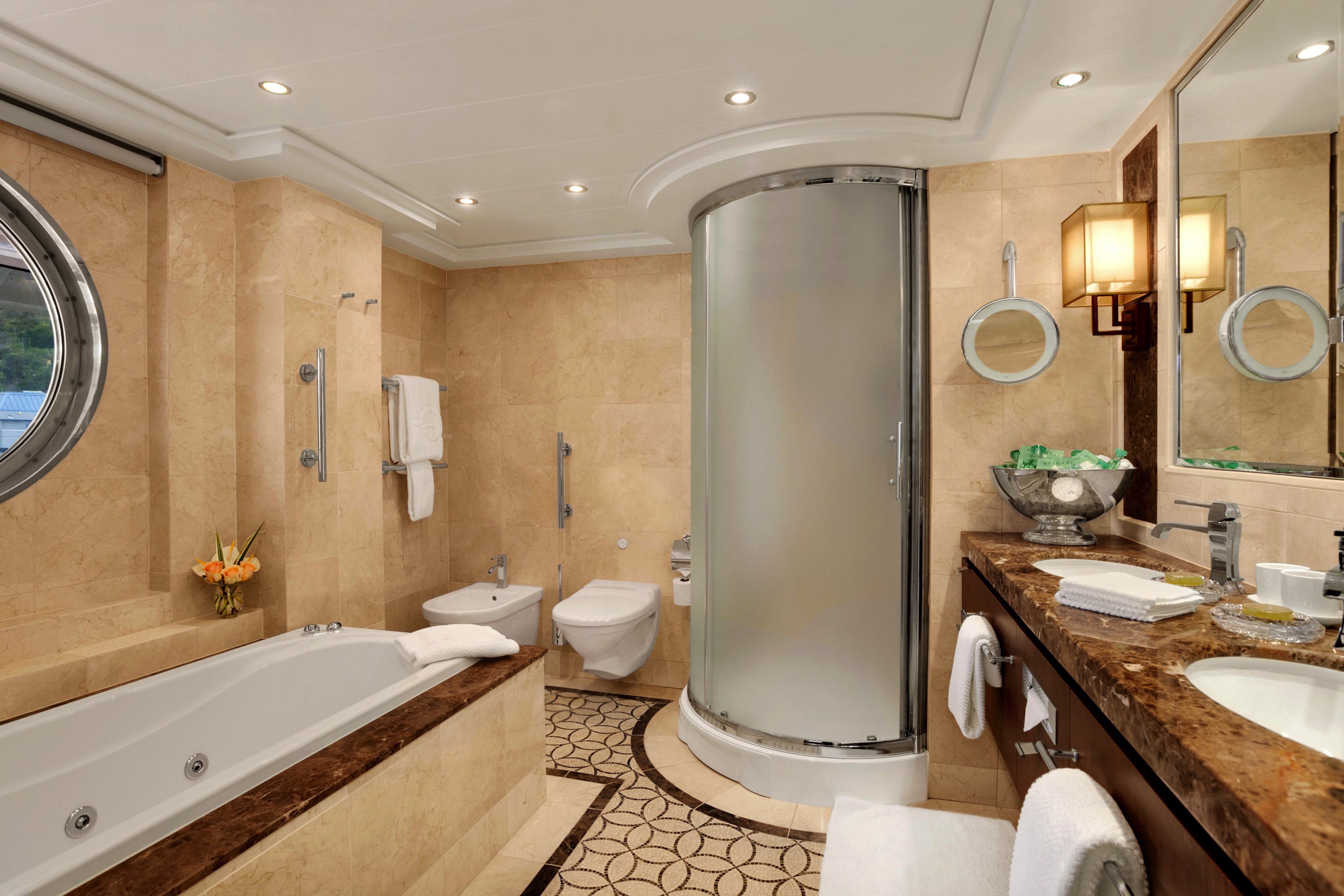





The Penthouse Suites are a marvel of harmonious decor and lavish finishes, encompassing an expansive 440 square feet. Enhanced features include custom lighting, a dining table, separate seating area, walk-in closet, private teak veranda and a marble-clad bathroom with newly added storage space and an expanded shower, all ingeniously laid out to amplify contentment. Naturally, enjoy the ministrations of a dedicated Concierge and exclusive access to the amenities of the elite Executive Lounge.
Penthouse Suite Privileges
+In addition to Concierge Level privileges
- Priority luggage delivery
- Exclusive card-only access to private Executive Lounge staffed by a dedicated Concierge featuring complimentary sodas, coffees and snacks throughout the day
- 24-hour Butler service
- Course-by-course in-suite dining*
- Order in from any of our specialty restaurants*
- Coordination of shoreside dinner and entertainment reservations
- Last-minute luggage collection
- Packing and unpacking upon request
- Complimentary garment pressing*
- Complimentary shoeshine service
- Gourmet evening canapés upon request
- Special services upon request
+Up to 20 garments per laundry bag; additional restrictions apply.
++Certain limitations apply.
Smoking in suites, staterooms and on verandas is strictly prohibited.
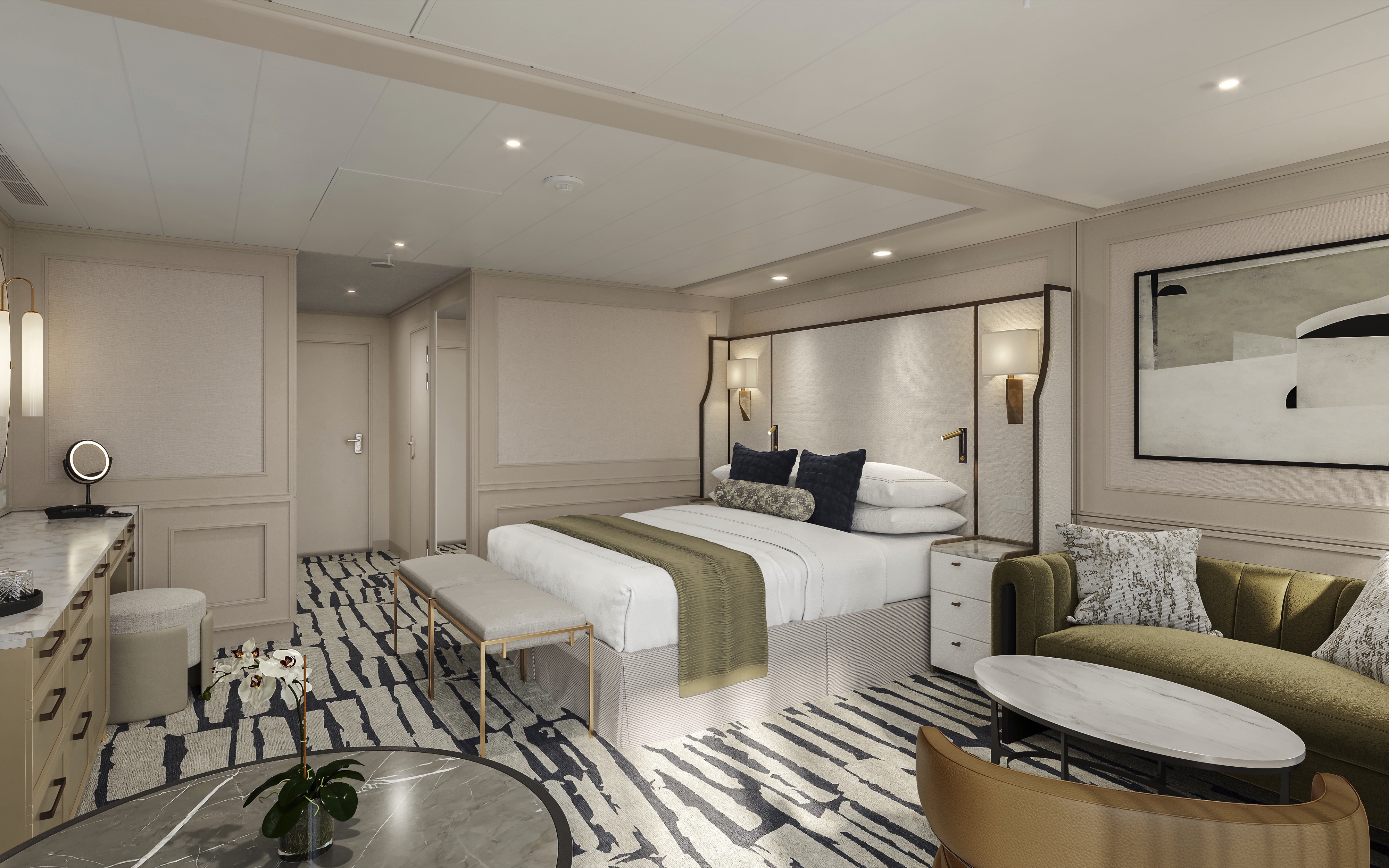
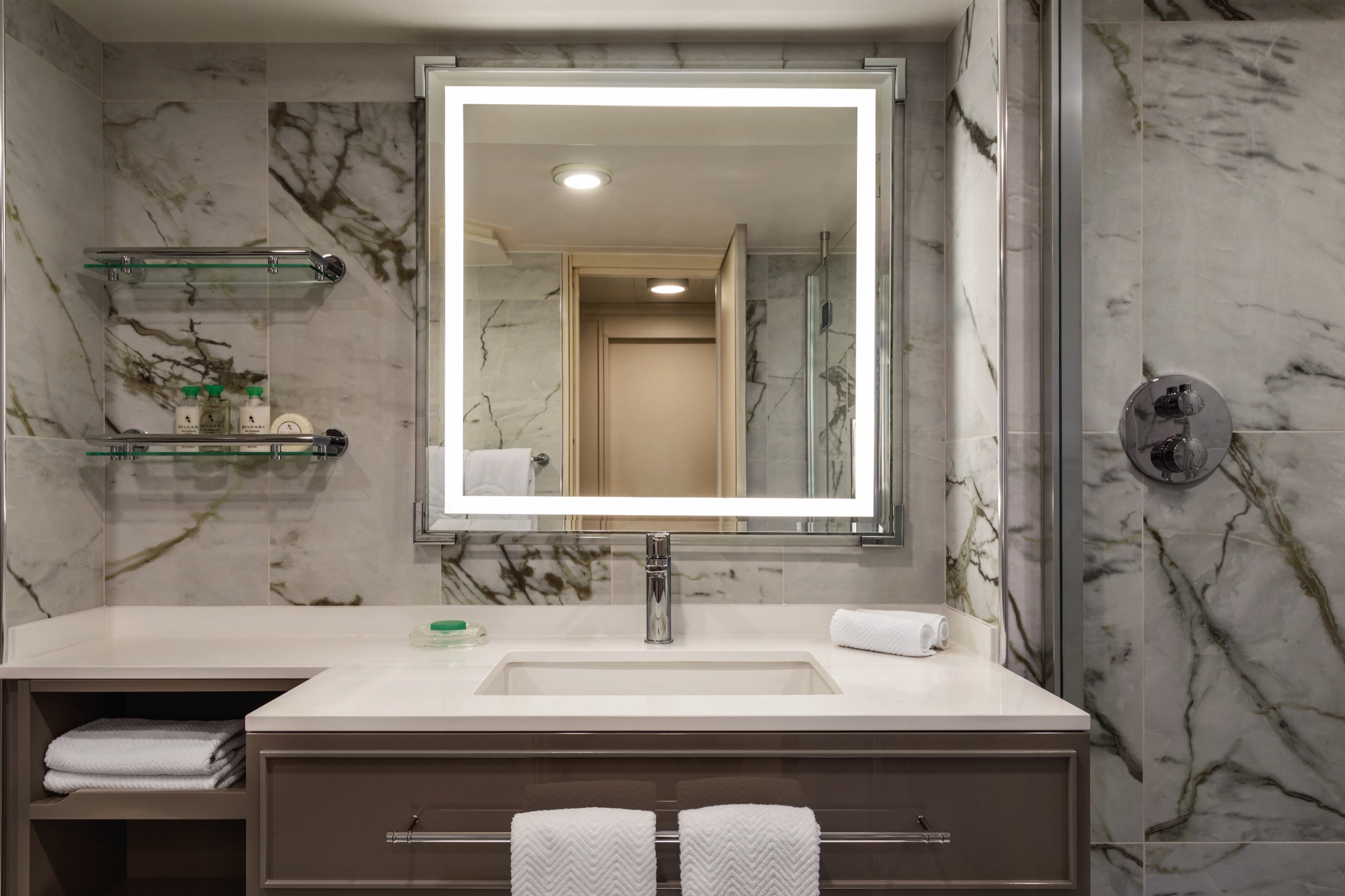
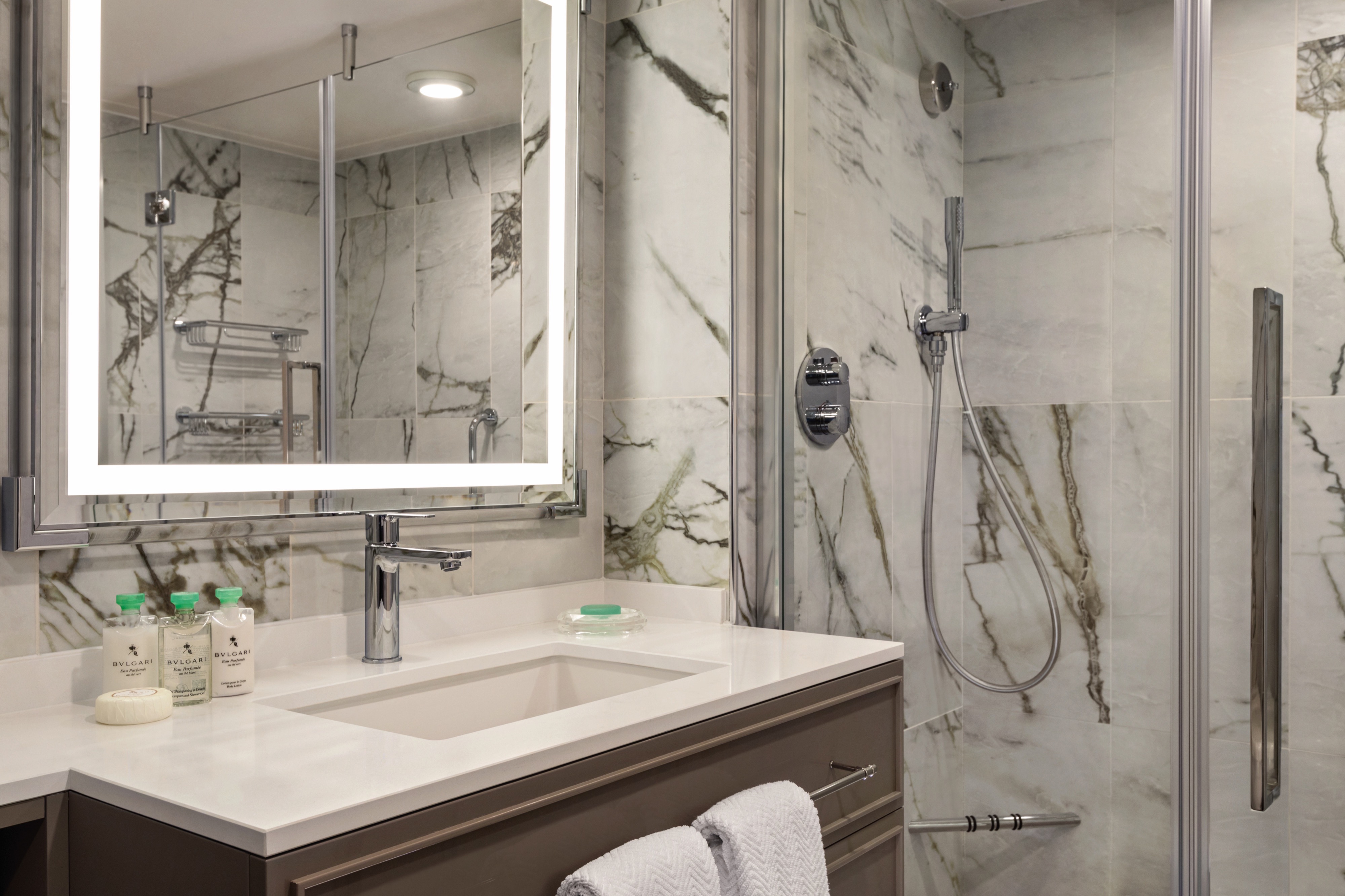






With nary a detail left untouched, our refreshed Concierge Level Veranda Staterooms boast an extravagant new Continental style throughout. These 291-square-foot retreats offer enticing amenities also found in our Penthouse Suites, such as a private teak veranda, gracious seating area, refrigerated mini-bar and an oversized bathroom featuring new storage space and an enlarged walk-in shower. In the private Concierge Lounge, relish the services of a dedicated Concierge and partake in an alluring array of beverages, daily treats and a selection of global newspapers and thought-provoking magazines.
Exclusive Concierge Privileges
+In addition to Stateroom amenities
- Expanded lunch and dinner room service menu from The Grand Dining Room
- FREE laundry service - up to 3 bags per stateroom+
- Private teak veranda††
- Exclusive card-only access to private Concierge Lounge staffed by a dedicated Concierge featuring complimentary sodas, coffees and snacks throughout the day
- Complimentary welcome bottle of Prosecco
- Priority online specialty restaurant reservations
- Unlimited access to the Aquamar Spa Terrace
- Complimentary Oceania Cruises logo tote bag
- Cashmere lap blankets, perfect for relaxing on your veranda
- Complimentary pressing of garments upon embarkation++
- Complimentary shoeshine service




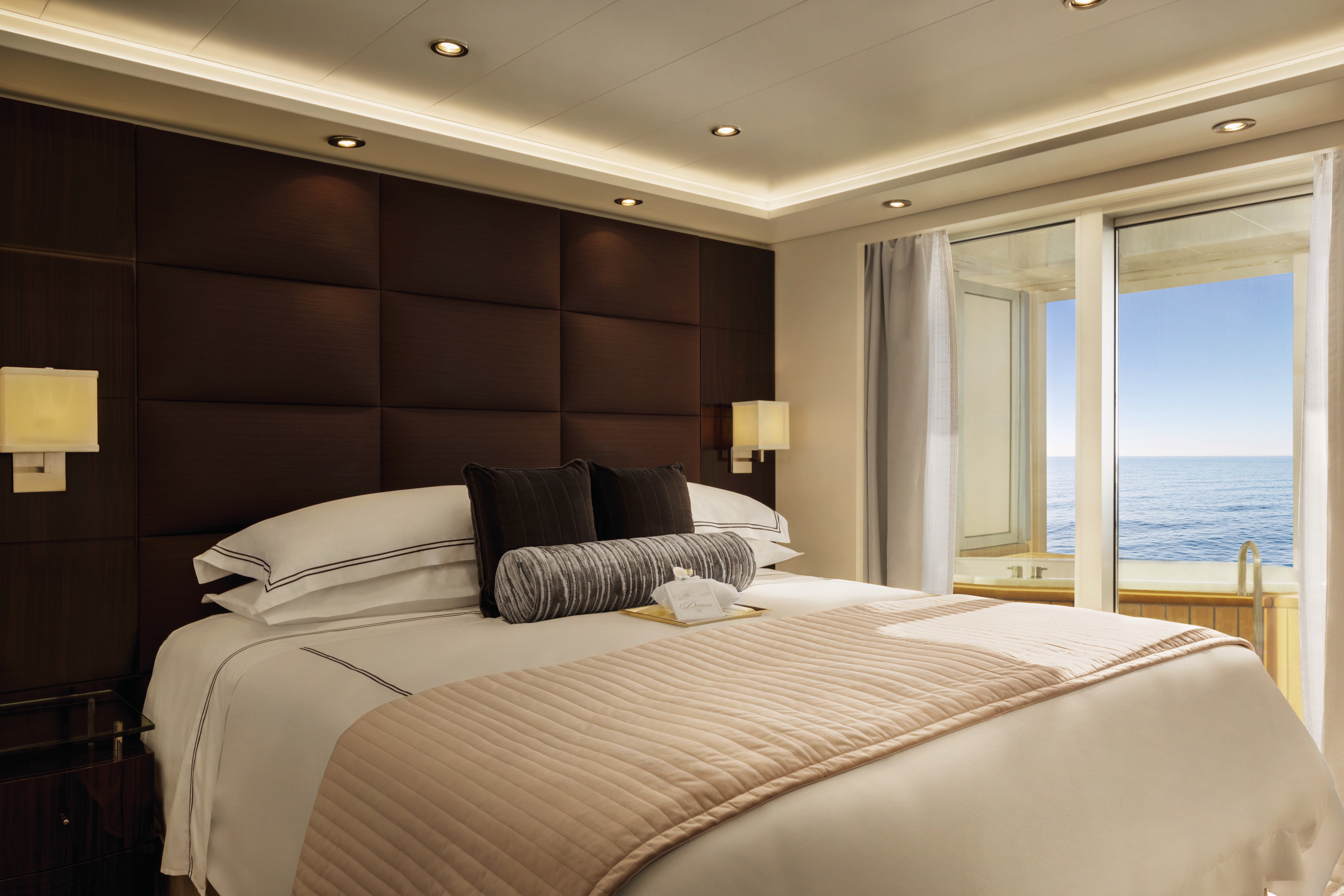
Our coveted 291-square-foot Veranda Staterooms, among the most generous at sea, have been imbued with sumptuous new furnishings in calming hues to create the ultimate sanctuary. There is ample room for leisurely pursuits, including a furnished private teak veranda. Indulgent amenities are plentiful, such as dazzling new lighting, an inviting seating area, refrigerated mini-bar, generous closet and a marble- and granite-sheathed bathroom showcasing new additional storage and an expanded walk-in shower.
Veranda Stateroom Amenities
- Tranquility Bed, an Oceania Cruises exclusive†
- FREE sodas replenished daily in your refrigerated mini-bar
- FREE still and sparkling Vero Water®
- Private teak veranda††
- Luxury bath amenities
- FREE room service menu 24 hours a day
- Daily housekeeping service
- Gourmet turndown chocolates upon request
- Interactive television system with on-demand movies, weather and more
- Starlink® WiFi service
- Writing desk and stationery
- Plush cotton towels, robes and slippers
- Handheld hair dryer
- Security safe
†King-size bed (cannot be converted into twin beds) for Owner’s, Vista and Oceania Suites and queen-size bed for all other suites and staterooms (Tranquility Bed available for purchase at OceaniaBedCollection.com)
†† Featured with all Veranda Staterooms
Smoking in suites, staterooms and on verandas is strictly prohibited
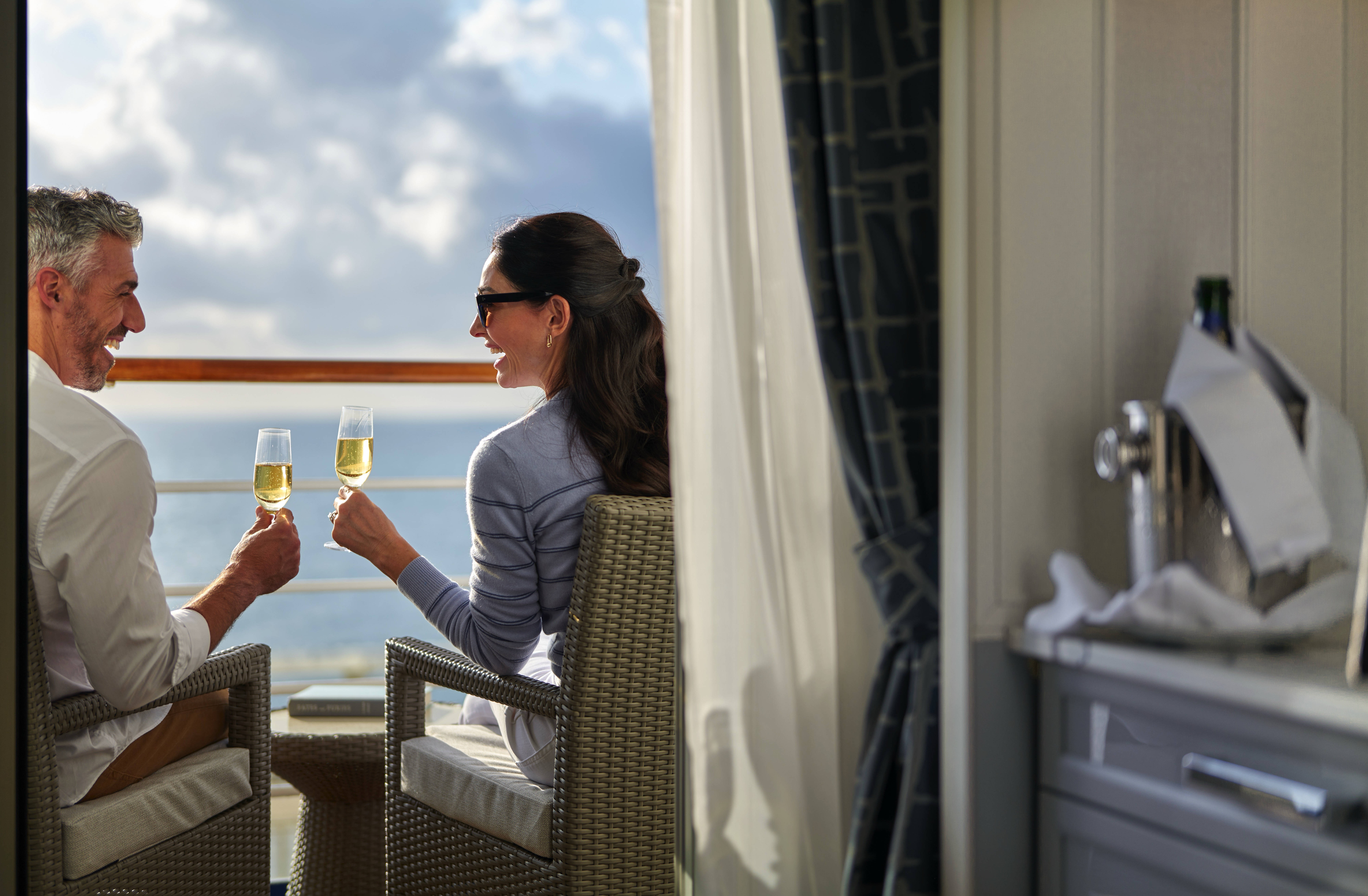



Highlighting floor-to-ceiling panoramic windows, our thoroughly renewed Deluxe Oceanview Staterooms deliver 240 square feet of sybaritic bliss. With curtains drawn open, natural light bathes the plush Tranquility Bed, convivial seating area, vanity desk, breakfast table and refrigerated mini-bar with a rich glow. Luxury also permeates the marble- and granite-clad bathroom, which features an expanded walk-in shower.
Deluxe Oceanview Stateroom Amenities
- Tranquility Bed, an Oceania Cruises exclusive†
- FREE sodas replenished daily in your refrigerated mini-bar
- FREE still and sparkling Vero Water®
- Luxury bath amenities
- FREE room service menu 24 hours a day
- Daily housekeeping service
- Gourmet turndown chocolates upon request
- Interactive television system with on-demand movies, weather and more
- Starlink® WiFi service
- Writing desk and stationery
- Plush cotton towels, robes and slippers
- Handheld hair dryer
- Security safe
†King-size bed (cannot be converted into twin beds) for Owner’s, Vista and Oceania Suites and queen-size bed for all other suites and staterooms (Tranquility Bed available for purchase at OceaniaBedCollection.com)
†† Featured with all Veranda Staterooms
Smoking in suites, staterooms and on verandas is strictly prohibited
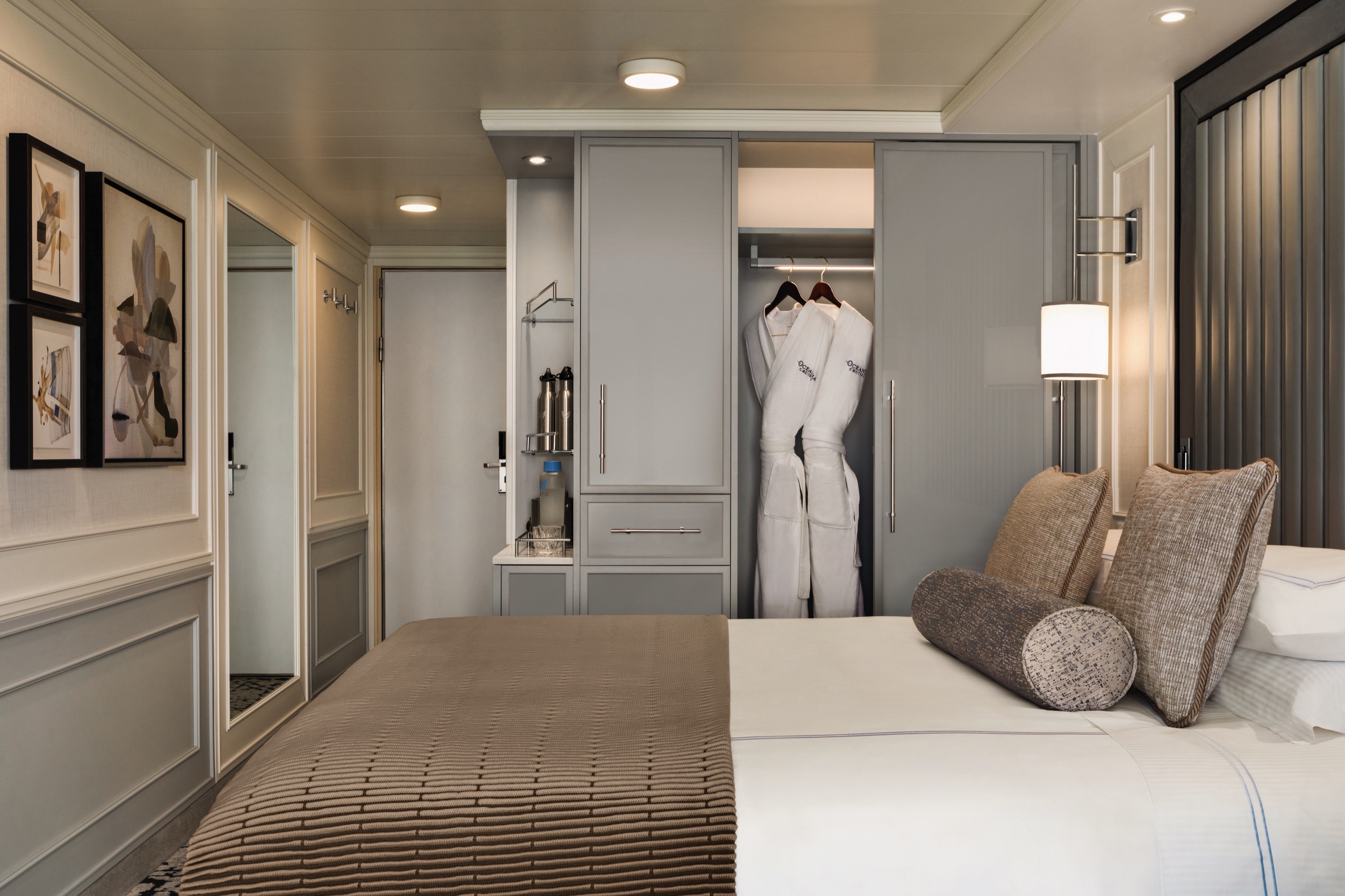

Our Inside Staterooms feature 174 square feet of refined elegance and idyllic solace. Freshly reimagined with stylish new furnishings and a restful palette, these sanctuaries feature thoughtful amenities such as a vanity desk, breakfast table, refrigerated mini-bar and a tony European stone-enveloped bathroom with a shower.
Inside Stateroom Amenities:
- Tranquility Bed, an Oceania Cruises exclusive†
- FREE sodas replenished daily in your refrigerated mini-bar
- FREE still and sparkling Vero Water®
- Luxury bath amenities
- FREE room service menu 24 hours a day
- Daily housekeeping service
- Gourmet turndown chocolates upon request
- Interactive television system with on-demand movies, weather and more
- Starlink® WiFi service
- Writing desk and stationery
- Plush cotton towels, robes and slippers
- Handheld hair dryer
- Security safe
†King-size bed (cannot be converted into twin beds) for Owner’s, Vista and Oceania Suites and queen-size bed for all other suites and staterooms (Tranquility Bed available for purchase at OceaniaBedCollection.com)
†† Featured with all Veranda Staterooms
Smoking in suites, staterooms and on verandas is strictly prohibited

Oceania Riviera
Sister ship to Marina, stunning Oceania Riviera was designed to be special in so many ways and reflects a new level of grace and elegance through designer touches, upholstery and fabrics throughout. She features multiple gourmet restaurants and along with Marina, offers unforgettable food and wine pairings at La Reserve by Wine Spectator as well as the opportunity for private dining at opulent Privée. From the Lalique Grand Staircase to the Owner's Suites furnished in Ralph Lauren Home, designer touches that create a casually elegant atmosphere are everywhere. Oceania Riviera's refined ambiance truly embodies the unparalleled Oceania Cruises experience.
Oceania Riviera blends sophistication with a contemporary flair to create a casually elegant ambiance. From the sparkling Lalique Grand Staircase to the stunning Owner's Suites, designer touches are everywhere, highlighting the finest residential design and furnishings. More than anything, Oceania Riviera personifies the Oceania Cruises experience.

Ship Facts
| Launch Year | 2012 | ||||||||
| Refit Year | 2022 | ||||||||
| Language | en | ||||||||
| Gross Tonnage | 66084 | ||||||||
| Length | 181 | ||||||||
| Width | 32 | ||||||||
| Currency | USD | ||||||||
| Speed | 20 | ||||||||
| Capacity | 1250 | ||||||||
| Crew Count | 800 | ||||||||
| Deck Count | 11 | ||||||||
| Cabin Count | 629 | ||||||||
| Large Cabin Count | 0 | ||||||||
| Wheelchair Cabin Count | 6 | ||||||||
| Electrical Plugs |
|
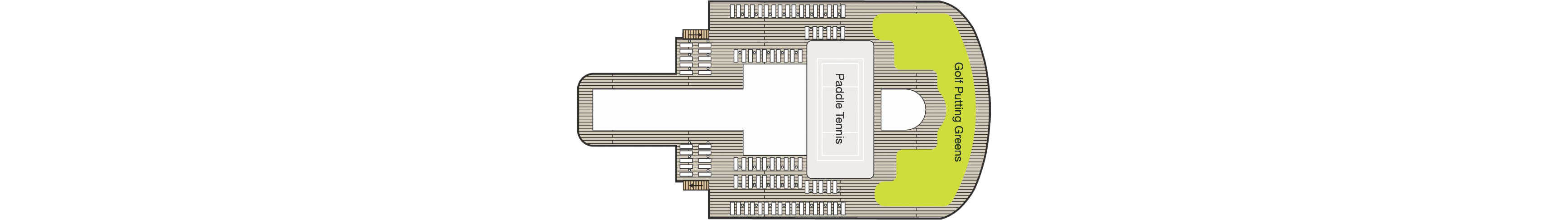
Deck 16
- Golf Putting Greens
- Paddle Tennis
Deck 15
- Croquet/Bocce
- Shuffleboard
- Fitness Track
- Elevator
- Horizons
- Bar

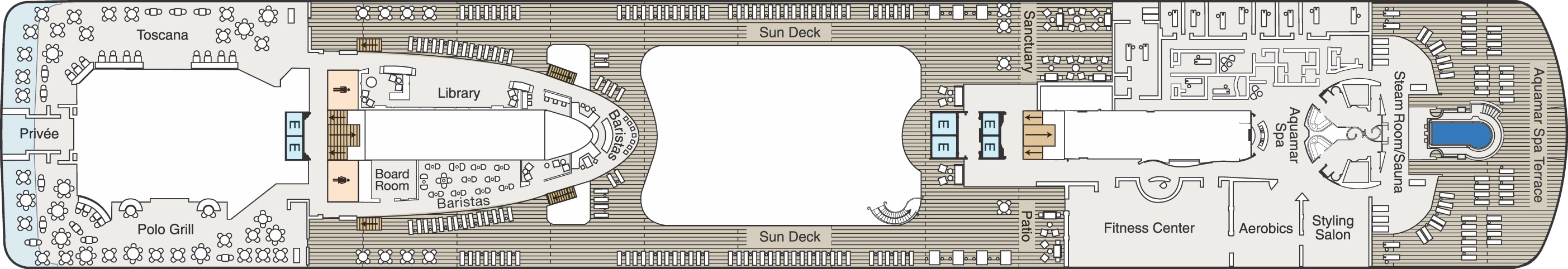
Deck 14
- Priveé
- Toscana
- Polo Grill
- Elevator
- Library
- Board Room
- Baristas
- Sun Deck
- Sanctuary
- Patio
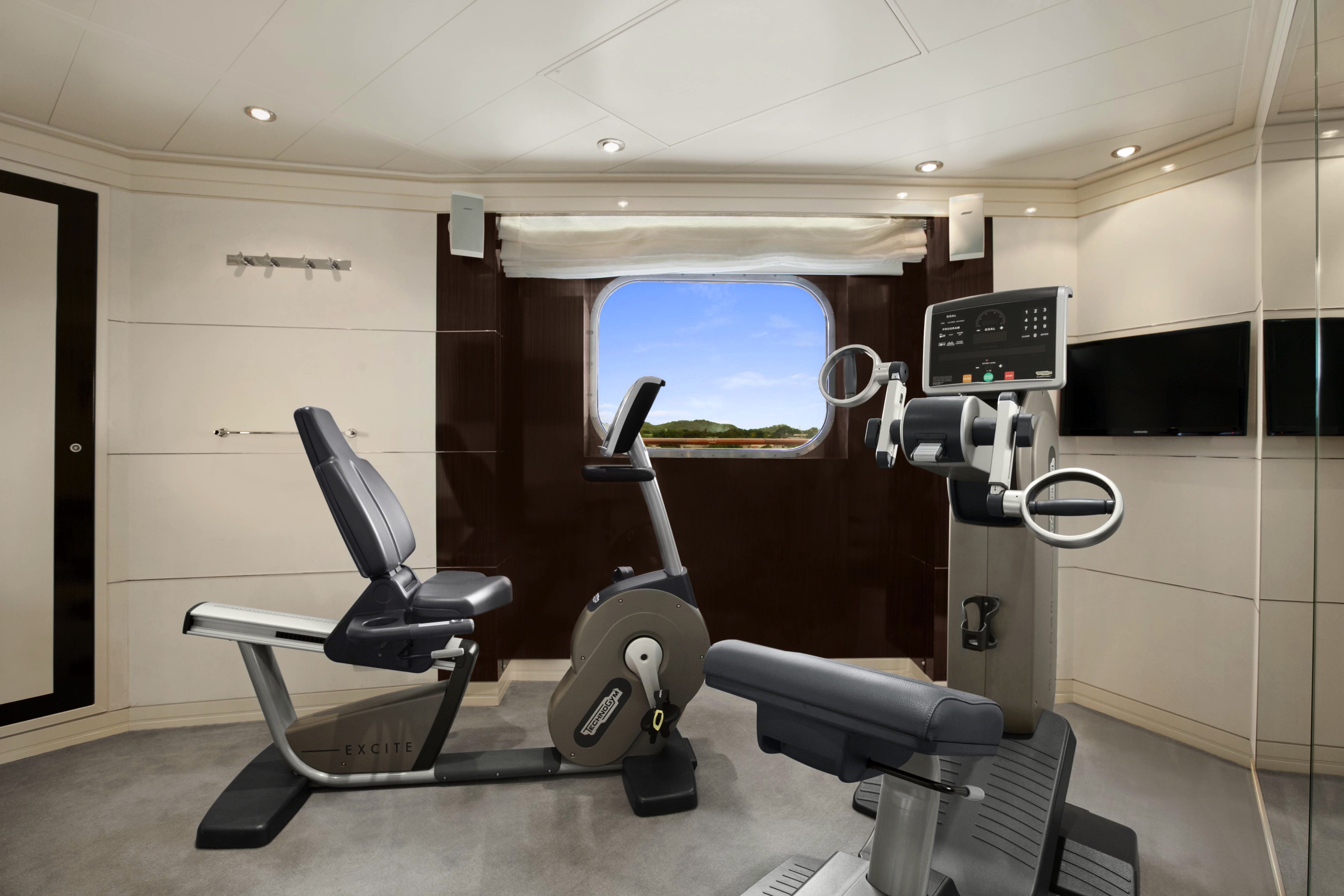
- Fitness Centre
- Aerobics
- Styling Salon
- Aquamar Spa
- Oceania@Sea
- Steam Room/Sauna
- Spa Terrace
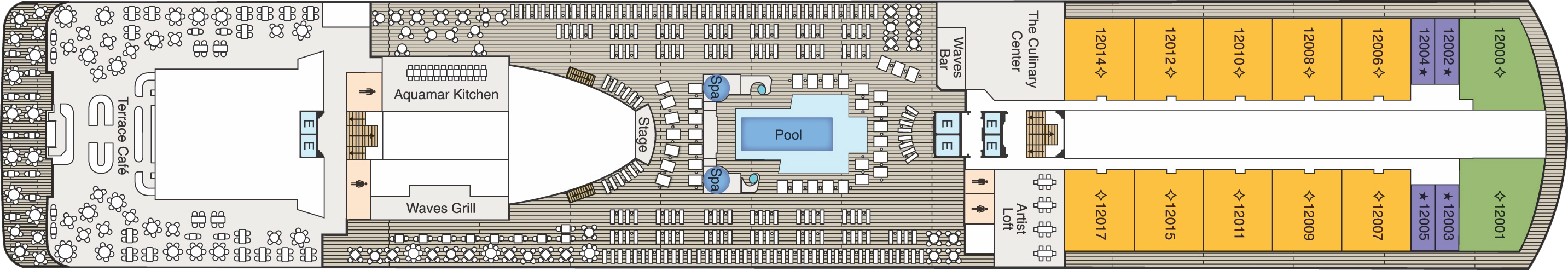
Deck 12
- Terrace Café
- La Reserve
- Waves Grill
- Stage
- Pool
- Whirlpools
- Waves Bar
- The Culinary Centre
- Artist Loft
- Elevator
- Concierge Level Veranda
- Oceania Suite
- Vista Suite
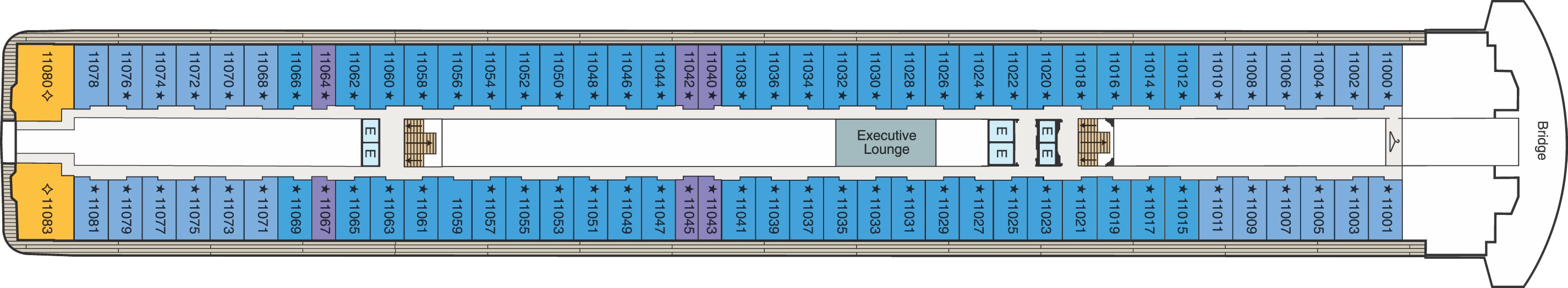
Deck 11
- Executive Lounge
- Bridge
- Concierge Level Veranda
- Oceania Suite
- Penthouse Suite
- Elevator
Deck 10
- Concierge Level Veranda
- Inside Stateroom
- Owner's Suite
- Penthouse Suite
- Vista Suite
- Elevator
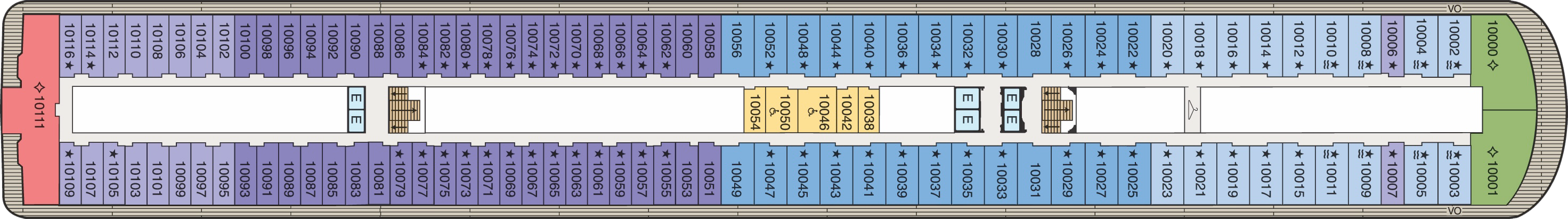
Deck 9
- Concierge Lounge
- Concierge Level Veranda
- Inside Stateroom
- Owner's Suite
- Penthouse Suite
- Vista Suite
- Elevator
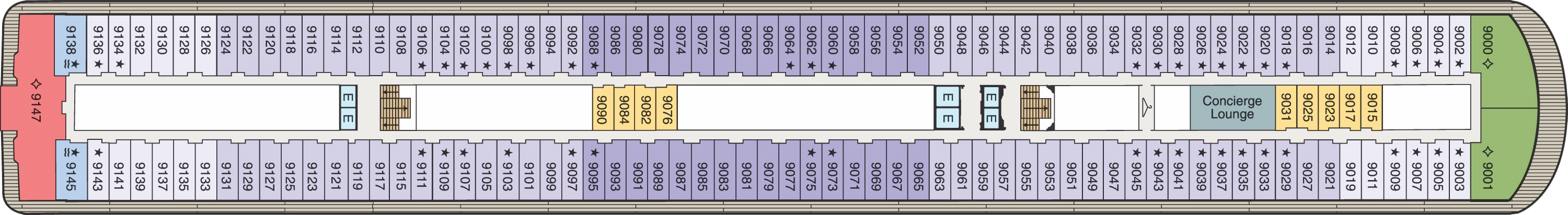
Deck 8
- Veranda Stateroom
- Inside Stateroom
- Owner's Suite
- Vista Suite
- Elevator
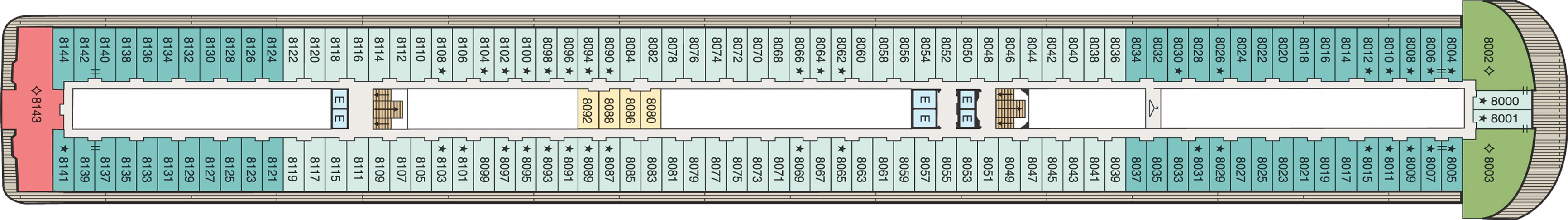
Deck 7
- Concierge Level Veranda Stateroom
- Veranda Stateroom
- Deluxe OceanView
- Penthouse Suite
- Elevator
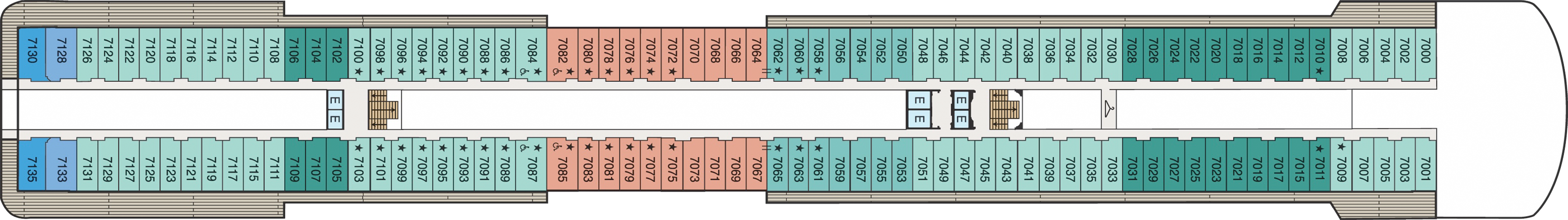
Deck 6
- The Grand Dining Room
- Casino Bar
- The Grand Bar
- Casino
- Martinis
- Upper Hall
- Elevator
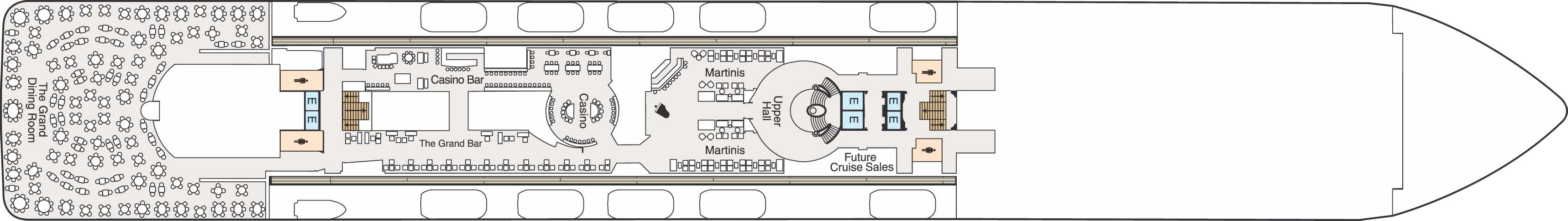
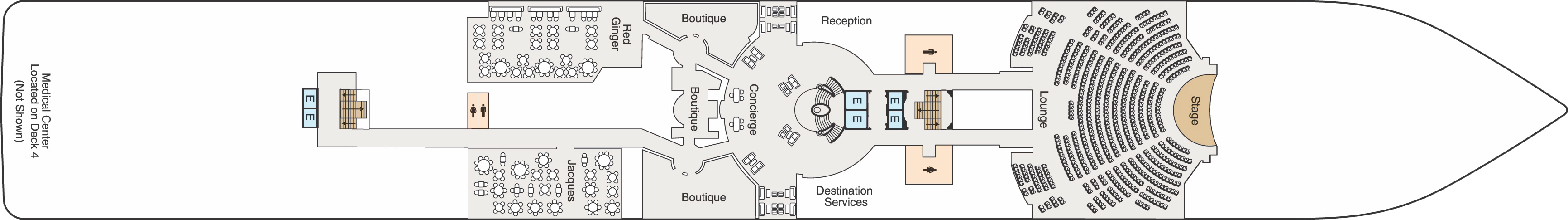
Deck 5
- Red Ginger
- Jacques
- Boutiques
- Concierge
- Reception
- Destination Services
- Elevator
- Lounge
- Stage
- Medical Centre - Located on Deck 4 (Not shown)
Culinary Masterpieces
Designed for epicureans and travel connoisseurs, Oceania Riviera features an array of complimentary specialty restaurants and unique dining experiences you’ll remember long after your cruise ends. The gourmet restaurants each serve a distinctive set of dishes created à la minute, from Continental and wellness-inspired cuisine at The Grand Dining Room and classic French fare at Jacques to vibrant Asian cuisine at Red Ginger and steakhouse favorites at Polo Grill.
The Luxury of Casual
You’ll savor cuisine renowned as the finest at sea no matter where you choose to dine or relax on Oceania Riviera– whether that means a poolside burger, a scoop of Humphry Slocombe’s bourbon-flavored cornflake-studded Secret Breakfast ice cream or a perfectly prepared cappuccino accompanied by freshly baked biscotti. Our culinary team’s attention to detail, passion for artisanal ingredients and dedication to technique extends to our casual dining, poolside experiences, Baristas coffee bar and the cherished ritual of Afternoon Tea.
In-Room Dining Experiences
After a day of enriching adventures ashore or an enjoyable day on board, dining in the privacy of your suite or stateroom with our compliments is always a welcome possibility. A complete menu of varied dining experiences is available around the clock, featuring an extensive array of delectable breakfast, lunch and dinner items. All suites and staterooms have the added luxury of enjoying a full, hot breakfast in-room and those staying in Concierge Level or above have the additional privilege of ordering from an expanded lunch and dinner room service menu from The Grand Dining Room. Suite guests have the ultimate indulgence of enjoying course-by-course meals from the comfort of their spacious sanctuaries. Revel in the private luxury of your suite or stateroom, and enjoy an exquisite meal on your tranquil veranda as you take in spectacular seascapes.
Exclusive Dining Experiences
Celebratory, indulgent and unforgettable – a night in either of Oceania Riviera’s exclusive culinary venues, Privée and La Reserve by Wine Spectator, offers a divine experience. La Reserve by Wine Spectator creates distinctive pairing dinners and also features sommelier-led tastings and wine seminars. Meanwhile, the opulent private dining venue of Privée transforms a dinner into a luxurious affair. Each creates an extraordinary evening to laugh, savor and remembe
The Grand Dining Room
DINING IN GRAND STYLE
The grande dame of the Oceania Cruises culinary world, The Grand Dining Room invites guests to a leisurely dining experience amidst an ambiance that soars to heights as lofty as the cuisine. Our marquee restaurant has always featured Jacques Pépin’s signature delights and a bevy of delicious Continental dishes and now offers even more exciting choices, Aquamar Vitality Cuisine and a wide spectrum of global flavors. Menus change daily, and the all-new Executive Chef’s Tasting Menu promises multiple courses of the chef’s most divine creations.
Open for breakfast, lunch and dinner. No reservations required.
Jacques
A PASSION FOR FRENCH CUISINE
Exquisitely decorated with heirloom antiques, pickled wood furnishings and art from Jacques Pépin’s personal collection, Jacques was modeled after a Parisian bistro. Comfortable and eclectic, the ambiance is pure French, as is the cosmopolitan yet wonderfully embraceable cuisine. Luscious aromas waft from the gleaming show rotisserie, where chicken, duck, pork, beef and veal roasts slowly turn. Each dish is a classic, ingeniously reinterpreted by Master Chef Pépin. Rotisserie roasted chicken falls off the bone, bursting with flavor, while his sea bass fillet pairs exquisitely with beurre blanc.
Open for dinner only. Reservations required.
Red Ginger
BOLD ASIAN CUISINE
With a nod to feng shui, Red Ginger radiates harmony and tranquility. The interior simply glows with ebony woods, ruby red leathers and striking, modern Asian artworks. To complement the stunning decor, Red Ginger’s chefs have created contemporary interpretations of Asian classics. Begin with a salad of spicy roast duck and watermelon with cashews, mint and Thai basil. Savor a Malaysian beef penaeng with coconut rice and paratha roti. Or try Thai vegetable curry with sweet potatoes, aubergine, mushrooms and basil in green curry sauce. In Red Ginger, the gustatory pleasures are as striking as the visual ones.
Open for dinner only. Reservations required.
Polo Grill
A CLASSIC STEAKHOUSE
Polo Grill embodies all the elements of a classic steakhouse, expressing them with timeless reverence. Mindful of tradition, the decor features crisp, white linen tablecloths, dark wood furnishings and supple, high-back, burgundy leather chairs. Each course stands as the very definition of time-honored favorites, most notably the beef dishes, all of which are USDA certified Angus and aged for a minimum of 40 days to enhance tenderness and flavor. Succulent seafood dishes such as grilled swordfish and whole Maine lobster gratinée are also classics in their own right. The classic Caesar salad, too, is prepared according to tradition, tableside and with gusto.
Open for dinner only. Reservations required.
Toscana
AUTHENTIC ITALIAN
Toscana means Tuscan, and just as Tuscan cuisine evolved from rich family traditions, many of our recipes originated with the mothers and grandmothers of our own Italian culinary staff. Presented on elegant, custom-designed Versace china, masterfully prepared dishes exemplify the essence of Tuscany and celebrate Italy’s culinary passion. Perhaps the evening begins with the octopus carpaccio with Champagne vinaigrette or the artichoke and parmesan cheese timbale with black truffle sauce. Classic dishes from other regions of Northern Italy are featured as well, such as the minestrone alla Genovese, lasagna alforno alla Bolognese and osso buco alla Milanese.
Open for dinner only. Reservations required.
Terrace Café
INFORMAL DINING
Informal and carefree, the Terrace Café is wonderfully inviting any time of day. During breakfast, the room is infused with natural sunlight from the floor-to-ceiling windows, stimulating the appetite for the sumptuous selections. Come lunch, the expansive menu of international-inspired dishes changes entirely, complemented by a flavorful roast and the magic of the pizzeria’s oven. Dine inside or alfresco at one of the shaded teak tables on the terrace. During the evenings, the cuisine takes on a more sophisticated flair, with lobster tails, chops and fresh fish prepared to order, and freshly made hand-cut sushi and sashimi. In addition, a diverse selection of bold and flavorful plant-based dishes is available.
Open for breakfast, lunch and dinner. No reservations required.
Waves Grill
ALFRESCO DINING
Sometimes, the ultimate luxury is casual dining on all-American favorites, a laid-back style Waves Grill epitomizes. Located in a spacious, shaded area steps from the swimming pool, Waves Grill offers an extensive and mouthwatering menu. Then try a decadent dessert such as a homemade passion fruit sorbet, a made-to-order hot fudge sundae, a hand-dipped milkshake or one of the new, whimsical ice cream flavors by Humphry Slocombe, such as Secret Breakfast, Elvis (the Fat Years) or our signature flavor, Regatta Royale.
The Pizzeria at Waves Grill
Visit Waves Grill in the evening to experience an atmospheric Neapolitan trattoria with a warm pizza oven at the epicenter. Pair savory antipasti, creamy burrata selections or spicy chicken wings with a crisp glass of sauvignon blanc or refreshing rosé. Hand-tossed pizzas feature delectable toppings ranging from smoky roasted bell peppers and earthy truffle oil to fiery chorizo and tart lemon chicken. The irresistible aromas will draw you in and the flavorful creations will make you want to linger over dinner just as they do in Italy.
HEALTHY MORNINGS
Raw Juice & Smoothie Bar
The only cold-pressed Raw Juice & Smoothie Bar at sea serves up tasty raw juices, plant-based smoothies and energy bowls at Waves Grill during breakfast on board Oceania Riviera.
Breakfast
7:00 am – 11:00 am
Lunch
11:30 am – 4:00 pm
The Pizzeria at Waves Grill
6:30 pm – 9:00 pm
Privée
A PRIVATE PARTY
For the ultimate in exclusivity, Privée may be reserved for the evening for parties of up to 10 privileged guests. Choose from several different gourmet menus to create an unforgettable experience in an exquisite, custom-designed setting illuminated by a golden Venini chandelier.
Reservations required. A room reservation surcharge applies.
La Reserve by Wine Spectator
EPICUREANS & WINE CONNOISSEURS
Wine is as essential to a great meal as the food itself, as it complements every bite, enhancing the dish’s flavors and elevating it to epic levels. With our La Reserve experiences, wine and Champagne take center stage. Dishes are created for the wine, rather than the other way around. One of our most coveted reservations is for the Dom Pérignon Experience, which pairs three of the best recent vintages of the house with six exquisite courses. La Cuisine Bourgeoise by Jacques Pépin and the Odyssey Menu are two other vinous and culinary delights that await you with a La Reserve reservation.
THE DOM PÉRIGNON EXPERIENCE
Champagne defines the most jubilant moments of our lives and in a magnificent stroke of brilliance, we have partnered with France’s esteemed Moët & Chandon to create the Dom Pérignon Experience at La Reserve, an exuberant six-course gustatory indulgence that pairs each course with a special Dom Pérignon vintage. Champagne is effortlessly matched with dishes which are thoughtfully crafted to bring out the nuances of the grapes and the ratio of the blend, playing off every aspect from subtle, effervescent nose to lively, satisfying finish. From Brittany Blue Lobster in Yellow Curry Broth with Coco Foam to Sashimi-Style Seared Wagyu Beef with Sautéed Arugula, Blood Orange-Soya Jus and Caviar Perlita, each beguiling bite is a celebration of the finer things in life. While the Dom Pérignon Experience is the perfect complement to any joyous occasion, it transcends even this lofty role. In true French spirit, it becomes the culinary manifestation of joie de vivre.
Available on board Oceania Marina, Oceania Riviera, Oceania Vista and Oceania Allura. Reservations required. Wine or Champagne experience surcharge applies.
Afternoon Tea
TIME-HONOURED PASTIME
Each afternoon, the parade of gleaming four-tiered pastry carts begins. Savor freshly made, flavorful smoked salmon and egg salad finger sandwiches. Enjoy mirror-glazed petits fours, tender scones with rich clotted cream and, of course, a wide assortment of fine teas. Soak in the ambiance of polished silver teapots reflecting the turquoise sea, the precision of white-gloved servers and the amusing enigma of a string quartet playing softly in the background. You’ll quickly realize that this is how afternoon tea should be.
Check your daily Currents for time and venue. No reservations required.
Baristas
A Neighborhood Gem
This delightful coffee bar is a favorite stop for java lovers. Enjoy complimentary illy® espressos, cappuccinos and lattes prepared by our master baristas, as well as the delicious pastries, finger sandwiches and homemade biscotti that draw so many to Baristas throughout the day.
Open daily until early evening. No reservations required.
Room Service
In-Room Dining Experiences
After a day of enriching adventures ashore or an enjoyable day on board, dining in the privacy of your suite or stateroom with our compliments is always a welcome possibility. A complete menu of varied dining experiences is available around the clock, featuring an extensive array of delectable breakfast, lunch and dinner items. All suites and staterooms have the added luxury of enjoying a full, hot breakfast in-room and those staying in Concierge Level or above have the additional privilege of ordering from an expanded lunch and dinner room service menu from The Grand Dining Room. Suite guests have the ultimate indulgence of enjoying course-by-course meals from the comfort of their spacious sanctuaries. Revel in the private luxury of your suite or stateroom, and enjoy an exquisite meal on your tranquil veranda as you take in spectacular seascapes.
Life On Board
From sipping fine vintages at a wine tasting to attending a show-stopping performance in the ship lounge, a wonderful spectrum of enriching activities and lively entertainment awaits you on board Oceania Riviera. Join one of our esteemed Guest Speakers to discover their unique cultural expertise, indulge in a treatment at Aquamar Spa + Vitality Center or take a hands-on cooking class at The Culinary Center. As the sun lowers, gather with friends in one of the convivial bars, attend a spectacular production show or take in an unforgettable musical performance.
Music & Entertainment
World-class musical performances will dazzle you, showcasing an ever-changing array of guest entertainers such as pianists, classical string quartets, dynamic vocalists and spectacular headliners. Oceania Riviera features a unique lineup of onboard shows and entertainers to ensure that your interests are constantly piqued. Unforgettable evenings at energetic, show-stopping performances are just steps from your suite or stateroom.
Bars & Lounges
From chic Martinis to the laid-back poolside Waves Bar, there's a perfect enclave on board Oceania Riviera for every mood. Visit the elegant Grand Bar for a pre-dinner cocktail, catch a headline act in the Lounge or watch the sun set in Horizons accompanied by a glass of wine and lively music. As you explore the world, these bars and lounges are the place to unwind, gather together, laugh and take in one-of-a-kind shows and musical performances.
Entertainment & Onboard Shows
DAZZLING PERFORMANCES
EXCLUSIVE PRODUCTION SHOWS
World-class musical performances will delight you, showcasing an ever-changing array of guest entertainers such as pianists, classical string quartets, dynamic vocalists and spectacular headliners.
Each of our ships features a unique lineup of onboard shows and entertainers to ensure that your interests are constantly piqued. Bold and crowd-thrilling, nostalgic and upbeat, or intimate and sophisticated – whatever you choose, the night is yours.
Oceania Riviera's versatile and talented cast performs the following diverse production shows:
Broadway in Concert
Come on along and listen to…the lullabies of Broadway! In this elegant concert-style review, our fabulous production cast vocalists pay tribute to some of the most iconic musicals of all time. You’ll experience songs you know and love, and maybe you'll discover one or two more contemporary gems. Let us entertain you…because, after all, “There’s no business like show business!”
Lights, Camera, Music
See your favorite cinematic classics come to life in this cultivated tribute to the most recognizable moments of the Hollywood movie musical, from the romantic glamour of the 1940s to the high-kicking can-can of the Moulin Rouge. So, curtain up…light the lights…as we proudly present…Lights, Camera, Music!
What the World Needs Now
What the World Needs Now celebrates song-writing legend Burt Bacharach. In the 1960s, he turned popular music on its head with his unique style. He broke musical boundaries as he composed some of the most recognizable melodies ever created. The production cast and show band orchestra take you on an elegant musical journey with vibrant dance numbers and beautiful heartfelt songs about love and its challenges.
World Beat
We’ll take you on a spectacular voyage through a world of music, rhythm and dance. This lively theatrical showcase pays tribute to just a few of the many cultures represented by our various crew members on board. Feel the organic rhythm of Tinikling from the Philippines, and dwell in the vibrant energy of the Bollywood musical hits of India. We’ll pay homage to the Chinese New Year and marvel at the precision of Irish dance — and the journey doesn’t end there.
Casino
EARN CASINO POINTS
The professional staff is happy to provide lessons on how games are played, the rules and proper table procedures. Unwind from a busy day ashore by playing your favourite games of chance and skill in our casino. Enjoy a fun and exciting range of ways to play, from card and table games such as blackjack and roulette to slot machines.
Getting started is easy. Stop by the casino cage and pick up your Oceania Cruises casino player card and start earning points today by inserting your player card while playing your favourite slot machines and table games. The more you play, the more you earn!
- Reel & Video Slots - For every $5 coin-in, receive 1 point.
- Video Poker - For every $10 coin-in, receive 1 point.
- Table Games - Points are based on average bet, session play or hands played and game type.
- Action-packed casinos designed with style
- Table game limits for players of all levels
- Diverse array of reel slot, video slot and video poker machines
- Dedicated and knowledgeable casino staff
- Industry-leading player tracking system
- Free gaming lessons
REDEEM CASINO POINTS
You’ve played. You’ve earned. Now you’re ready to redeem. Downloading points for play is quick and easy. Redeem your casino points for play right at your machine by following the on-screen prompts or stop by the casino cage – the choice is yours.
- Earn points for all your casino play
- Redeem points for play right at your machine
CASINO CASH & CREDIT
Front Money deposits are accepted for gaming in the form of cash, traveler’s checks, cashier’s checks and wire transfers delivered to us prior to embarkation. All cashier’s checks require prior verification. For more information, please give us a call at 877.625.2094.
Cashless Wagering
Charge gaming to your onboard account directly from your game of choice or at the casino cashier, using your stateroom key card. Convenience fees, daily limits and cruise limits apply. Euros may be exchanged at the casino cashier; exchange rates apply. All gaming is in US Dollars.
- Cashless wagering allows you to game with your key card
Credit
Casino credit is available to all players with an existing reservation. The minimum application amount is $10,000.00 and a personal check is required on board to activate the credit line. Applications are processed 1 month prior to sailing. The application process is easy and there is no fee to apply. To get started, click here for our credit application or for more information email us at casinocredit@ncl.com or call us at 877.625.2094.
- Casino credit available
Boutique Shopping
UNIQUE GIFTS, JEWELLERY & MORE
Our stylish boutiques feature a tastefully curated selection of items ranging from sundries to chic resort wear and fine jewelry. Discover thoughtful gifts for friends and family or the perfect memento to remind you of your special cruise experience.
DUTY-FREE ON BOARD OCEANIA RIVIERA
Browse through our collection of duty-free merchandise including fine jewelry, watches, fragrances and Oceania Cruises logo wear. Also find shipboard keepsakes, designer handbags, sunglasses, books and more.
Library
QUIETUDE AT SEA
Pick up a steaming cappuccino and settle in to the welcoming ambiance of our classic library on board Oceania Riviera with the novel or bestseller you’ve been meaning to read. Relax and feel right at home with more than 2,000 books and periodicals to choose from as you sail from one destination to the next.
Just as sailing aboard Oceania Cruises recalls the elegance of the Golden Age of Travel, our inspired English-style library is reminiscent of a charming English country estate where you can while away the hours in ultimate comfort. There is something magical about the dark, rich woods; the plush high back chairs; the cozy fireplaces and rows of books lining the walls, each a new world waiting to be discovered.
Oceania@Sea Internet Centre
Stay in touch with family and friends, monitor business developments and more in our 24-hour Internet centre, Oceania@Sea.
For personalised service, Oceania@Sea is fully staffed as follows:
- Sea Days: 8 a.m. - 7 p.m.
- Port Days: 8 a.m. - 11 a.m. and 3 p.m. - 7 p.m..
Oceania Cruises also offers wireless Internet access throughout the ship, allowing you to connect through your laptop or mobile device. And as an added convenience, an iPad® is available upon request for all suite and Concierge Level guests.
Letters and postcards with the appropriate postage can be mailed at the Reception Desk. Postage for mail may be purchased at the Reception Desk for a nominal fee. Mail will be collected one hour prior to sailing from each port of call. Incoming mail or faxes received by the ship on your behalf will be delivered directly to your stateroom.
PHONE
Oceania Cruises offers Wireless Maritime Services (WMS) for all GSM mobile phones and GPRS devices such as Blackberry® when the ship is at sea. You can make and receive phone calls, send and receive text messages and use other data services when the ship is at sea. You will be billed by your mobile phone provider and calls or messages will appear as roaming charges on your bill. While using the WMS service, international maritime roaming rates will apply. Please consult your wireless service provider for detailed rates and service zones.
Martinis
Martinis serves numerous incarnations of this famous cocktail in a sophisticated yet affable atmosphere reminiscent of an exclusive New York members’ club, featuring live piano music.
The Grand Bar
Before sitting down to a gourmet meal, sample a rare vintage or savour your favourite apéritif as you enjoy spirited conversation with newfound friends amid the refined atmosphere of the convivial Grand Bar.
Riviera Lounge
From headline acts to comedians, magicians and lively jazz ensembles, head to the Oceania Riviera Lounge to discover the centre of nightly entertainment aboard Oceania Cruises.
Horizons
An elegant observation lounge with dramatic floor-to-ceiling windows and a country club casual ambiance, Horizons transforms into a sophisticated evening venue by night. Dance the night away to the sounds of a lively musical group and enjoy cocktails with friends at the welcoming bar.
Waves Bar
Located in a shaded area just steps from the swimming pool, Waves Bar offers a wide variety of libations to enhance your poolside experience. Revel in the perfect afternoon on deck with your favorite cocktail, glass of wine or chilled beer. Come happy hour, signature cocktails and frosty beverages create a delightfully carefree segue to the lively evening ahead as the sun sets.
Casino Bar
Try your hand at exciting table games such as blackjack, poker and roulette while enjoying a delightful cocktail from the casino bar.
Sanctuary
Sit back, relax and enjoy the stunning panoramic ocean views in the shaded comfortable Sanctuary as you sail to the next exciting destination.
Executive Lounge
Enjoy the fully-stagged Executive Lounge with Complimentary beverages and snacks throughout the day and evening.
Patio
Sit back, relax and enjoy the stunning panoramic ocean views in the shaded, comfortable Patio as you sail to the next exciting destination.